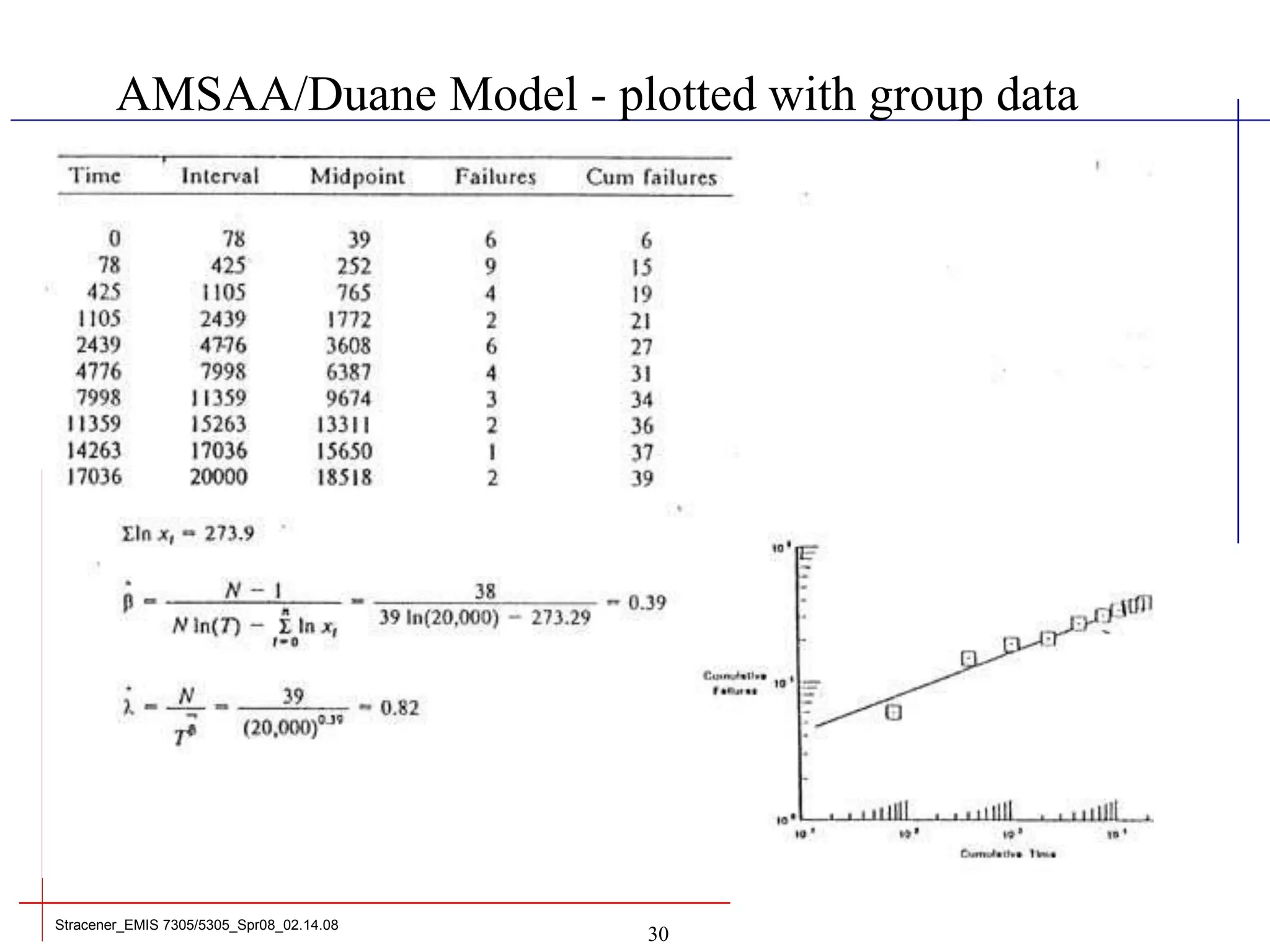
This document discusses reliability growth modeling and analysis. It defines reliability development testing and describes the test, analyze, and fix (TAAF) process used to achieve reliability growth. The document focuses on the Duane reliability growth model, explaining how it models mean time between failures (MTBF) and failure rate as a function of cumulative test time using parameters like growth rate. Graphs demonstrate how Duane models can fit reliability data and be used for reliability growth assessment and forecasting.