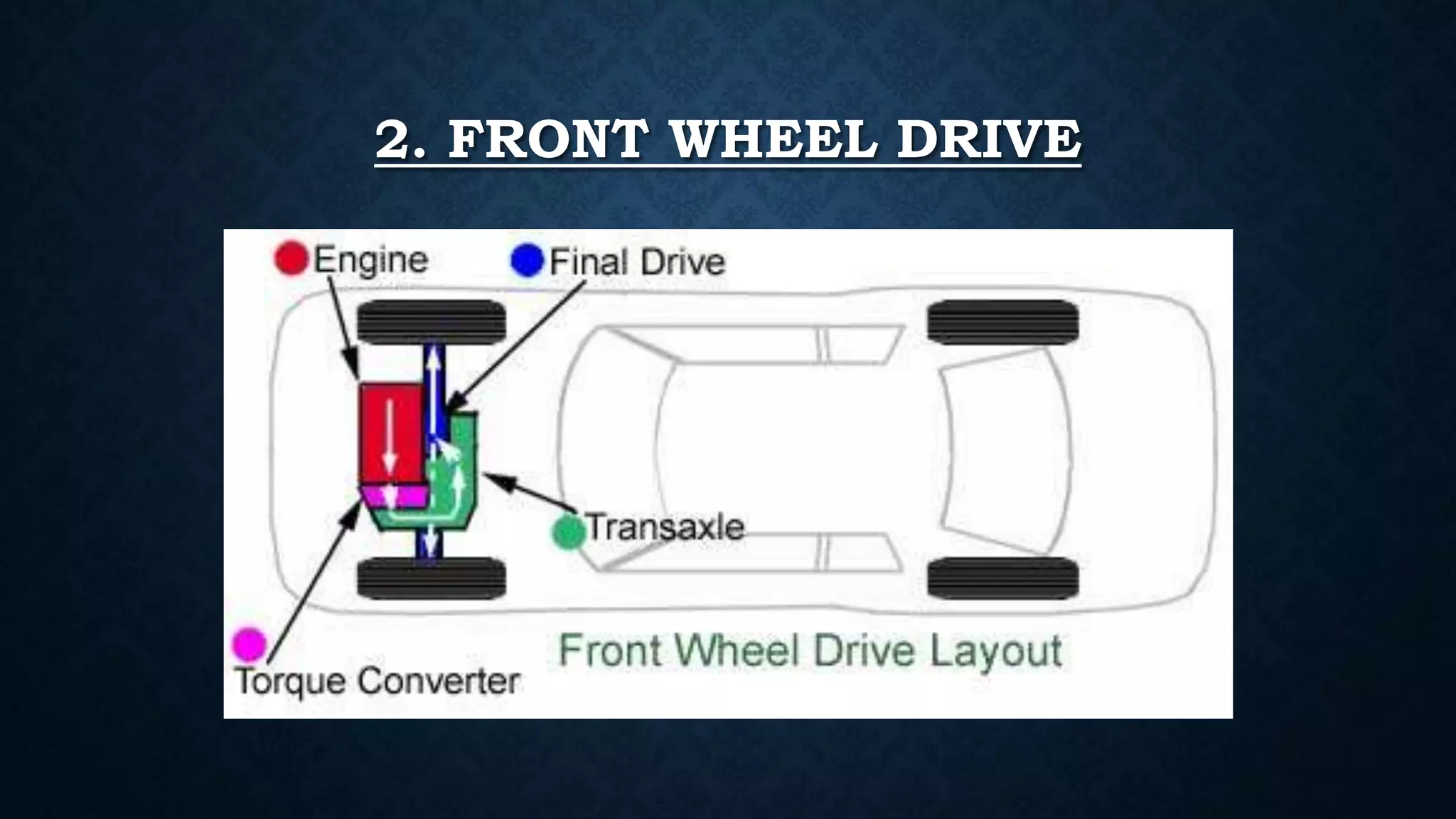
The document discusses the complexities of automatic transmission systems in modern vehicles, detailing their mechanical, hydraulic, electrical, and computer components. It outlines the types of automatic transmissions, their key components such as clutch packs and torque converters, as well as their operational principles. The conclusion highlights the growing use of automatic transmissions in the automobile industry, while noting their inefficiencies compared to manual transmissions due to the extra power demands of their systems.