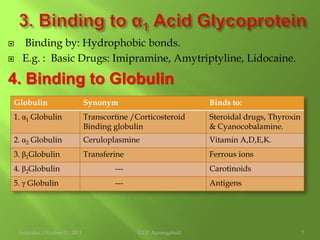
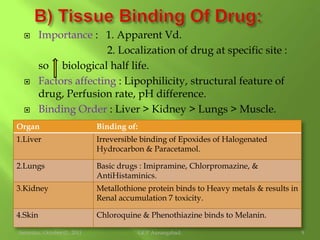
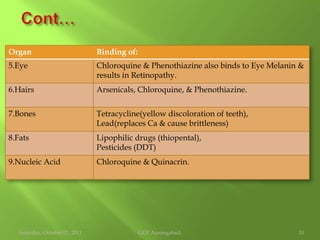
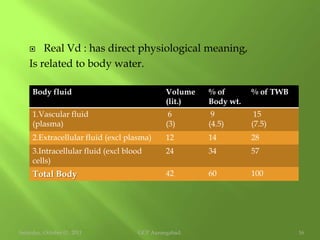
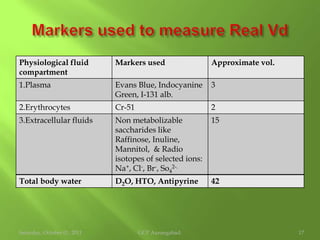
This document discusses protein binding of drugs in the body. It explains that bound drugs are pharmacologically inert and that various bonds like hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic bonds, and ionic bonds are responsible for binding. It then discusses in detail binding to blood components like plasma proteins (albumin, alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, lipoproteins, globulins), blood cells, and various tissues. Finally, it covers factors that affect protein binding like drug properties, protein/tissue characteristics, drug interactions, and patient factors. It also defines volume of distribution and distinguishes between apparent and real volume of distribution.