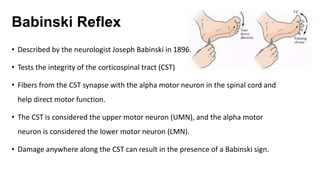
The Babinski reflex is elicited by stimulating the lateral plantar aspect of the foot and normally causes plantar flexion of the toes. A positive Babinski sign, in which the big toe extends upward, suggests damage to the corticospinal tract in the brain or spinal cord. This allows abnormal spread of sensory input beyond the typical dermatome, causing the extension response. The presence of an intact Babinski reflex is normal in infants under 2 years old.