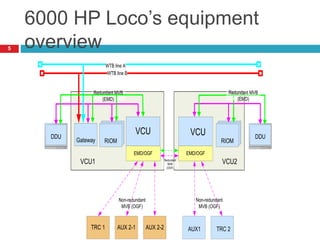
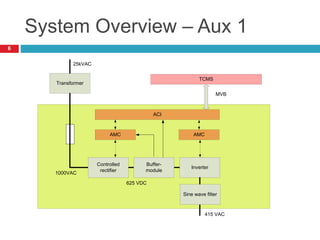
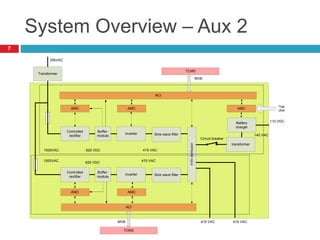
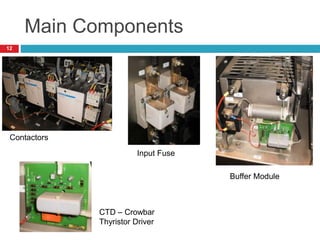
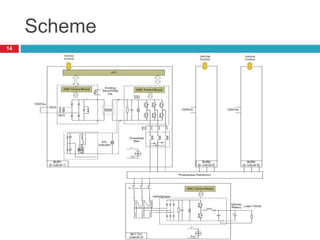
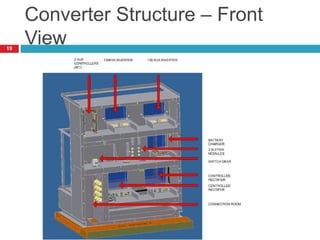
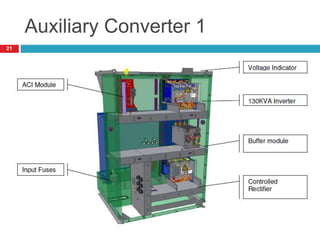
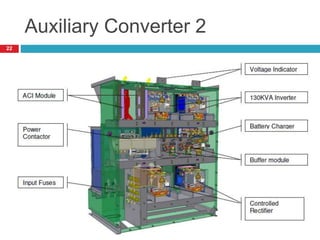
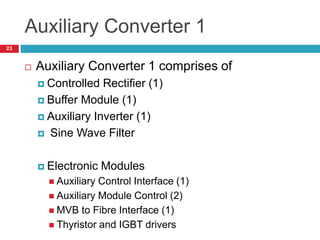
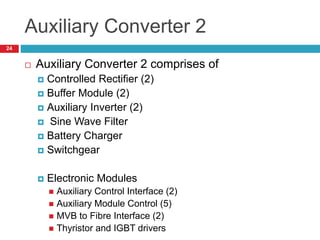
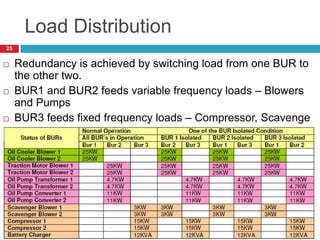
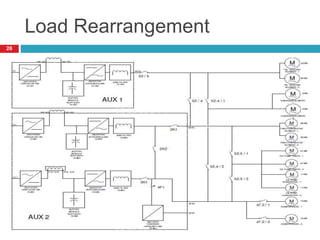
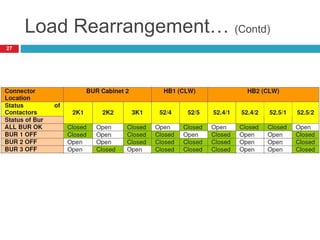
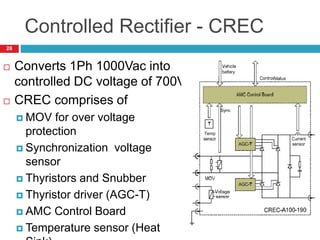
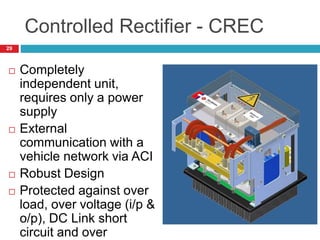
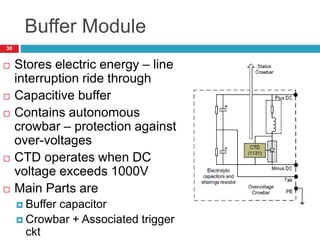
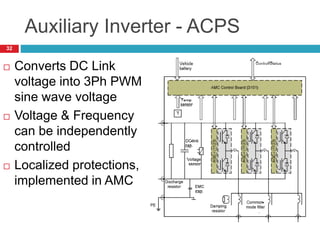
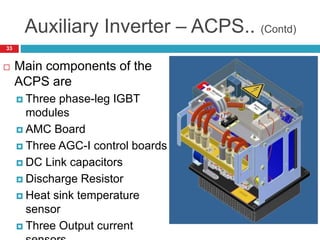
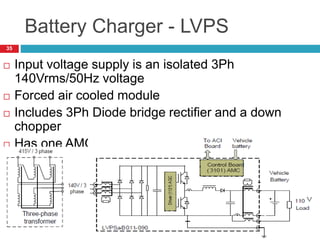
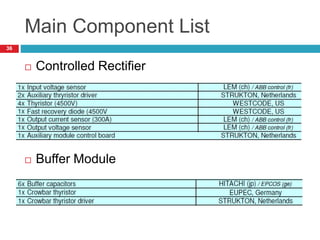
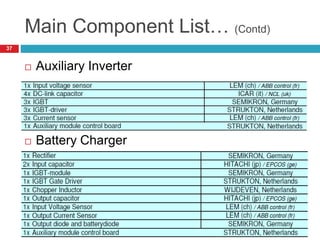
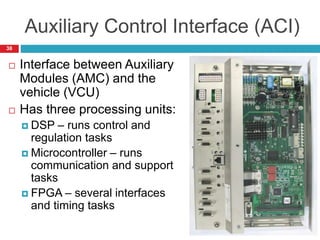
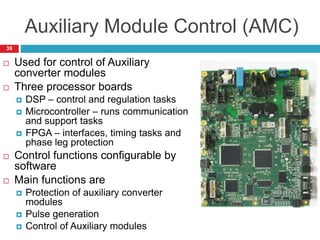
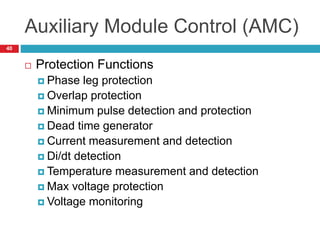
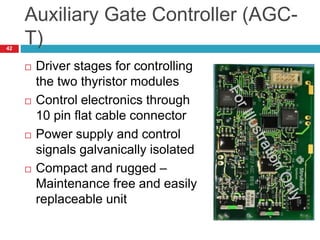
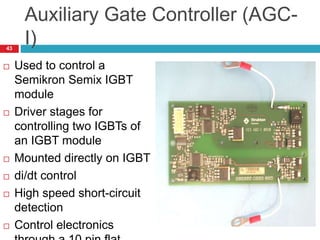
The document summarizes the auxiliary converter system used for electric locomotives. It includes two auxiliary converters (Aux 1 and Aux 2) that generate 415V AC power from the 1000V auxiliary winding of the traction transformer. Aux 1 powers variable frequency loads while Aux 2 includes an additional battery charger. The main components are controlled rectifiers, buffer modules, auxiliary inverters, and various electronic control modules. Load is distributed and rearrangement is possible between the three auxiliary converters for redundancy.