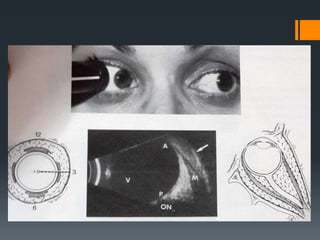
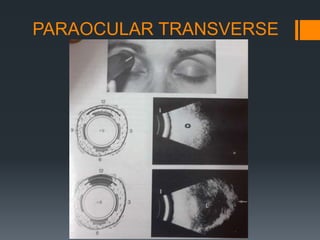
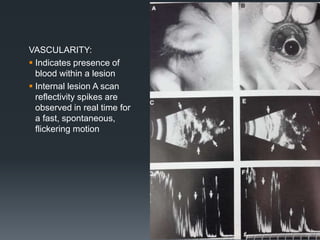
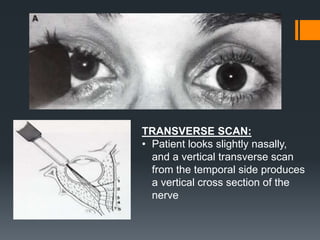
Ultrasound is a useful tool for evaluating orbital diseases. It uses high frequency sound waves to create images of intraocular and orbital structures. A systematic ultrasound examination involves evaluating the orbital soft tissues, extraocular muscles, and retrobulbar optic nerve. Abnormalities are identified based on changes in location, size, shape, internal reflectivity, and mobility compared to the normal structures. This allows differentiation of various pathologies, such as cysts, masses, muscle thickening, and optic nerve swelling. A comprehensive ultrasound examination provides valuable information for diagnosing and monitoring orbital diseases.