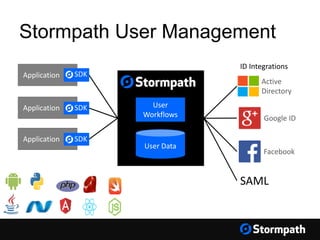
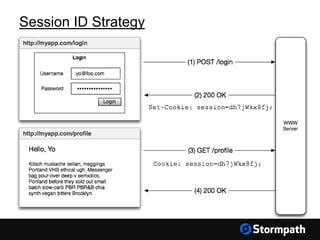
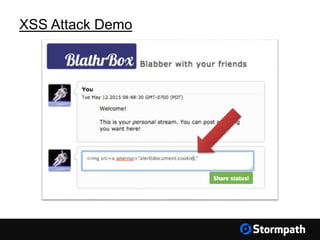
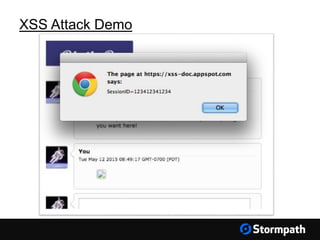
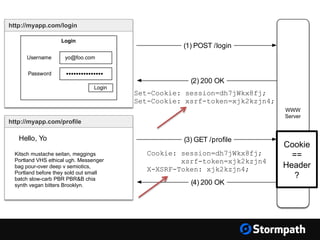
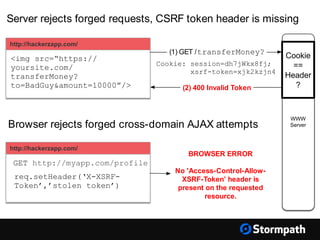
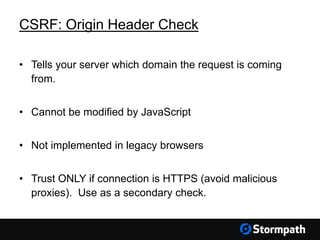
The document outlines key aspects of browser security, particularly for modern web applications, focusing on threats like XSS, CSRF, and MITM attacks. It discusses best practices for securing user credentials, sessions, and communication, along with the use of cookies and session identifiers. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of utilizing frameworks and tools for effective security measures in application development.