The document outlines the Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) system and its role in immunity, transplant mechanisms, and rejection types in organ transplants. It details various graft types, the pathogenesis of solid organ rejection, including hyperacute, acute, subacute, and chronic rejections, and discusses the Graft vs Host Disease. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of donor-recipient matching and immunosuppressive therapies to improve graft survival.

![SPECIFIC LEARNING OBJECTIVES
• ROLE OF HLA / MHC IN IMMUNITY
• ROLE OF HLA A,B,D [MHC 1&2] IN IMMUNITY
• TYPES OF TRANSPLANTED GRAFTS
• ALLOGRAFTS
• TYPES OF TRANSPLANT REJECTIONS
• PATHOGENESIS OF SOLID ORGAN REJECTION
• TYPES OF SOLID ORGAN REJECTION
• GRAFT VS HOST DISEASE
• TYPES OF GVHD
• MCQs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-3-320.jpg)

![MHC MOLECULES
(Gene Products)
HLA A & B [MHC 1]
• Expressed on all nucleated cells and platelets on the surface
of the cell,
• It is a glycoprotein & antigenic.
•T8 lymphocytes recognize & interact with it to
become activated & cause cytolysis
• They are involved in graft rejection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-5-320.jpg)
![MHC MOLECULES
(Gene Products)
HLA D [MHC II]
• Expressed on all APC’s, i.e., Langerhans cells, macrophages,
dendritic cells & B lymphocytes on cell surface
• It is a glycoprotein & antigenic
•T4 lymphocytes interact with it and are activated
immunologically
• It is primarily responsible for graft vs host disease](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-6-320.jpg)
![TYPES OF GRAFTS [TRANSPLANTS]
• AUTOGRAFT ( autogenic ) – graft from self eg, skin grafting
• ISOGRAFT ( syngraft ) – graft from identical twin
• ALLOGRAFT ( homograft ) - graft from genetically unrelated
member of same species
• XENOGRAFT( heterograft ) – graft from different species](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-7-320.jpg)

![REJECTION OF TRANSPLANT [SOLID ORGAN]
PATHOGENESIS
• PRESENCE OF PREFORMED ANTI DONOR ANTIBODIES
• RECOGNITION OF FOREIGN MHC MOLECULES ON GRAFT BY
HOST IMMUNE SYSTEM
DIRECT RECOGNITION via DONOR MHC
INDIRECT RECOGNITION VIA HOST APC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-10-320.jpg)

![REJECTION OF SOLID ORGAN TRANSPLANT
DIRECT RECOGNITION via DONOR MHC
DIRECT RECOGNITION OF FOREIGN MHC MOLECULES ON
GRAFT BY HOST IMMUNE SYSTEM
DIRECT RECOGNITION – via donor MHC 1 on all nucleated
donor cells
MHC I (HLA-A,B) on donor cells is
• Recognized directly by CD8+TL of host,
• Which are then activated to form cytotoxic T lymphocytes
[CTL],
• Causing apoptosis of donor cells](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-12-320.jpg)

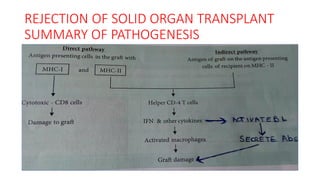
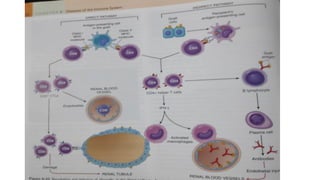
![REJECTION OF SOLID ORGAN TRANSPLANT
ROLE OF CD 8+ T LYMPHOCYTES
CD8+TL ARE IMMUNOLOGICALLY ACTIVATED TO TRANSFORM
INTO CYTOTOXIC T LYMPHOCYTES, WHICH RESULT IN:
• Apoptosis / necrosis of donor parenchymal cells
• Apoptosis / necrosis vascular endothelium [donor tissue],
leading to
• Thrombosis & ischemia
• All above factors contribute to necrosis of graft i.e., rejection
of graft](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-17-320.jpg)
![REJECTION OF SOLID ORGAN TRANSPLANT
ROLE OF CD 4+ T LYMPHOCYTES
CD4+TL ARE IMMUNOLOGICALLY ACTIVATED AND
TRANSFORM INTO VARIOUS SUBSETS LIKE Th 1 & Th 17
Activated Th1 &17 subsets leads to type 4 [delayed type of]
hypersensitivity reaction, as well as activation of B
lymphocytes to produce antibodies
• DTH & PROLONGED DTH lead to inflammation & granuloma
formation
• ANTIBODIES formed against donor vascular endothelium are
most important and lead to type 2&3 hypersensitivity
reactions, which activate complement – inflammation -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-18-320.jpg)
![TYPES OF SOLID ORGAN [KIDNEY] REJECTION
• HYPERACUTE
• ACUTE
• SUBACUTE
• CHRONIC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-19-320.jpg)

![ACUTE REJECTION
OCCURS WITHIN DAYS DUE TO CELLULAR & HUMORAL
REACTIONS
CELLULAR RECATIONS
CD8+TL & CD4+TL ( DTH ) reaction, leading to
• Endothelitis of glomerular & peritubular capillaries,
• Infiltration by lymphocytes,
• Edema & hemorrhage,
• Necrosis of tubular cells, causing acute renal failure [ARF]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-21-320.jpg)


![CHRONIC REJECTION
Appears much later, after many months & years
• It is due to cytokines, which cause
• Proliferation of vascular intimal smooth muscles & increased
extracellular matrix
• Narrowing of lumen of BV – decreased blood flow & slow
ischemia, resulting in
• Atrophy & fibrosis of glomeruli, tubules & interstium, leading
to chronic renal failure[CRF]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-25-320.jpg)

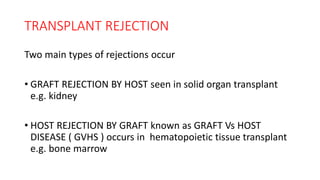
![GRAFT Vs HOST DISEASE
• IMMUNOCOMPETENT DONOR T LYMPHOCYTES [CD 4&8]
PERCEIVE RECIPIENT (HOST) Ags AS FORGIEN & REACT
• HOST IS IMMUNOCOMPROMISED, NO HOST REACTION TO
DONOR CELLS
[before hematopoietic transplant , host is immune depleted]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa9-200812104627/85/TRANSPLANT-REJECTION-TYPES-MECHANISM-27-320.jpg)