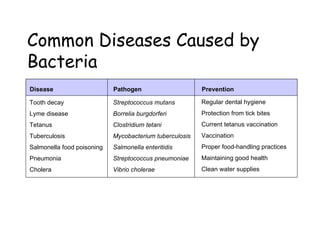
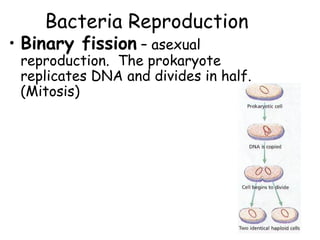
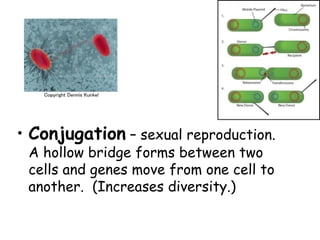
Bacteria can cause disease in organisms by directly damaging tissues or releasing toxins. Common diseases caused by bacteria include tooth decay, Lyme disease, tetanus, tuberculosis, and pneumonia. Antibiotics can block bacterial growth and reproduction. Controlling bacteria involves sterilization, disinfectants, refrigeration, and cooking. Some bacteria are helpful by fixing nitrogen in soil, breaking down organic matter, producing flavors and antibiotics, assisting waste treatment, and providing vitamins. Bacteria reproduce through binary fission or conjugation.