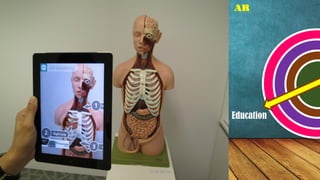
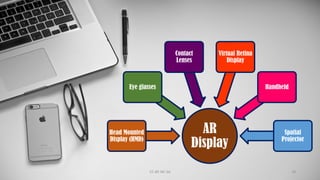
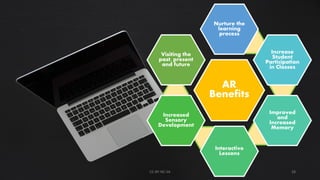
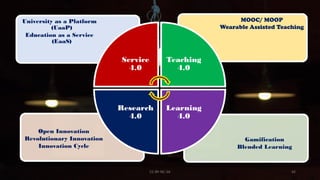
The document discusses augmented reality (AR), highlighting its integration in education and other fields, where it enhances real-world environments with digital information. Various types of AR are described, including marker-based, markerless, location-based, and projection-based AR, each offering unique interactive experiences. AR is presented as a valuable educational tool that boosts student engagement, memory, and collaboration.