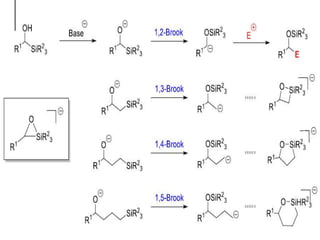
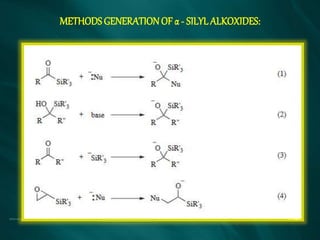
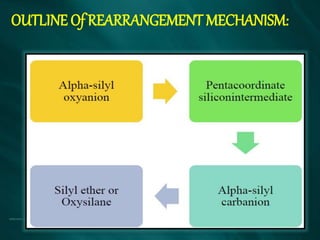
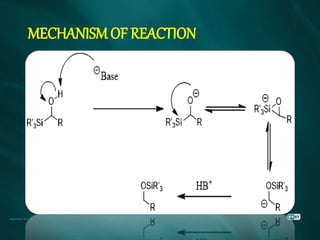
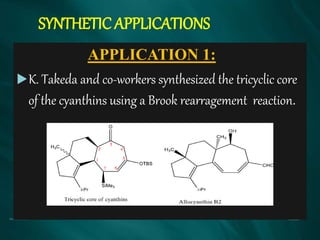
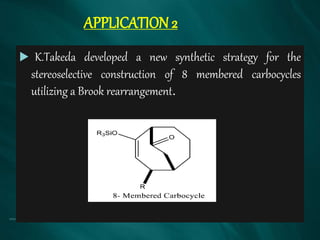
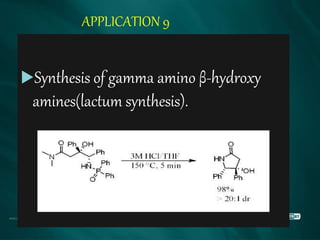
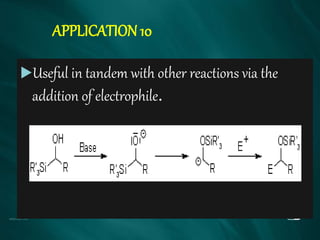
The document summarizes the Brook rearrangement reaction. It was discovered in 1957 by Adrian Brook and involves the migration of a silyl group from carbon to oxygen under basic conditions. The mechanism proceeds through the formation of a pentavalent silicon intermediate. The rearrangement has various applications in synthesis, such as constructing 8-membered rings and chiral silyl ethers. It has been used to synthesize compounds like gamma-amino-beta-hydroxy amides and alpha-hydroxy acid derivatives.