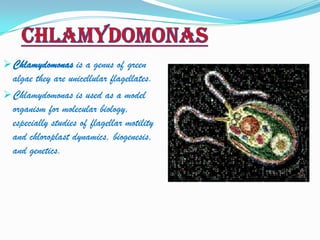
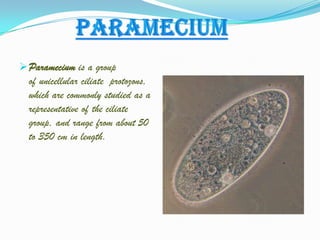
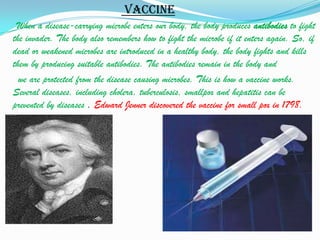
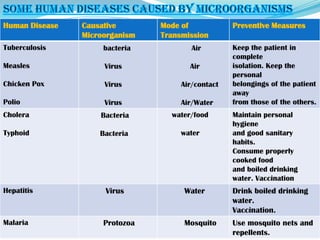
Microorganisms are tiny organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. They can live in various environments ranging from ice cold climates to hot springs. Microorganisms include bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and some algae. Viruses are also considered microbes though they can only reproduce inside host cells. Some microorganisms are useful for producing medicines and alcohol, while others decompose organic waste and help clean the environment. However, some microorganisms can also cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants.