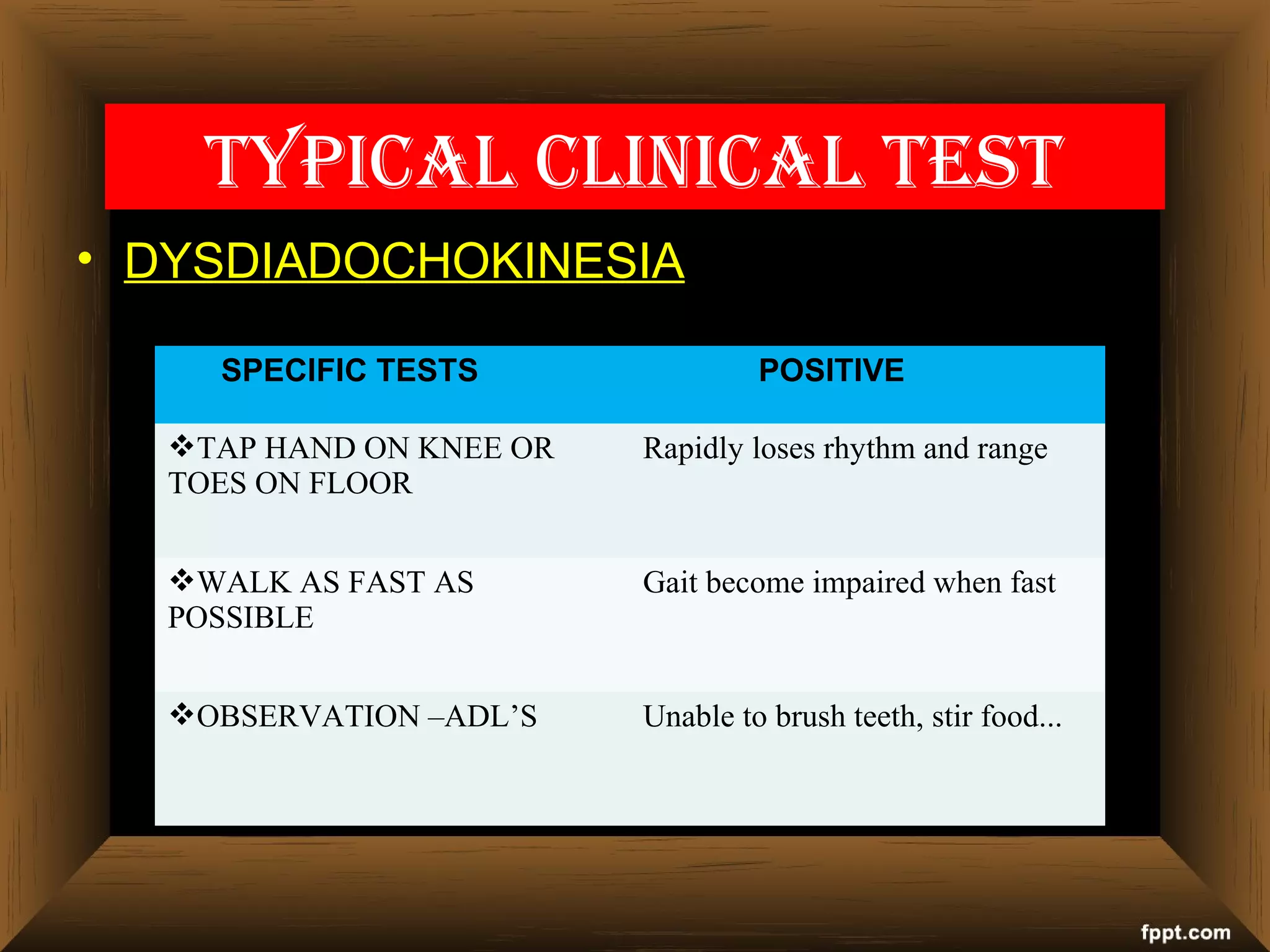
This document provides information on diagnostic investigations and assessments for cerebellar ataxia. It lists various tests that can be done as part of the diagnostic workup including blood tests, imaging studies, genetic testing, and neurological exams. Specific tests are described to evaluate factors like balance, coordination, gait, dysmetria, and oculomotor performance that may be impaired with cerebellar ataxia. A thorough patient history and neurological exam incorporating several assessment scales are important for evaluating ataxia.