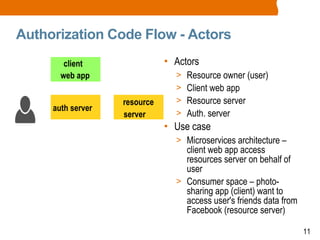
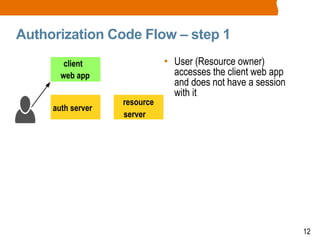
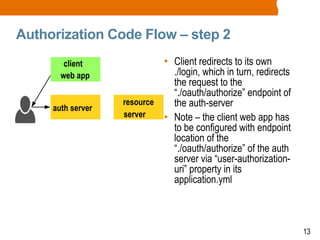
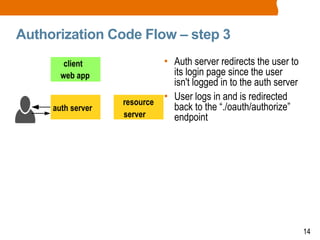
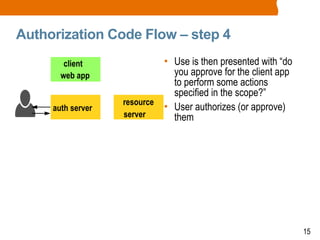
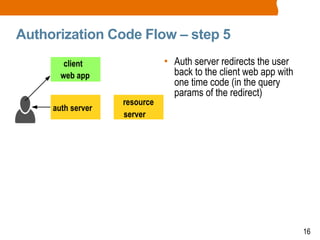
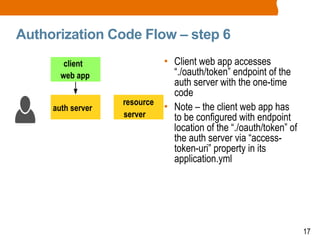
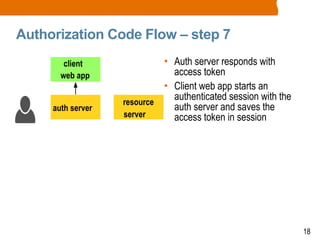
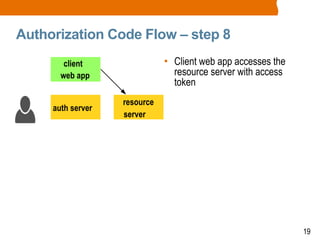
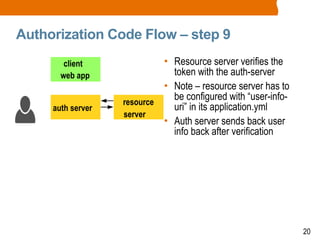
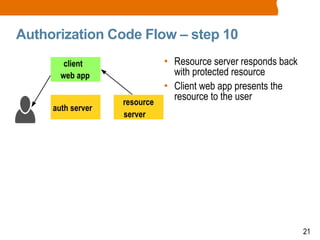
The document discusses OAuth2 and the authorization code flow. OAuth2 is a protocol for authorization that allows clients to obtain limited access to user accounts and reduces the scope of access. It involves four main actors: a resource owner (user), client app, authorization server, and resource server. The authorization code flow involves the client redirecting the user to the authorization server to log in, the user authorizing access, and the authorization server issuing an authorization code to the client, which can then request an access token to access protected resources from the resource server on the user's behalf.