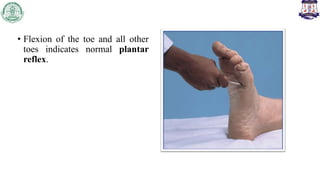
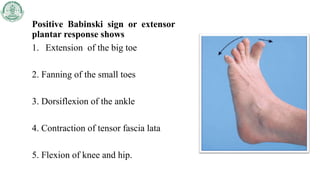
The Babinski sign is a pathological reflex indicating upper motor neuron (UMN) lesions in the corticospinal tract, which can arise from various conditions such as stroke or traumatic brain injury. The reflex is tested by stimulating the plantar surface of the foot; a positive response includes toe extension and fanning. In infants, the Babinski reflex is normal, but its presence after age two may suggest corticospinal tract damage.