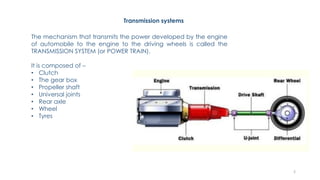
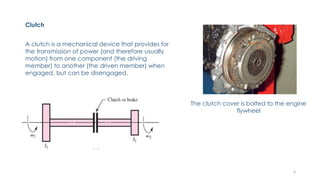
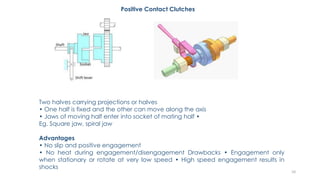
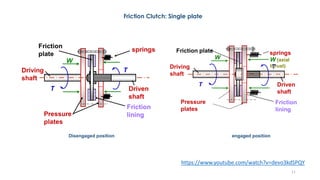
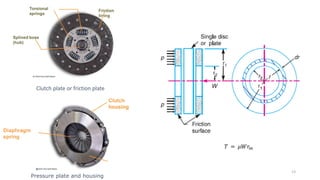
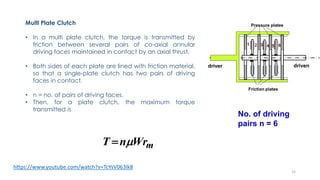
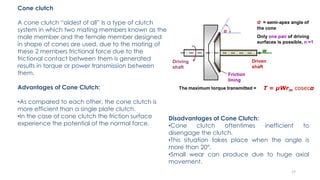
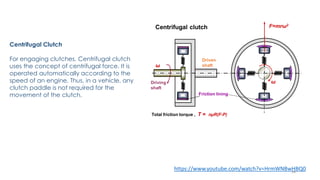
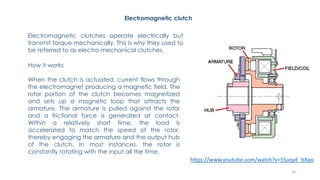
The document discusses various types of vehicle transmission systems. It begins by defining the transmission system and its main components like the clutch, gearbox, propeller shaft, etc. It then lists the key requirements of an effective transmission system. The rest of the document focuses on different types of clutches used in vehicles - including single plate, multi-plate, cone, centrifugal, electromagnetic, and torque converter clutches. For each type, it provides details on parts, operation, applications, and advantages/disadvantages.