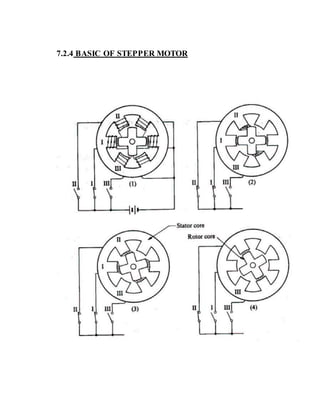
Here are the key points about stepper motors:
- A stepper motor rotates in discrete step angles in response to an applied digital signal. The motor's position is controlled by pulsing the motor windings on and off.
- Stepper motors can be rotated in both directions in incremental steps, making them ideal for open-loop control applications where precise positioning is required, such as 3D printers and CNC machines.
- They are made up of a rotor with permanent magnets and a stator with wound coils. The stator windings are energized in a sequence to rotate the motor. Different winding sequences produce different step angles.
- Bipolar stepper motors have four or more wires connecting