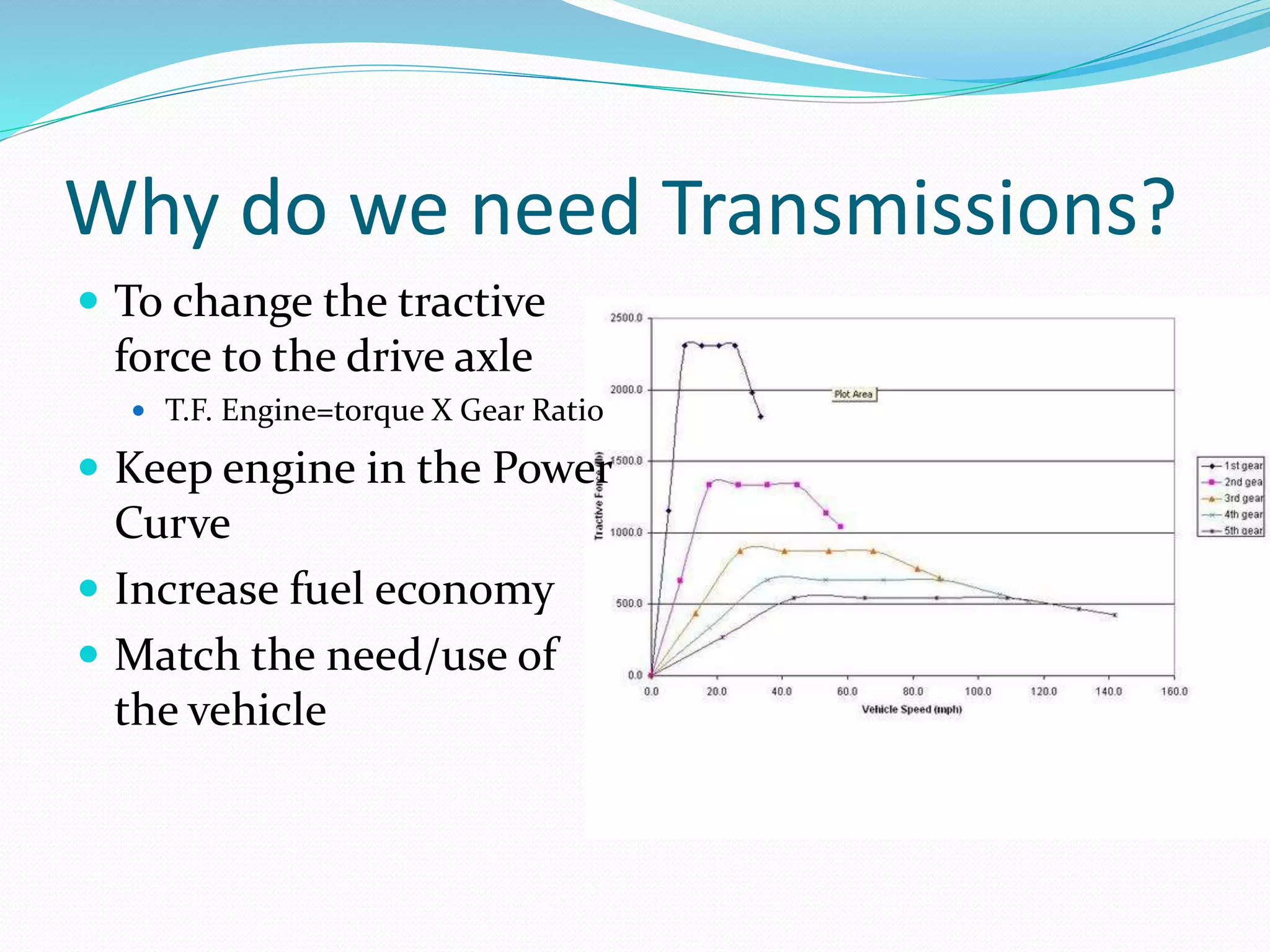
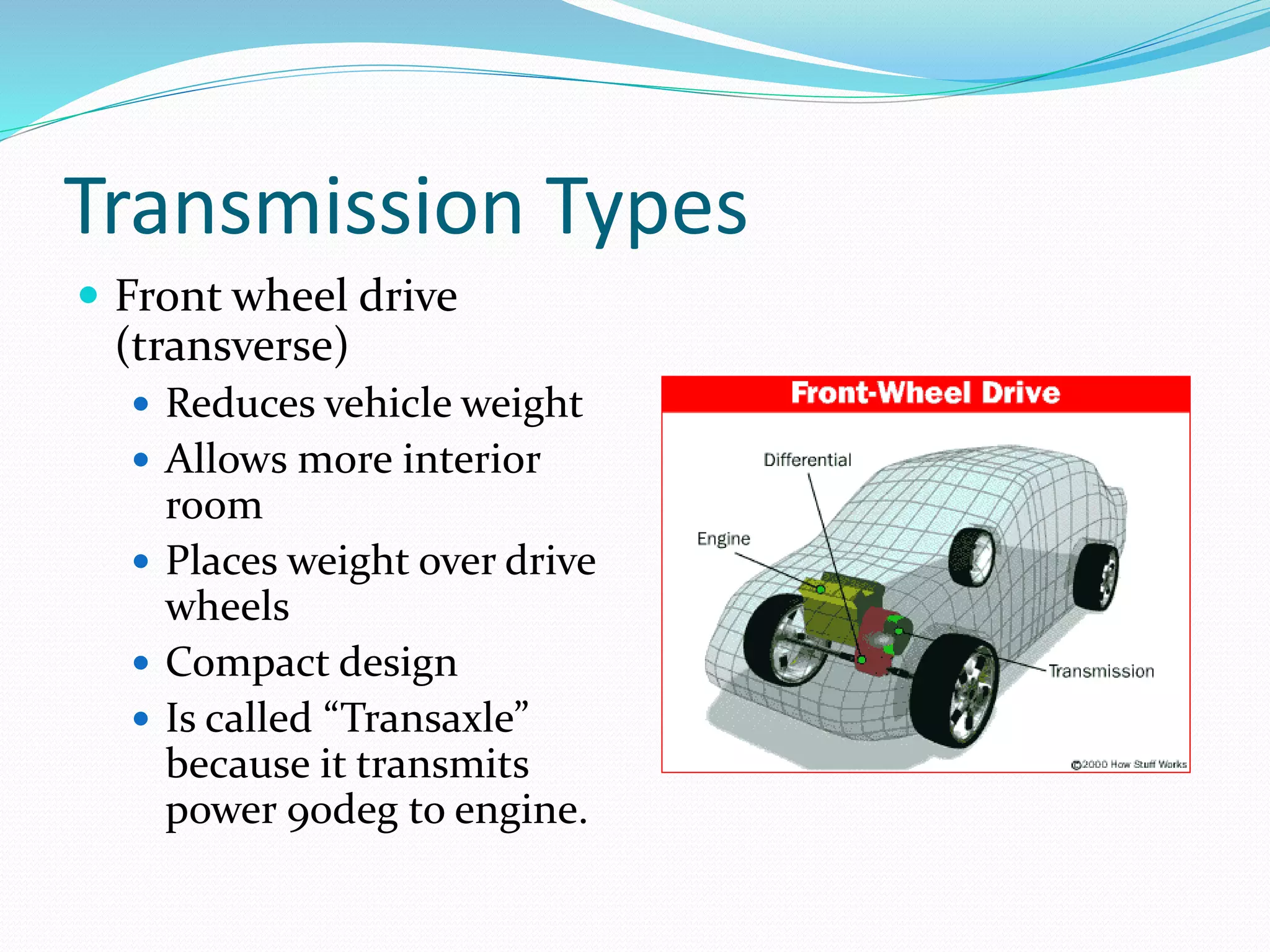
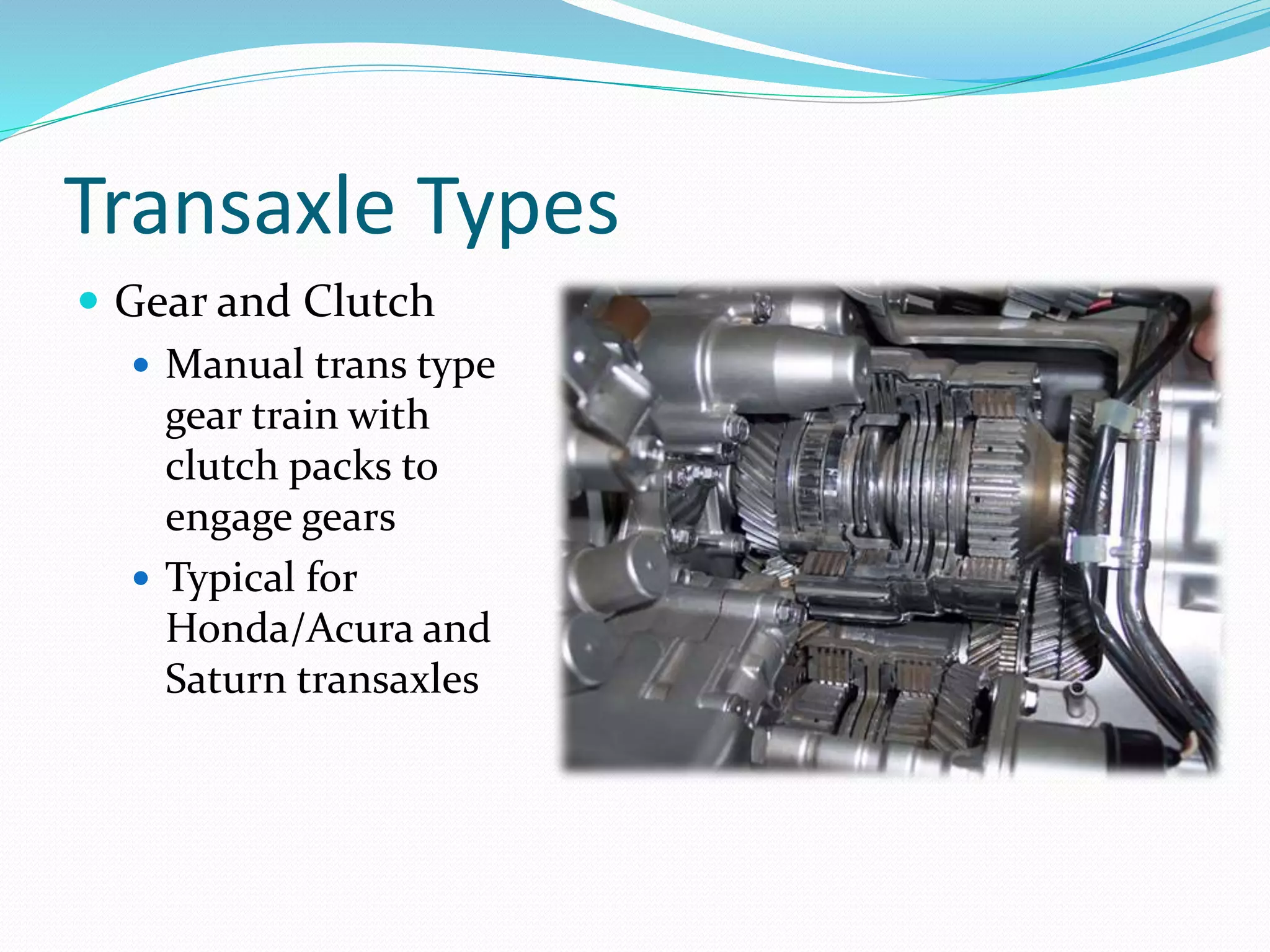
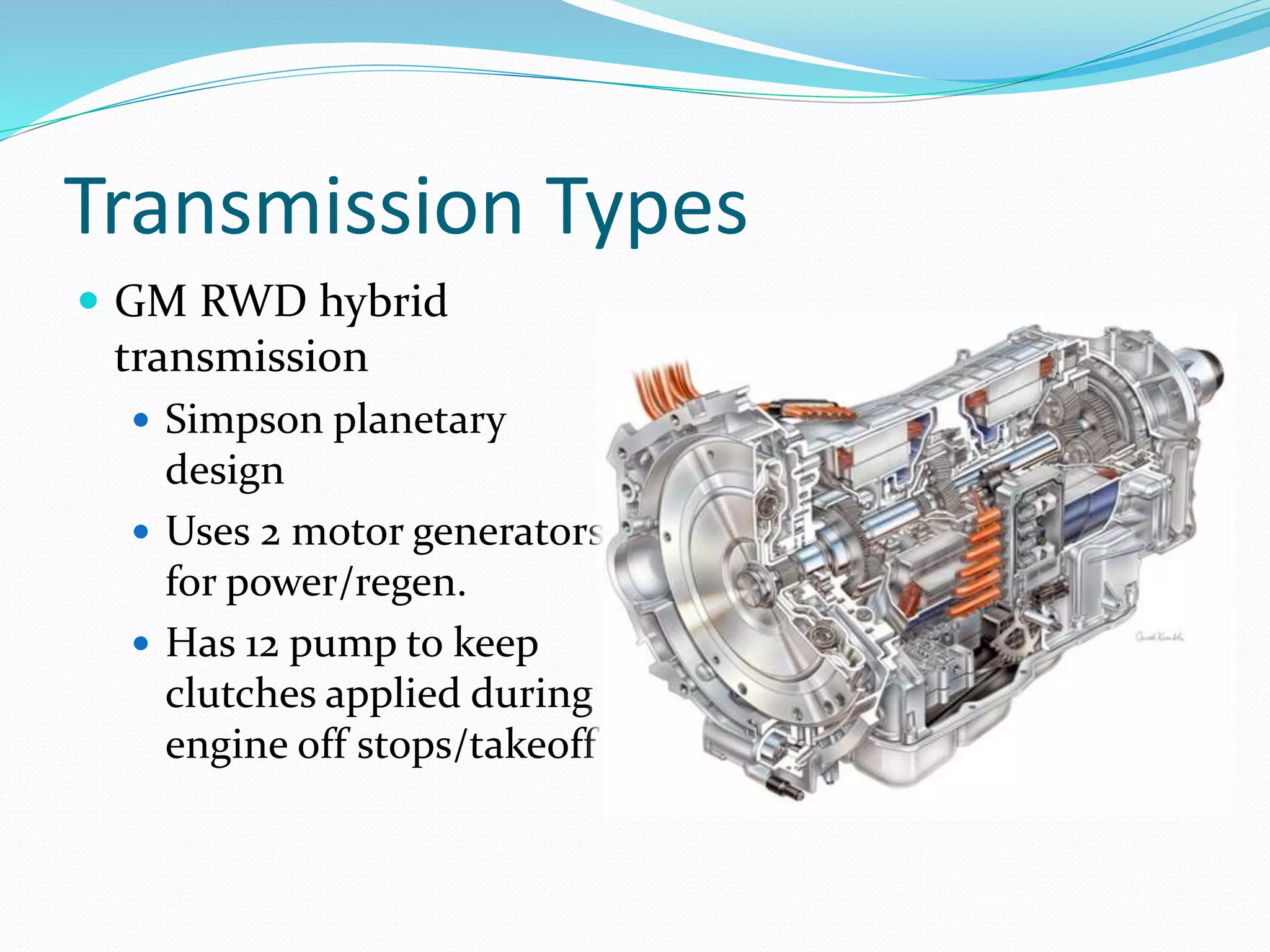
Transmissions are needed to change the tractive force delivered to the drive axles and keep the engine operating in its optimal power curve for increased fuel efficiency. The main types are front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive, and all-wheel drive/4-wheel drive. Front-wheel drive transmissions are called transaxles and place weight over the drive wheels while rear-wheel drive is more robust. Transaxle designs include planetary gear sets, gear and clutch types, belt-driven continuously variable transmissions, and dual clutch transmissions. Safety precautions must be followed when working on hybrid vehicle transmissions.