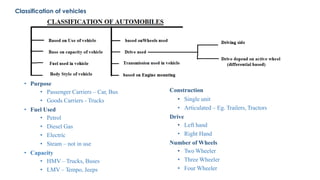
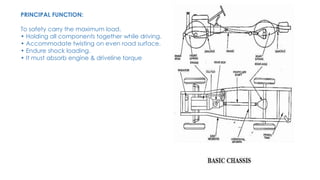
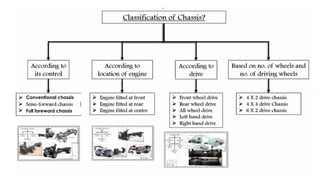
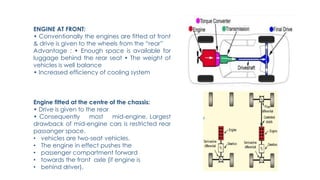
An automobile is a self-propelled vehicle used for transporting goods and passengers on the ground. Examples include mopeds, scooters, motorcycles, cars, jeeps, trucks, tractors, ships, aircrafts, and rockets. The history of automobiles began in 1801 with the steam carriage and progressed through important milestones like the first gas-powered automobile in 1885. Automobiles are classified based on their purpose, fuel used, and capacity. The main components of an automobile include the chassis, engine, brakes, steering system, and wheels. The chassis provides the main supporting structure and consists of the engine, brakes, steering, and wheels mounted on a frame.