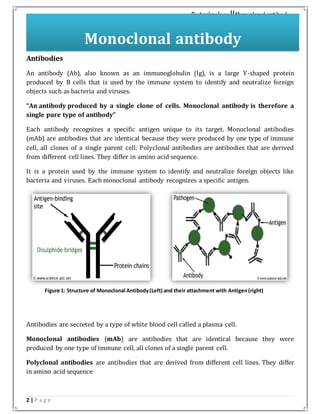
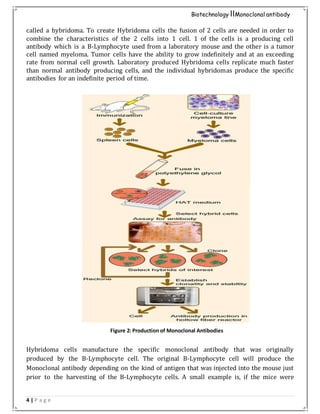
Monoclonal antibodies are identical antibodies produced by a single clone of cells that recognize a specific antigen. They are produced through the fusion of antibody-producing B cells with myeloma cells to form a hybridoma that can produce the antibody indefinitely. Monoclonal antibodies have advantages like homogeneity and specificity since each recognizes the same epitope. They have various applications like cancer treatment and treating rheumatoid arthritis. Some common monoclonal antibodies are Bevacizumab, Rituximab, Abciximab, and Palivizumab which are used to treat conditions like cancer, arthritis, and respiratory infections.




![7 | P a g e
Biotechnology IIMonoclonal antibody
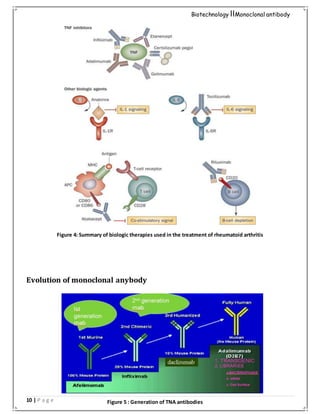
Autoimmune diseases
Monoclonal antibodies used for autoimmune diseases include infliximab and adalimumab,
which are effective in rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease and ulcerative Colitis by their
ability to bind to and inhibit TNF-α.[31] Basiliximab and daclizumab inhibit IL-2 on
activated T cells and thereby help prevent acute rejection of kidney
transplants. Omalizumab inhibits human immunoglobulin E (IgE) and is useful in moderate-
to-severe allergic asthma.
Monoclonal antibodies for cancer treatment
Three mechanisms that could be responsible for the cancer treatment.
A. mAbs act directly when binding to a cancer specific antigen and induce
immunological response to cancer cells. Such as inducing cancer cell apoptosis,
inhibiting growth, or interfering with a key function.
B. mAbs was modified for delivery of a toxin, radioisotope, cytokine or other active
conjugates.
C. it is also possible to design bispecific antibodies that can bind with their Fab regions
both to target antigen and to a conjugate or effector cell
Figure 3 : action of Monoclonal antibodies for cancer treatment
ADEPT- antibody directed
enzyme prodrug therapy;
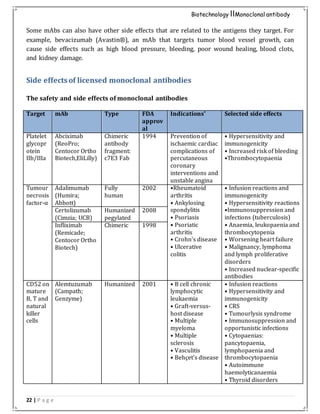
ADCC- antibody
dependentcell-mediated
cytotoxicity;
CDC- complement
dependentcytotoxicity;
MAb- monoclonal
antibody;
ScFv- single-chainFv
fragment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment-180711085055/85/Assignment-7-320.jpg)


![11 | P a g e
Biotechnology IIMonoclonal antibody
Chimeric mAbs: chimers combine the human constant regions with the intact rodent
variable regions. Affinity and specificity unchanged. Also cause human antichimeric
antibody response (30% murine resource)
Humanized mAbs: contained only the CDRs of the rodent variable region grafted
onto human variable region framework
Recombinant monoclonal antibodies: Recombinant antibody engineering involves
the use of viruses or yeast to create antibodies, rather than mice. Phage display
library: construction of VH and VL gene libraries and expression of them on a
filamentous bacteriophage. The phage expressing an antigen-bonding domain specific
for a particular antigen to screen the mAbs
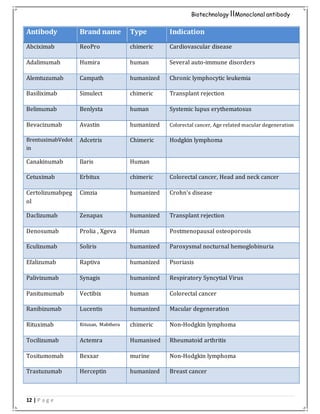
List of FDA’s Approved Monoclonal antibody
The first approved mAbs was OKT-3 [1986], which is a murine IgGa2 protein to deplete T
cells in patients with acute rejection of renal allotransplant.
Until Feb 24, 2013, 312 mAbs were approved by FDA, which were applied in the treatment
of organ transplant, Cancer, Asthma, Hematopoietic malignancies and psoriasis.
Figure 6 : FDA’s Approved Monoclonal antibody](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment-180711085055/85/Assignment-11-320.jpg)







![20 | P a g e
Biotechnology IIMonoclonal antibody
Abciximab
Brand Name :ReoPro
Abciximab is a type of "blood thinner" used to prevent blood clots during certain
procedures used to open up the blood vessels in the heart (e.g., balloon angioplasty,
coronary stent placement, percutaneous coronary intervention-PCI). It is usually used with
heparin and aspirin.Abciximab works by preventing platelets in the blood from sticking to
each other. When platelets stick to each other, they may form blood clots that may cause a
heart attack or cause the opened blood vessel in the heart to close back up.
Indications for use
Abciximab is indicated for use in individuals undergoing percutaneous coronary
intervention (angioplasty with or without stent placement). The use of abciximab in this
setting is associated with a decreased incidence of ischemic complications due to the
procedure and a decreased need for repeated coronary artery revascularization in the first
month following the procedure.[4] Research also shows that this drug can be of use for
patients with diabetes and chronic renal insufficiency. It is not the appropriate drug of
choice if a patient is scheduled for an emergency surgery (i.e., heart surgery) because
bleeding time may take about 12 hours to normalize.
Pharmacokinetics
Abciximab has a plasma half-life of about ten minutes, with a second phase half-life of about
30 minutes. However, its effects on platelet function can be seen for up to 48 hours after the
infusion has been terminated, and low levels of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor blockade are
present for up to 15 days after the infusion is terminated. Abciximab does not require renal
dose adjustment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment-180711085055/85/Assignment-20-320.jpg)