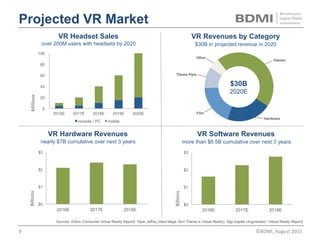
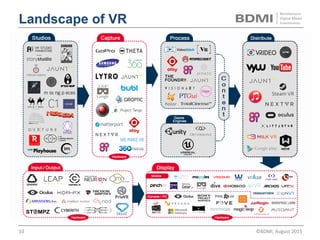
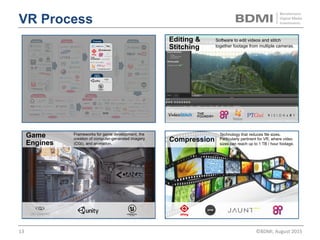
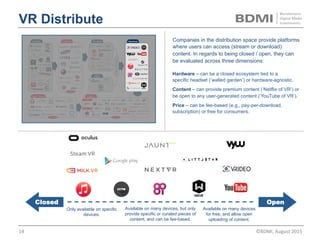
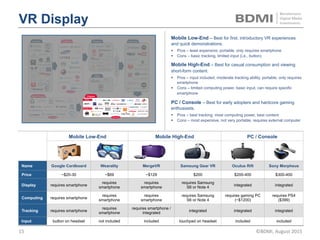
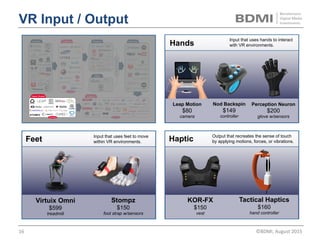
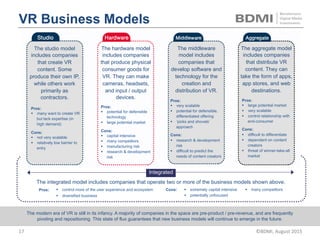
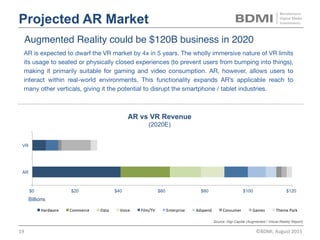
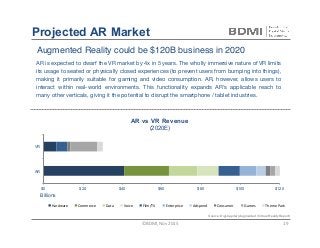
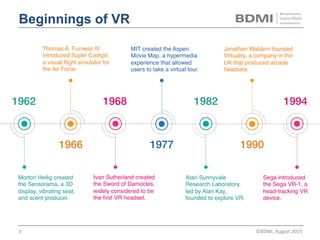
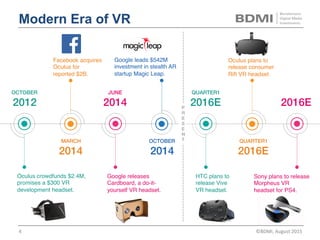
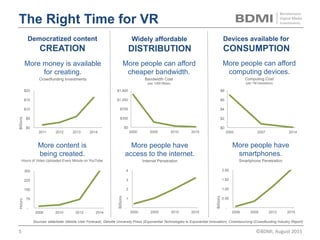
This document provides an overview of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), including their definitions and histories. It discusses how VR began in the 1960s and progressed through early prototypes in the 1970s-1990s. The modern era of VR began around 2011 with efforts by Valve, Oculus, and others. The document outlines the growing VR market potential in areas like gaming, film, education and more. Industry projections show rapid growth in VR users, revenues, and category spending over the next few years. It also maps the current VR landscape including studios, capture methods, engines/tools, distribution platforms, hardware types, input methods, and business models.


![GAMES
ADVERTISING
FILM
“Working on game
development, we always try
to create a new kind of
experience, and having VR
technology is almost unfair.”
Shuhei Yoshia
President of Sony PS Studios
“We’re right on the cusp of a
major upheaval of the
entertainment world once [VR]
technology really kicks in.”
Peter Jackson
Director of Lord of the Rings Trilogy
“[VR] is a percepCon changer
for any adverCser that wants
to associate with a new
fronCer in media.”
Mitch Gelman
VP of Product for Gannet Digital
SOCIAL
“[VR] has the potenCal to
be the most social plaEorm
ever. Immersive, virtual and
augmented reality will be
part of people’s daily lives.”
Mark Zuckerberg
CEO of Facebook
Disruptive Potential of VR
EDUCATION
“[VR] is going to be really
important for educaCon.
Because kids don’t learn best
from reading a book or looking
at a chalk board.”
Palmer Luckey
Creator of the Oculus RiO
MUSIC
“I can only do so many
concerts. So to be able to have
more people experience
them through VR…
that would be epic.”
Miley Cyrus
Singer / Songwriter
©BDMI, Nov 2015 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bdmivrlandscape-151106222430-lva1-app6892/85/The-Emerging-Virtual-Reality-Landscape-a-Primer-7-320.jpg)