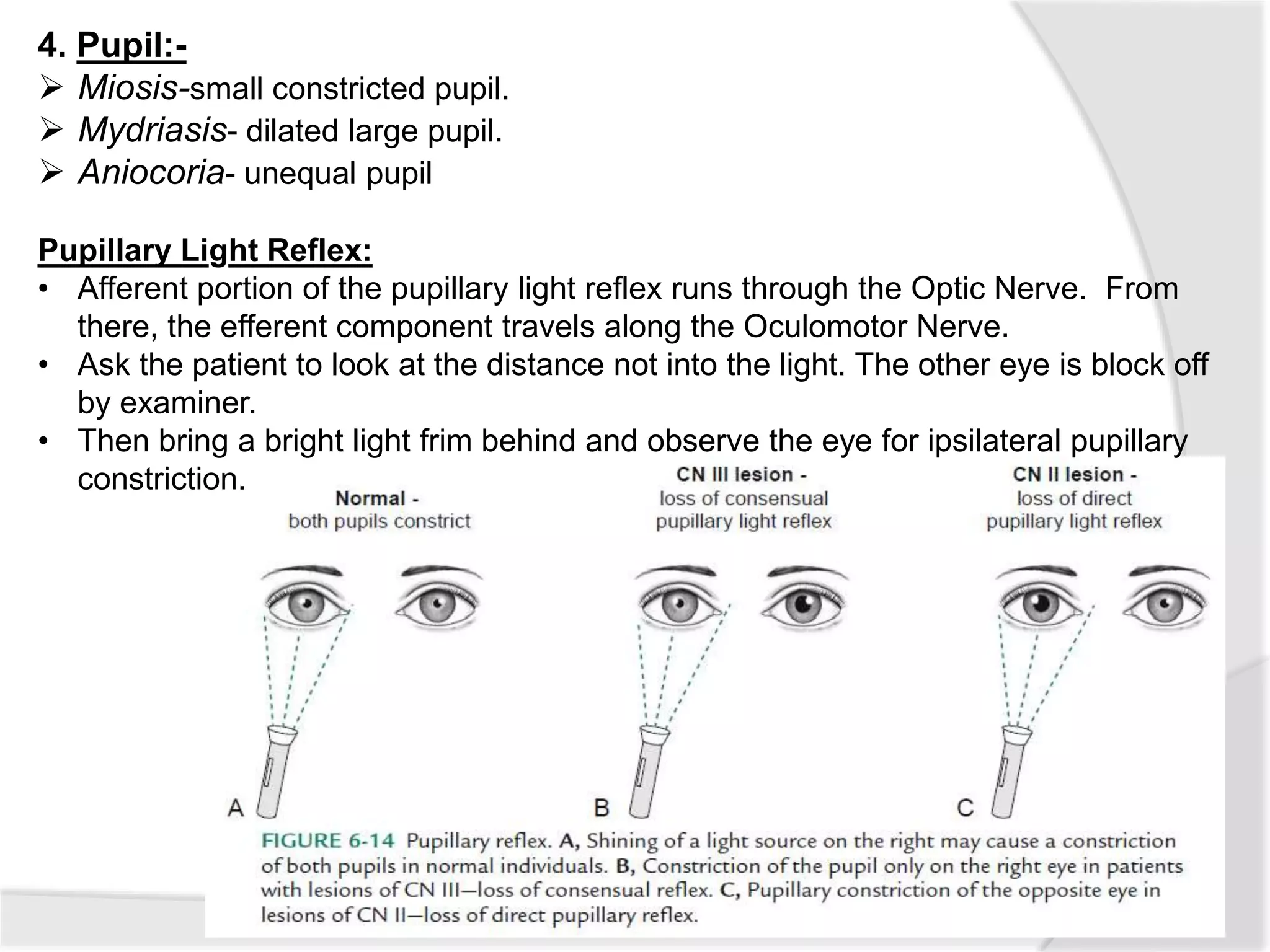
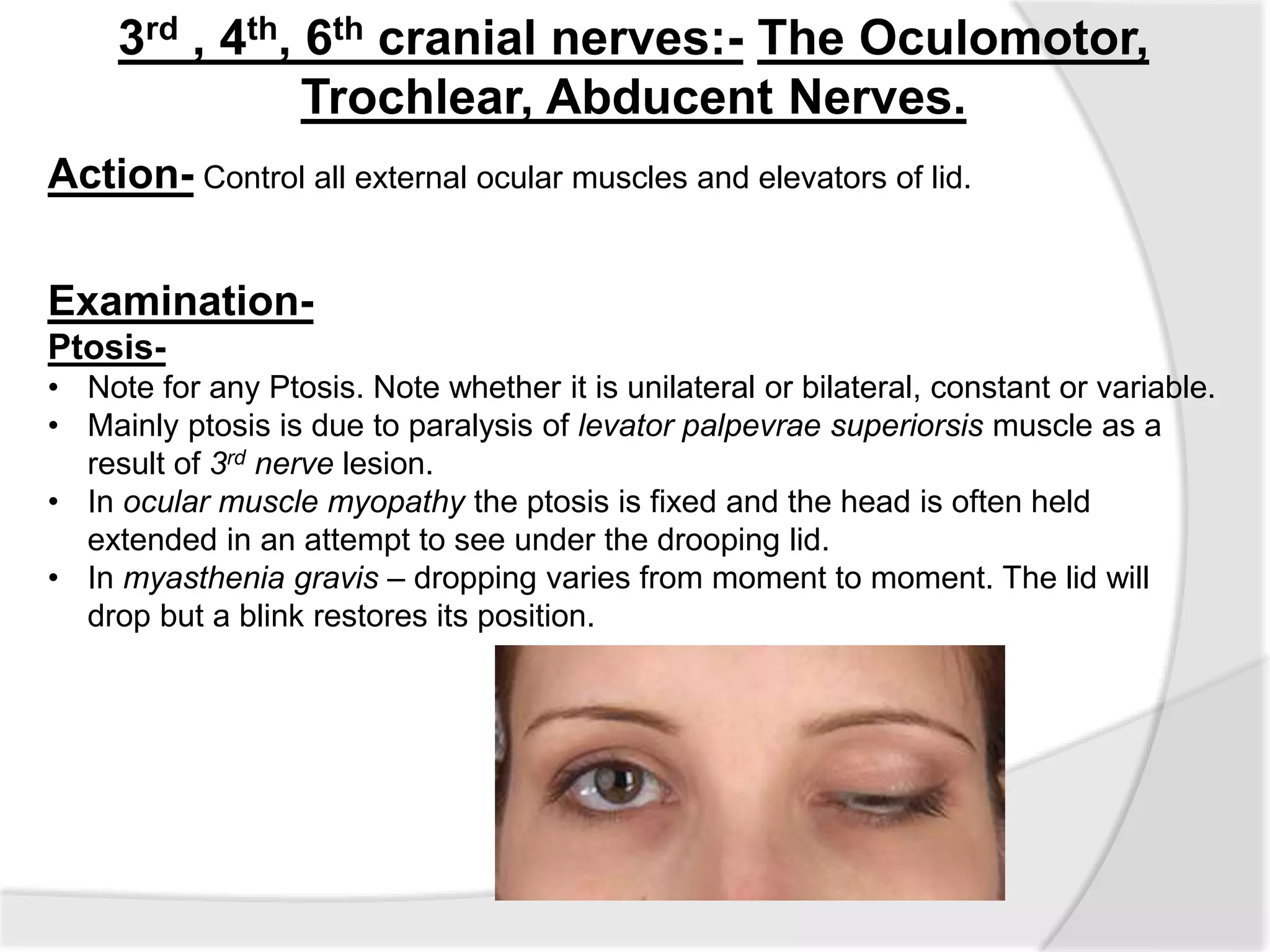
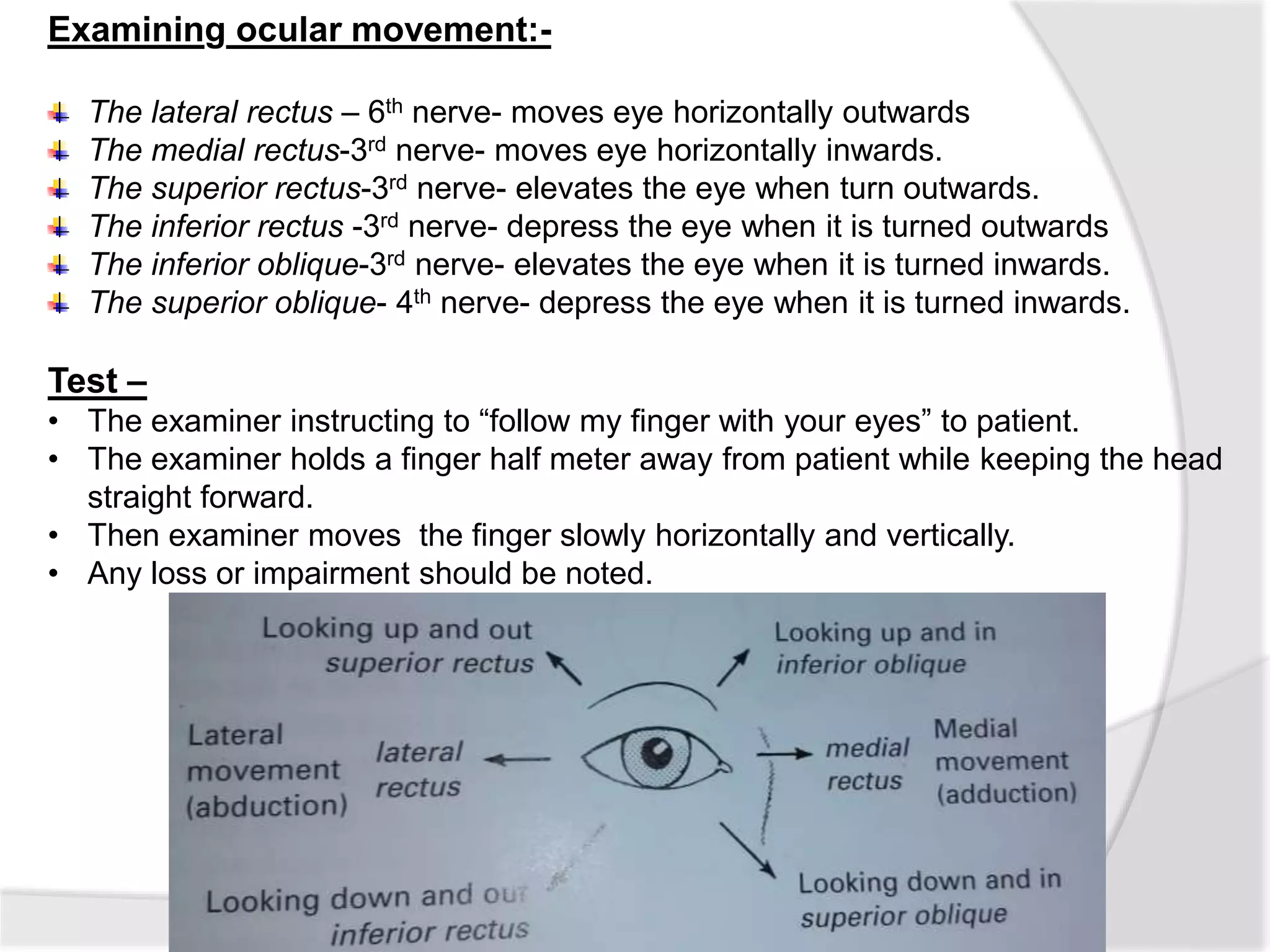
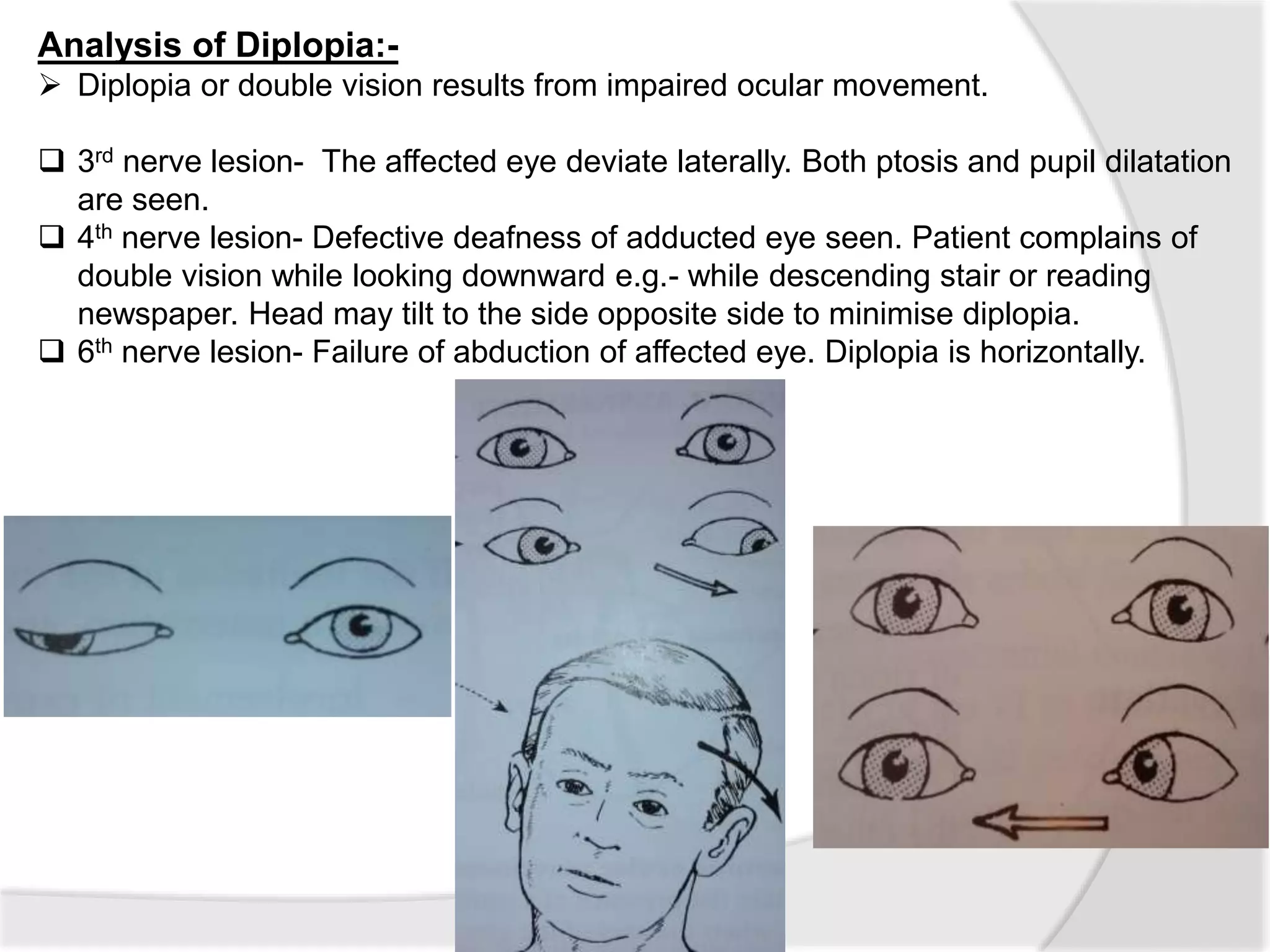
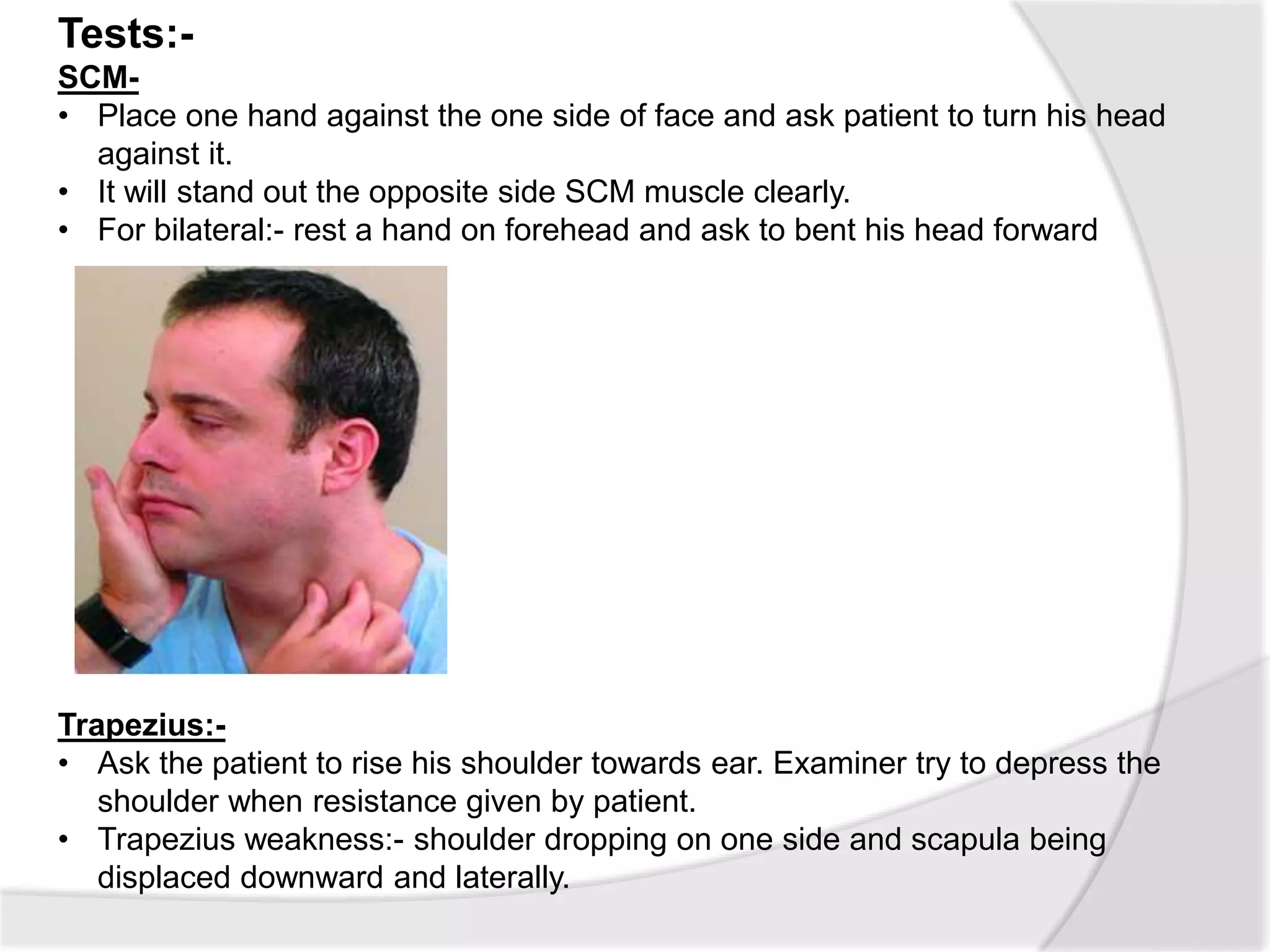
This document summarizes the examination of the 12 cranial nerves. It describes the function and tests for each nerve. For the first cranial nerve (olfactory nerve), it explains how smell tests are performed using familiar odors. For the second cranial nerve (optic nerve), it outlines tests for visual acuity, visual fields, color vision, and pupillary reaction. It then discusses examination of eye movements and analysis of diplopia for the third, fourth, and sixth cranial nerves. The document provides a high-level overview of testing sensation and motor function for the remaining cranial nerves.