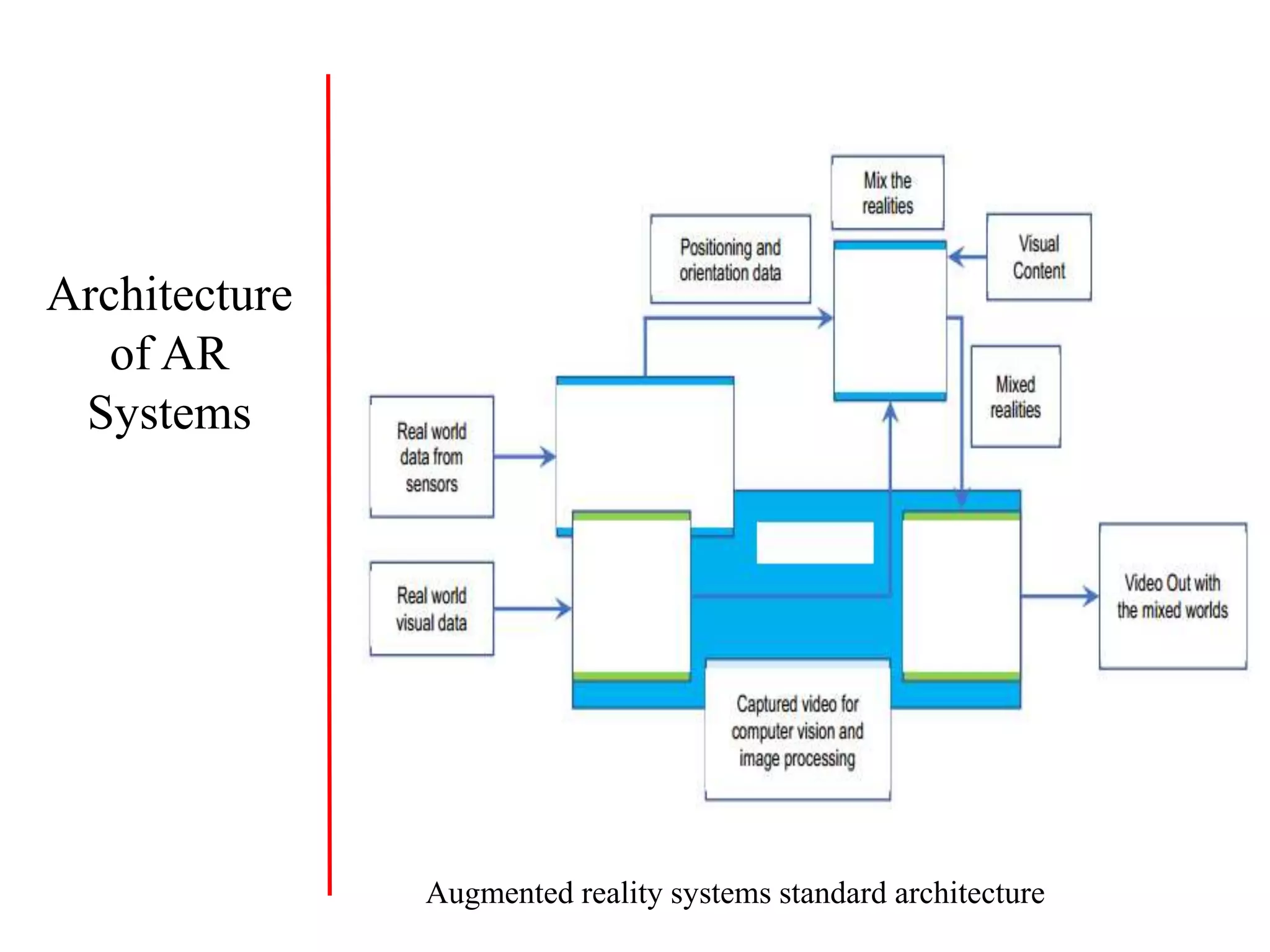
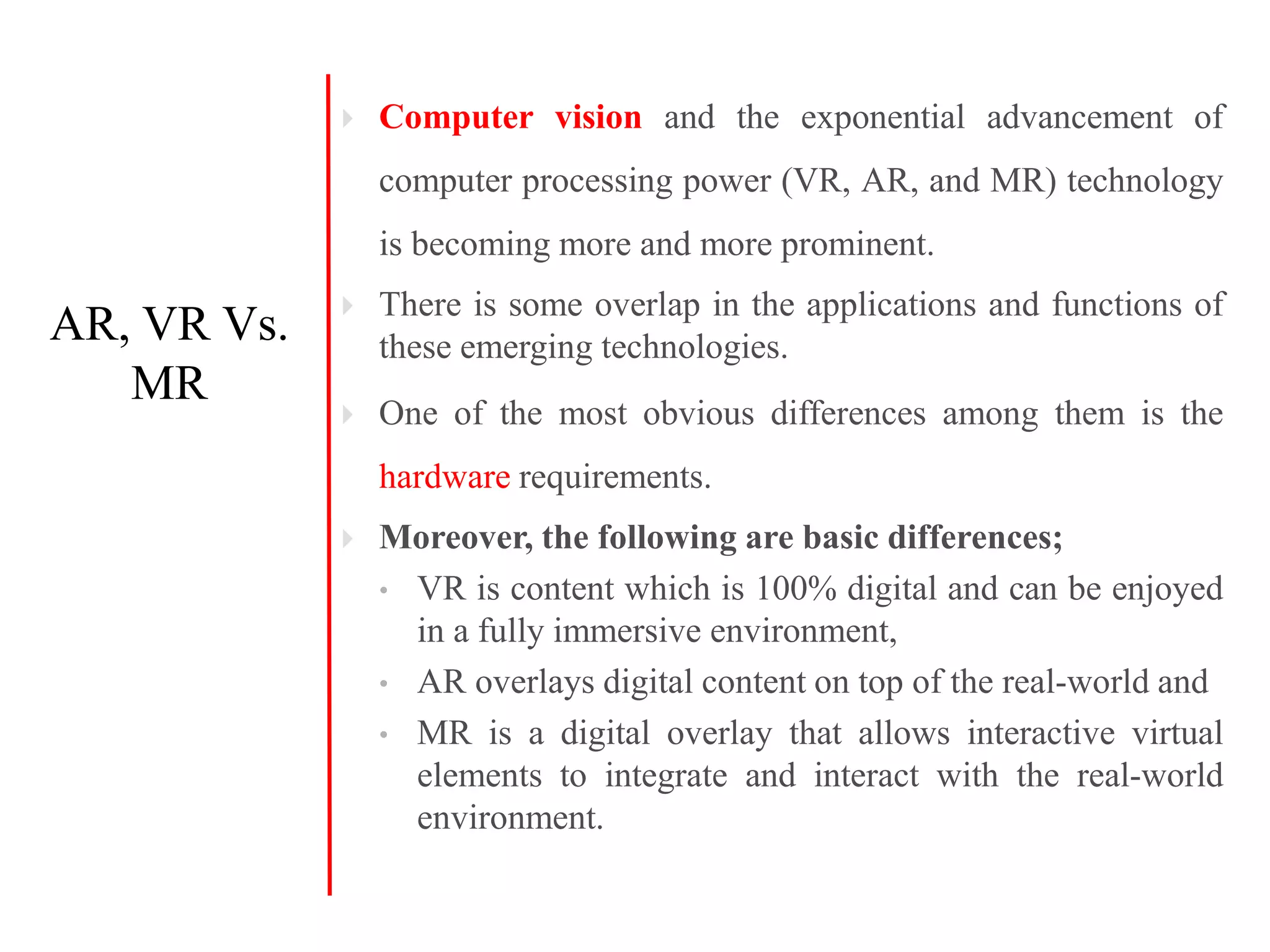
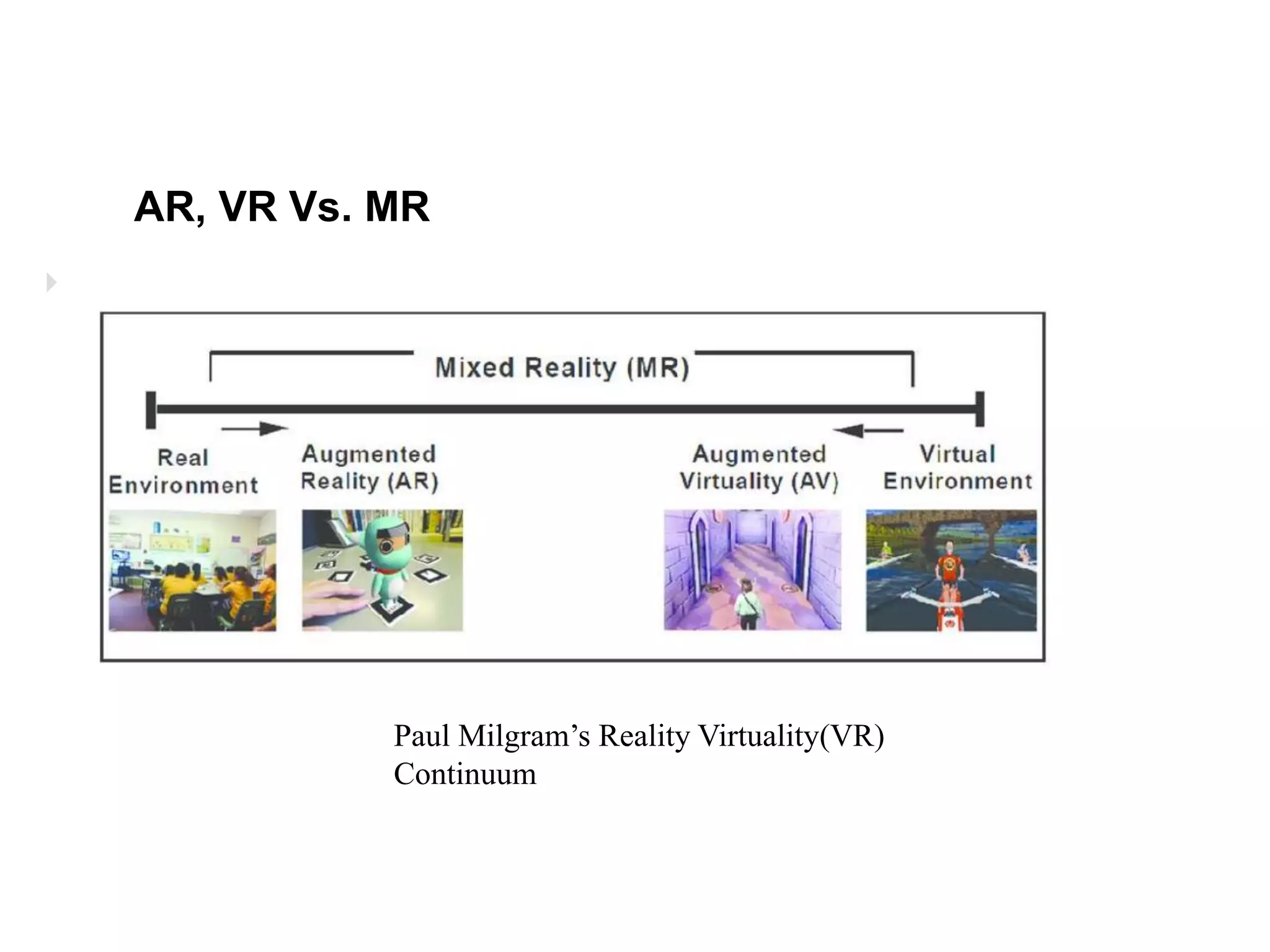
This document discusses augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR). It defines each term and distinguishes the key differences. AR overlays digital content on the real world, VR fully immerses users in virtual environments, and MR merges real and virtual worlds. The document also covers AR architectures, applications in education, medicine, and entertainment, and provides examples of AR, VR, and MR systems and devices.