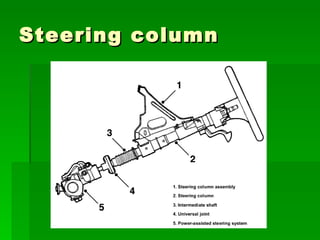
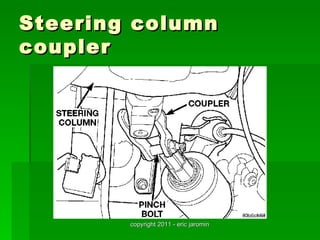
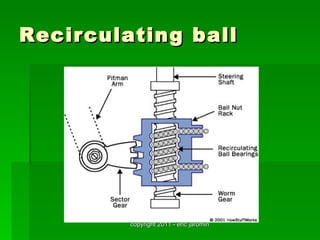
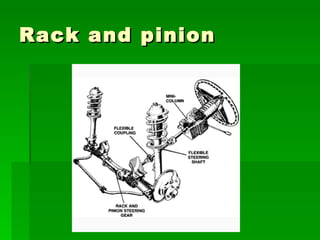
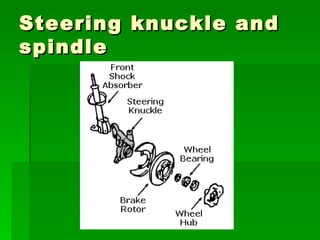
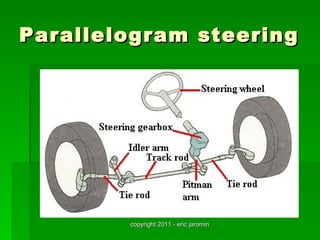
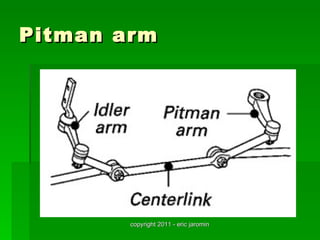
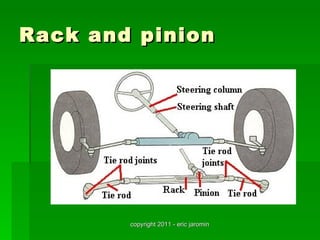
The document discusses the key components of steering systems, including the steering wheel, column, shaft, gear, linkage, and joints. It describes the function of each part and how they work together to translate driver input into wheel movement. The main types of steering gear systems - recirculating ball and rack and pinion - are explained in detail through diagrams and descriptions of how they operate.