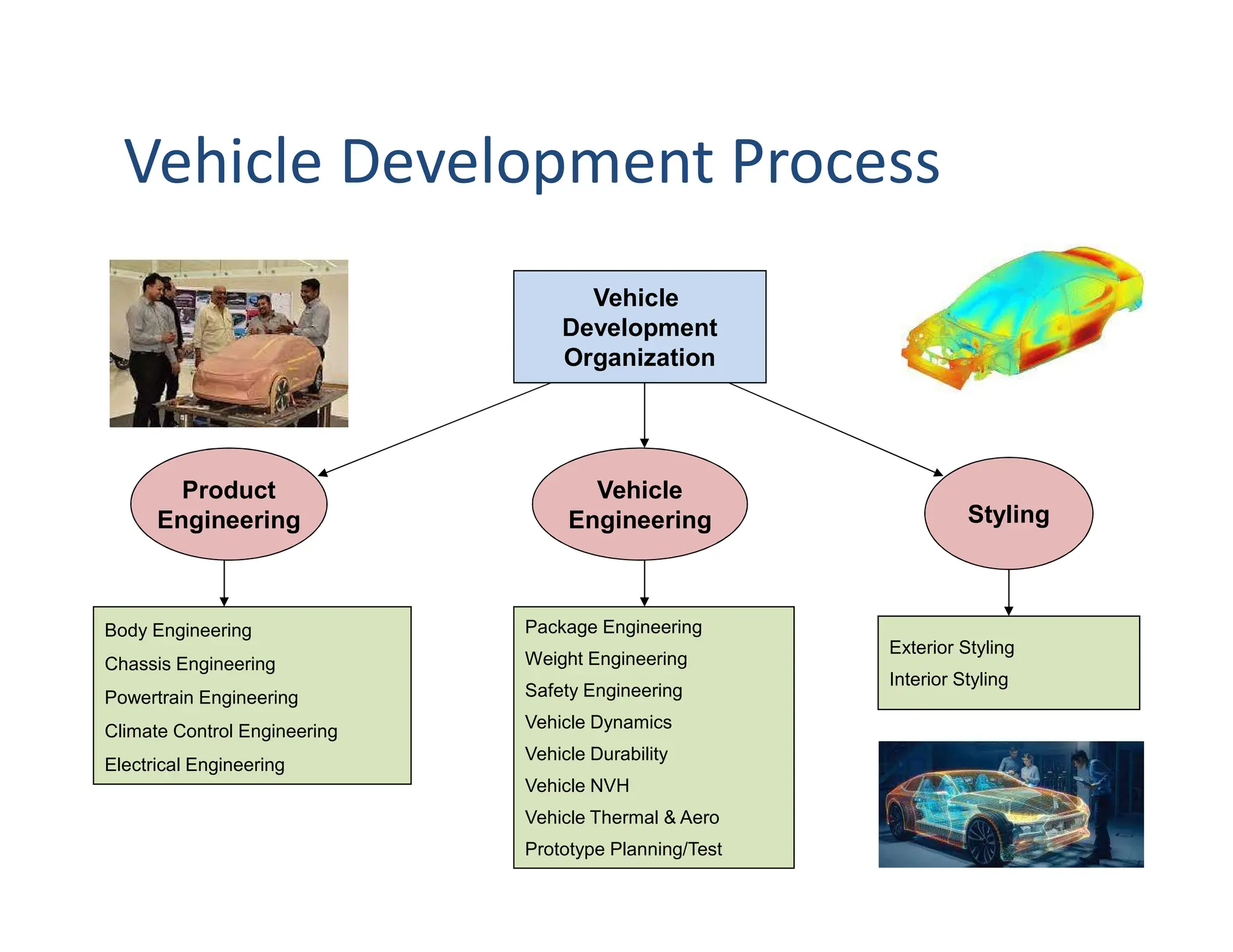
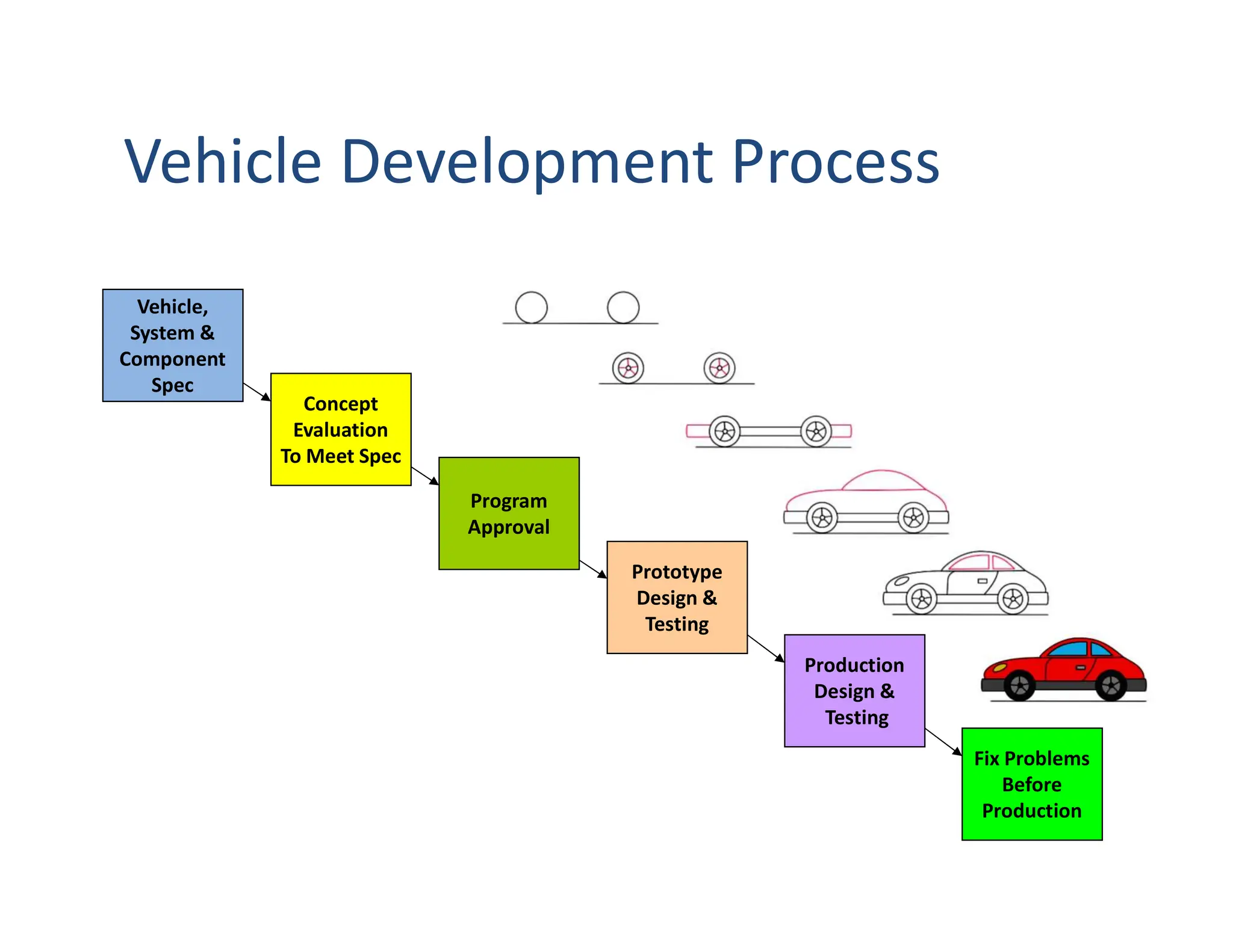
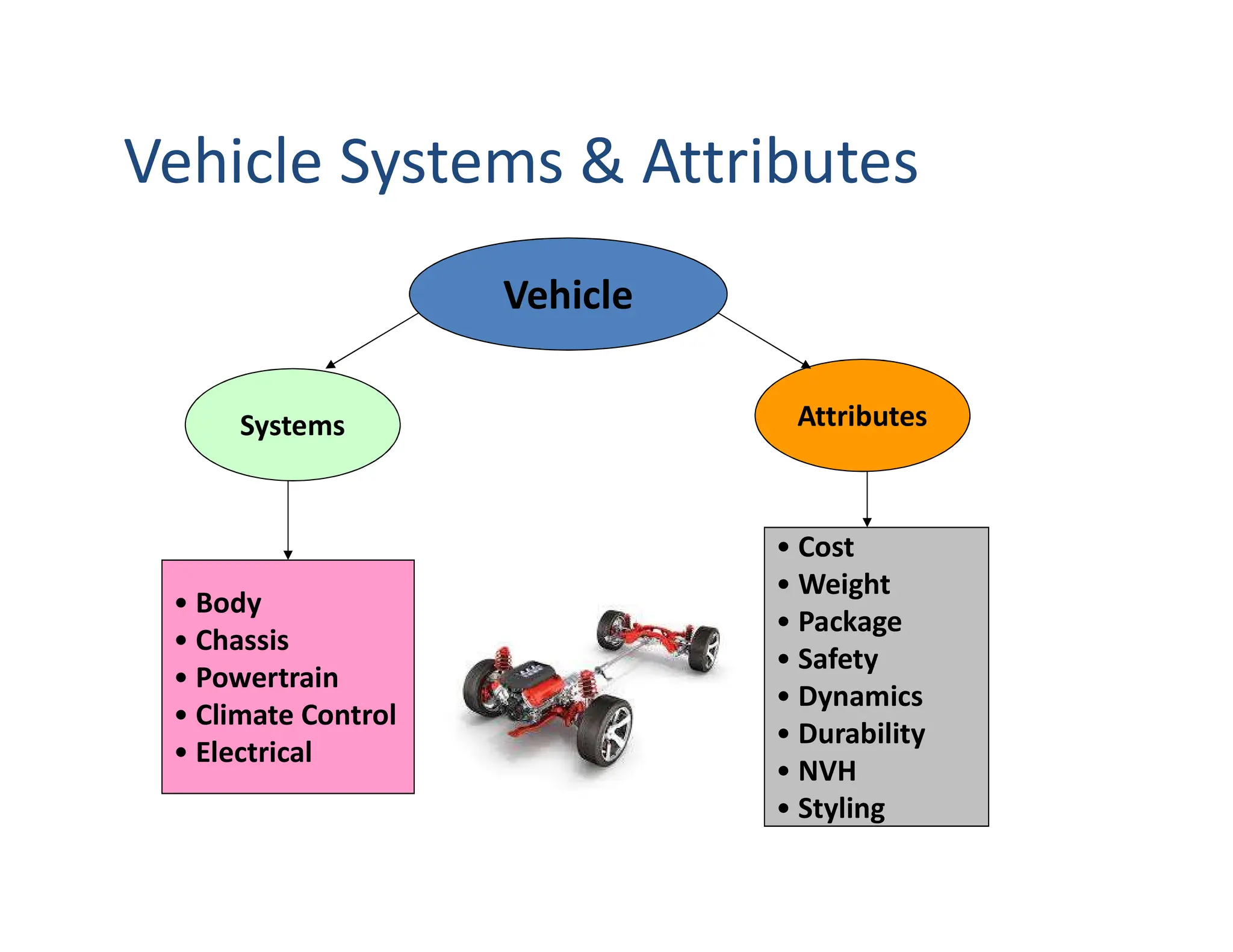
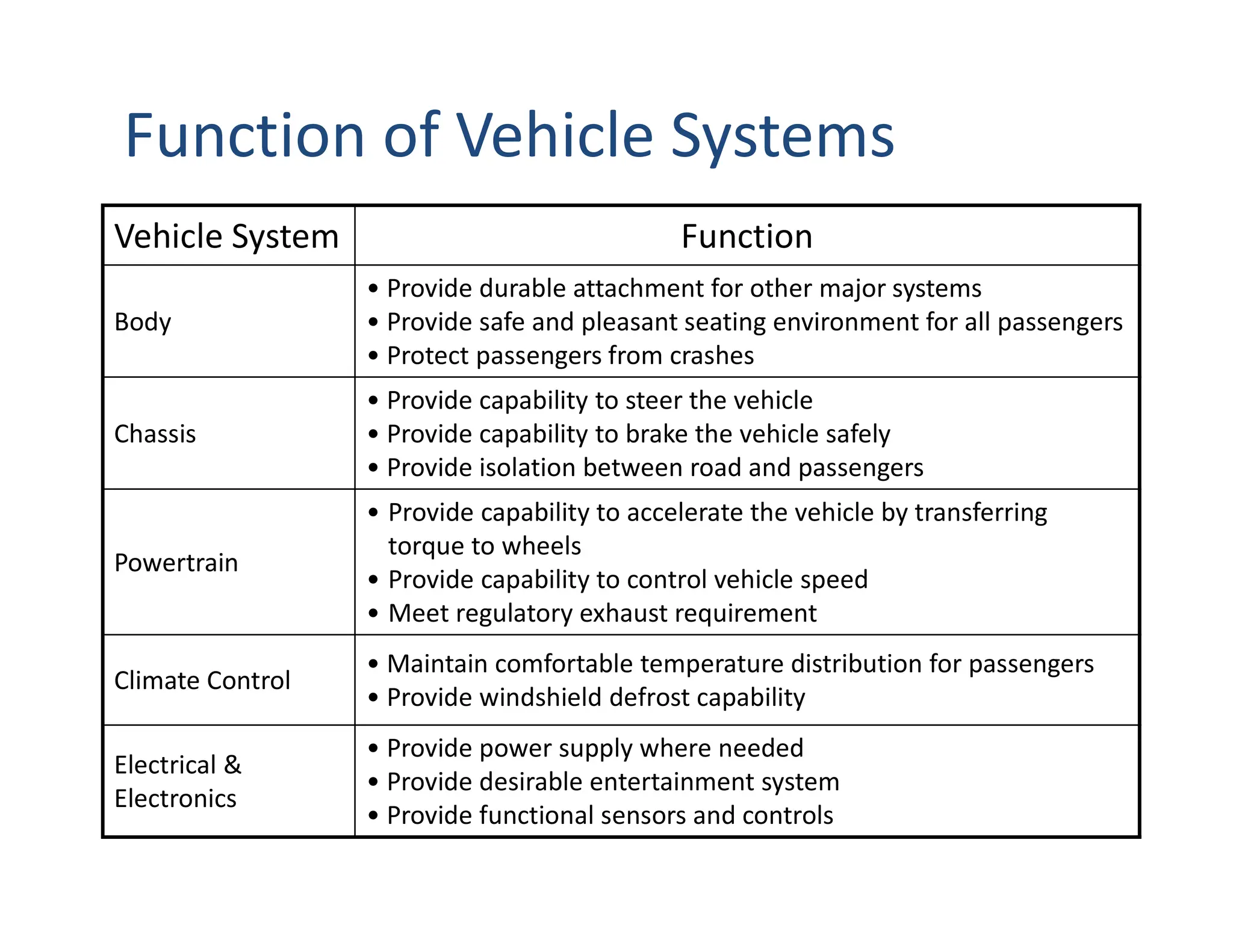
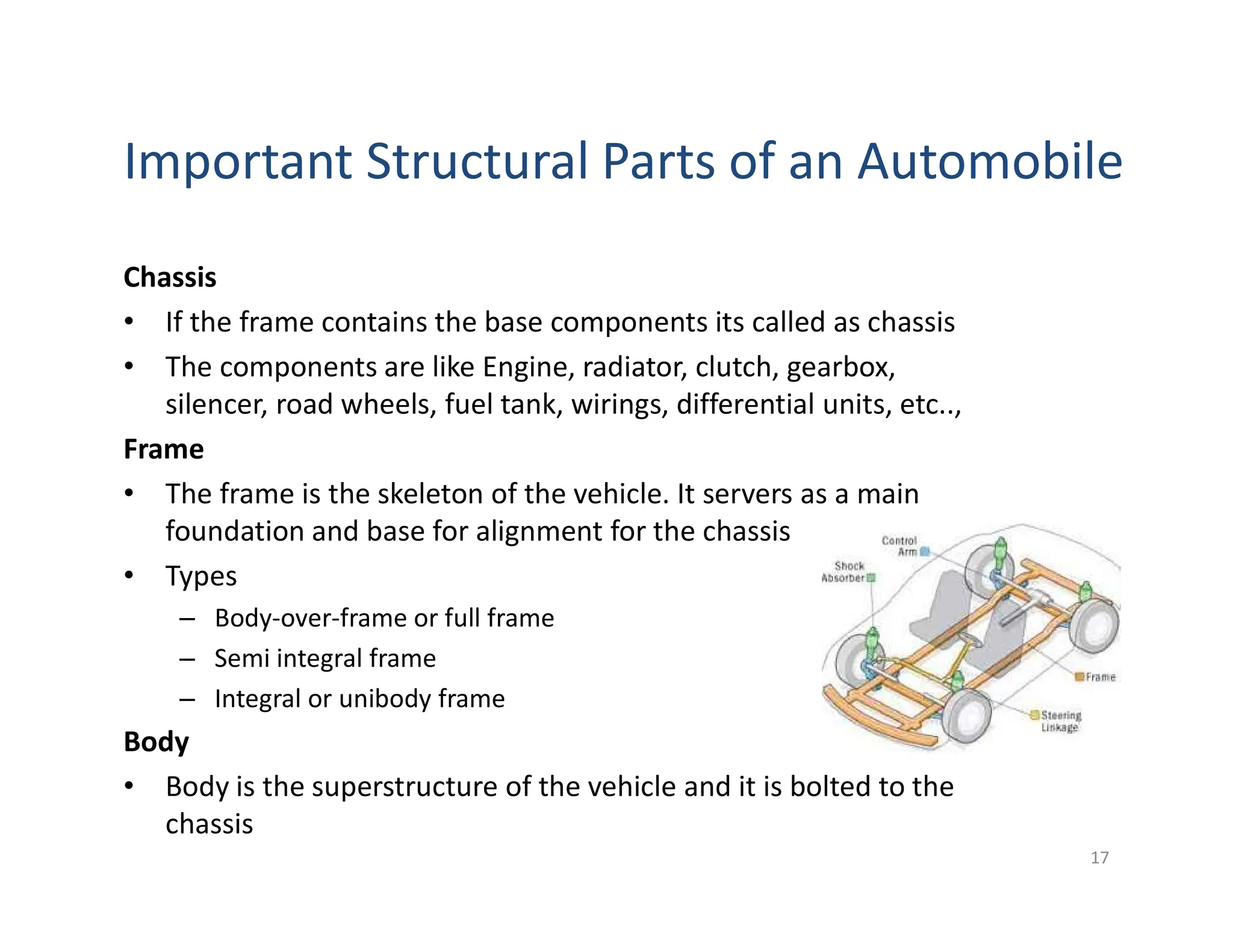
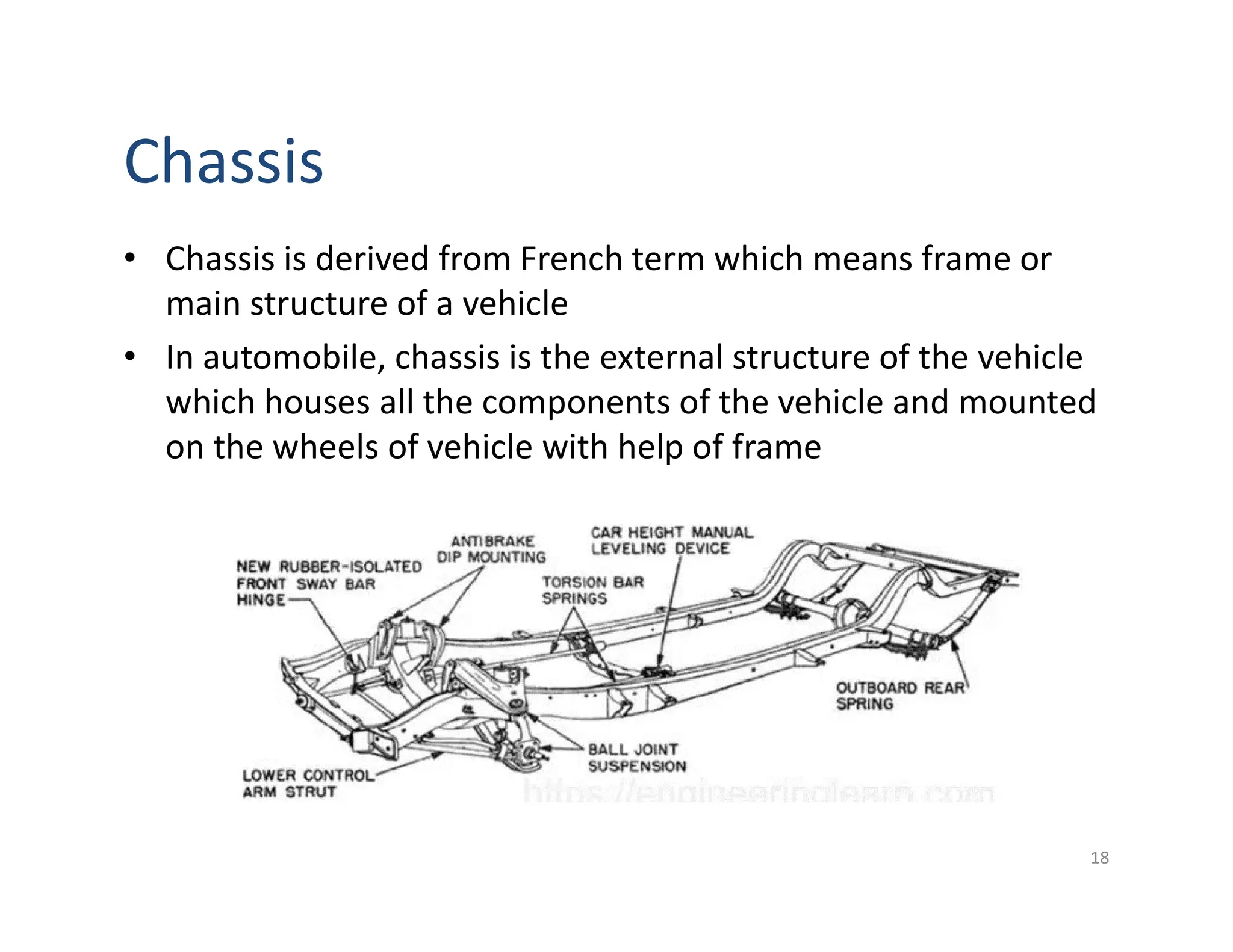
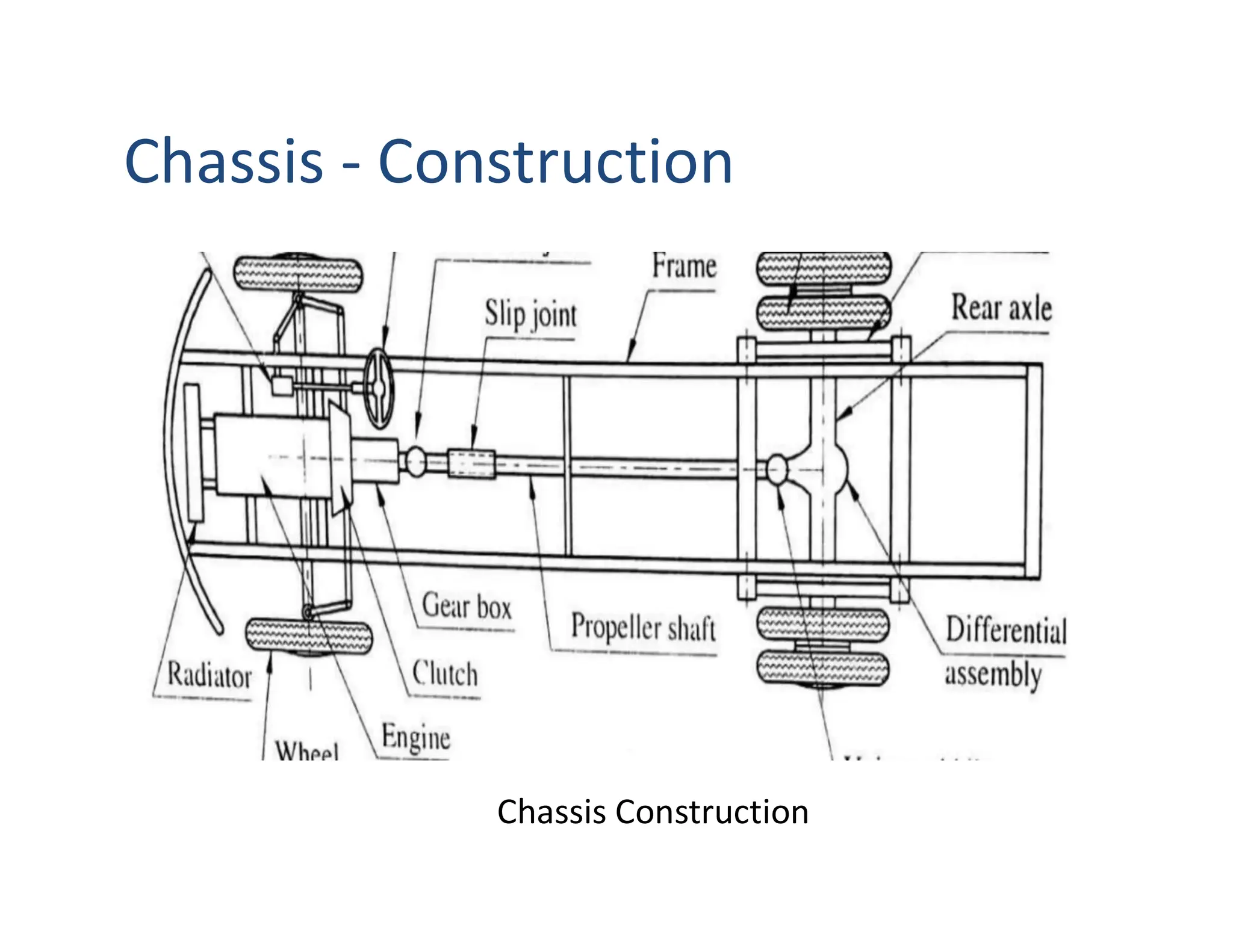
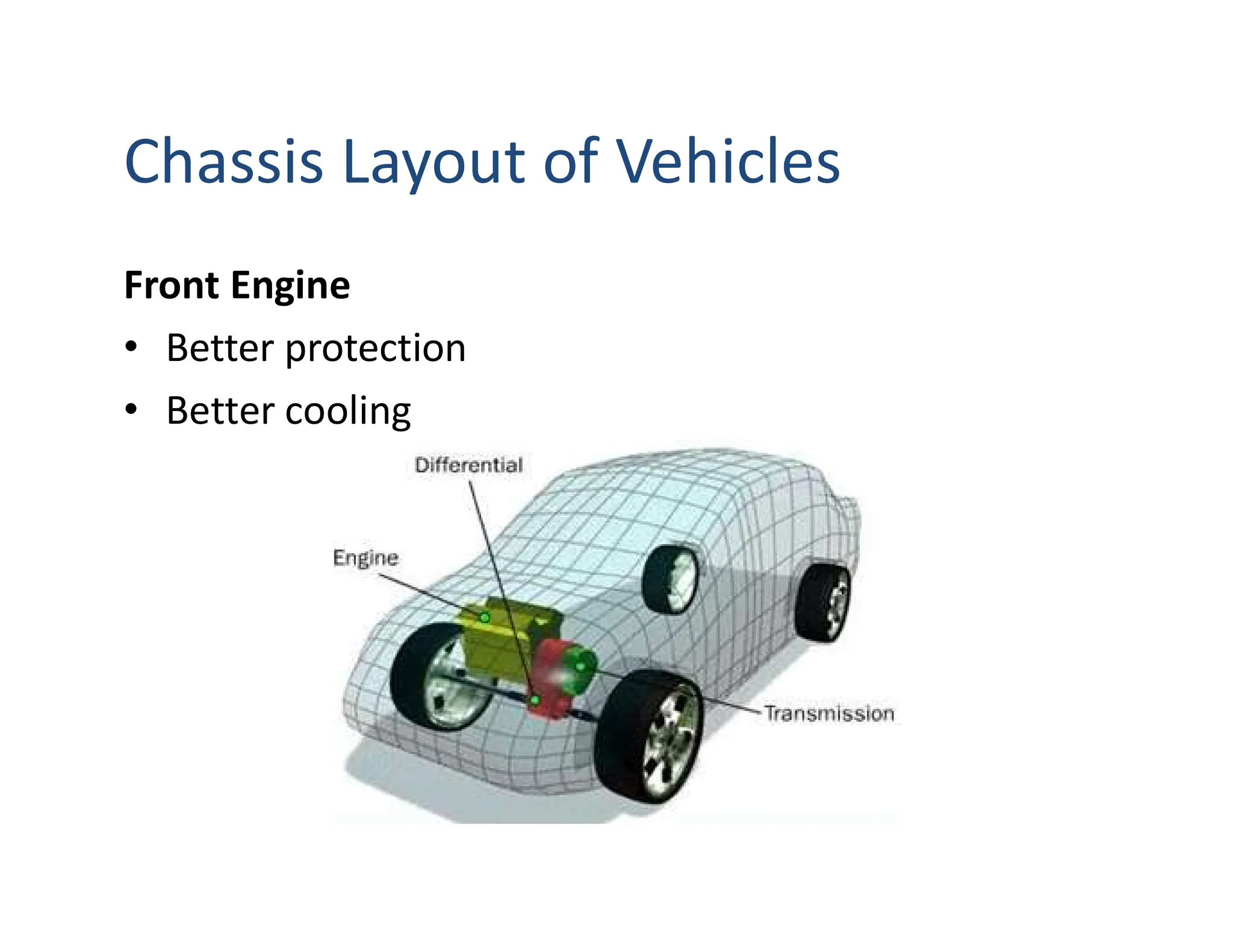
This document provides an overview of an introductory course on basic automobile engineering. It discusses various vehicle components and systems including types of automobiles based on fuel, body style, wheels, load capacity and more. It describes common vehicle layouts such as front-engine front-wheel drive, rear-engine rear-wheel drive, and discusses different frame and chassis types including ladder, perimeter, subframe, and unitized body construction. The document also covers aerodynamic drag forces on vehicles and vehicle performance parameters.




























![Bharat NCAP - Crash Test Norms
• Car crash worthiness is very important as India has seen more road deaths
per year than any other nation since 2006, costing lives at the rate of
230,000 annually.
• Bharat NCAP 2023 is similar to Global NCAP 2023,[10] which is based on
Latin NCAP 2016
• Bharat NCAP started the official testing from December 2023 onwards.
• The car testing protocols is defined by the Automotive Research
Association of India (ARAI) and published in AIS 197.
(AIS-Automotive Industry Standard)
• The impact test includes:
– Offset Deformable Barrier (ODB) Frontal Impact Test (64 km/h speed)
– Mobile Deformable Barrier (MDB) Side Impact Test (50 km/h speed)
– Pole Side Impact Test (29 km/h speed)
• Points would be awarded to the car based on crash test results and the
safety features in the car like ABS, seat belt reminders, child lock, and
Electronic Stability Control.
78](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1-automobileengineering-intro-240321122540-8dc346e9/75/Unit-1-Automobile-Engineering-Intro-pdf-78-2048.jpg)


