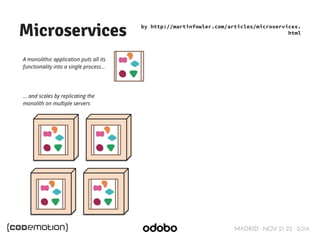
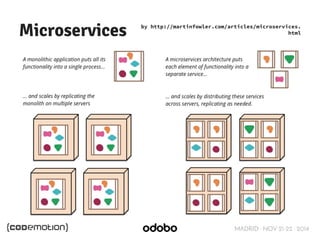
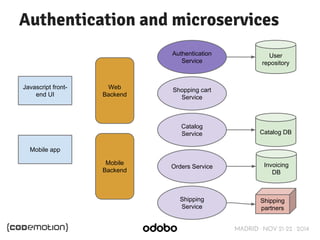
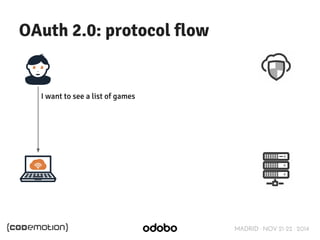
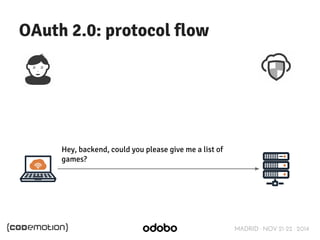
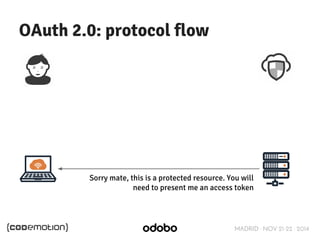
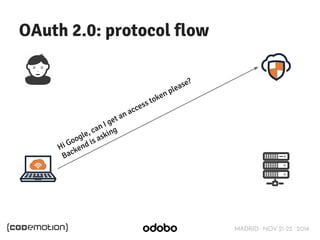
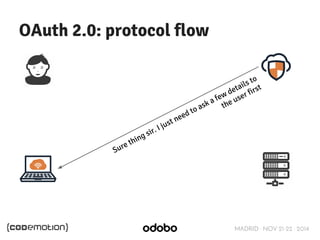
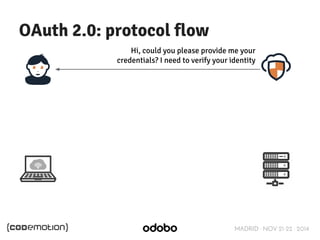
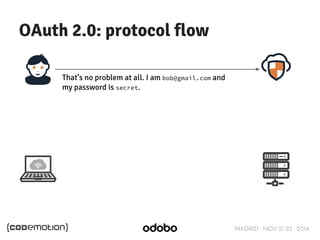
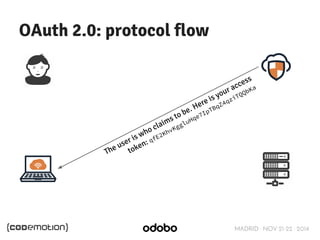
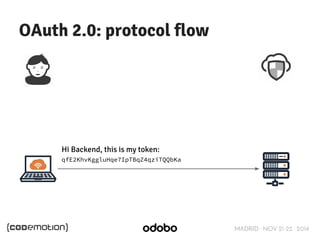
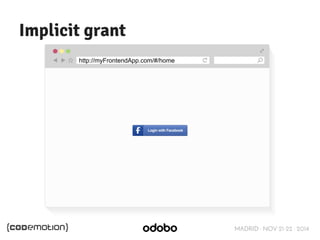
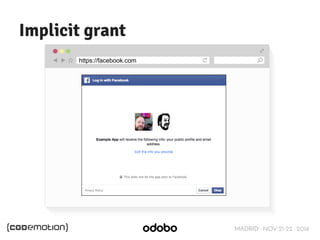
The document discusses stateless token-based authentication mechanisms for front-end applications, focusing on OAuth 2.0 and JSON Web Tokens (JWT). It contrasts traditional stateful authentication in monolithic applications with the demands of microservices, stressing the need for statelessness. A detailed agenda is provided, covering topics like authentication methods, OAuth roles, and practical implementation considerations for developers.

















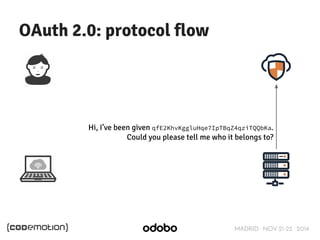
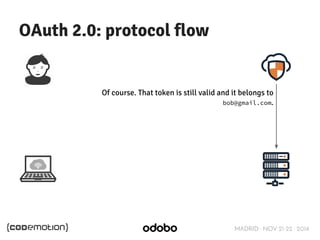
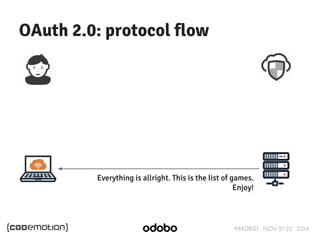

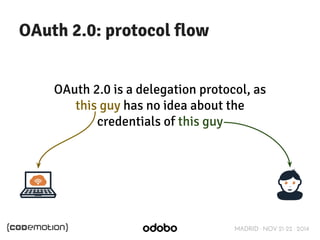
























![MADRID · NOV 21-22 · 2014
JWT Claims
{
"exp": 1416471934,
"user_name": "user",
"scope": [
"read",
"write"
],
"authorities": [
"ROLE_ADMIN",
"ROLE_USER"
],
"jti": "9bc92a44-0b1a-4c5e-be70-da52075b9a84",
"client_id": "my-client-with-secret"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/authenticationformicroservices1-141121081359-conversion-gate02/85/Stateless-token-based-authentication-for-pure-front-end-applications-66-320.jpg)






