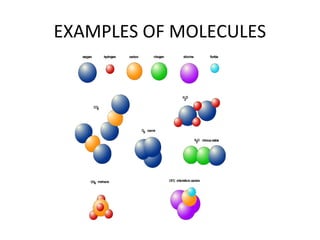
Atoms are the smallest particles that elements are made of and cannot be further broken down while still retaining their chemical properties. Atoms consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons have no charge. Molecules are the smallest particles of an element or compound that can exist and retain the chemical properties of that element or compound. They are made of two or more atoms and their molecular formula gives the composition in terms of the number and type of atoms present.