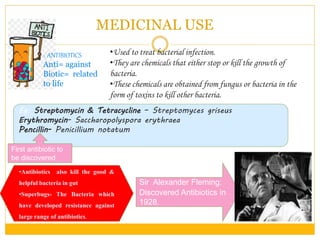
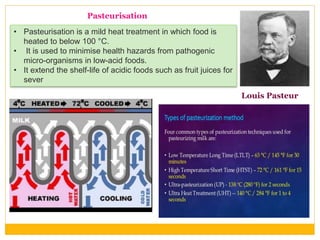
This document summarizes the various uses of microorganisms. It discusses how microorganisms are used commercially in industries like dairy, beverages, baking, and processing. It also discusses their medicinal uses in producing antibiotics and vaccines. Microorganisms are used agriculturally for nitrogen fixation and in environmental applications like sewage treatment and oil spill cleanup. The document also covers how some microorganisms can cause diseases in humans, animals and plants by acting as pathogens or through transmission by carriers. Food spoilage and various food preservation methods using microorganisms are also summarized.