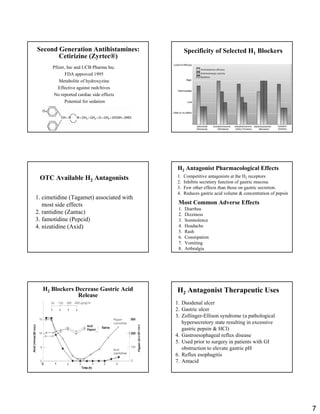
Histamine and antihistamines are discussed. Histamine is released from mast cells during allergic reactions and causes effects through H1, H2, and H3 receptors. Antihistamines block the H1 receptor, preventing histamine's effects. First generation antihistamines are sedating due to crossing the blood brain barrier, while second generation antihistamines are non-sedating as they do not cross as readily. Specific antihistamines discussed include diphenhydramine, loratadine, cetirizine, and fexofenadine. H2 antagonists like cimetidine and famotidine competitively block the H2 receptor to inhibit gastric acid secretion