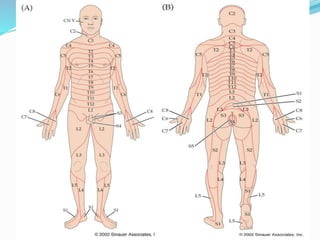
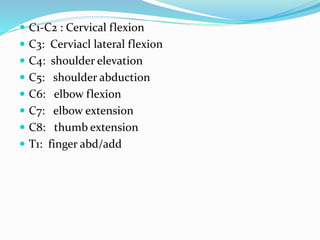
The document explains dermatomes and myotomes, detailing their definitions and clinical significance. Dermatomes refer to the sensory distribution of nerve roots across the skin, while myotomes pertain to muscle groups supplied by these nerve roots, with patterns varying across different segments of the spinal cord. Understanding these concepts is important for localizing neurological conditions and assessing muscle weakness in relation to spinal injuries.