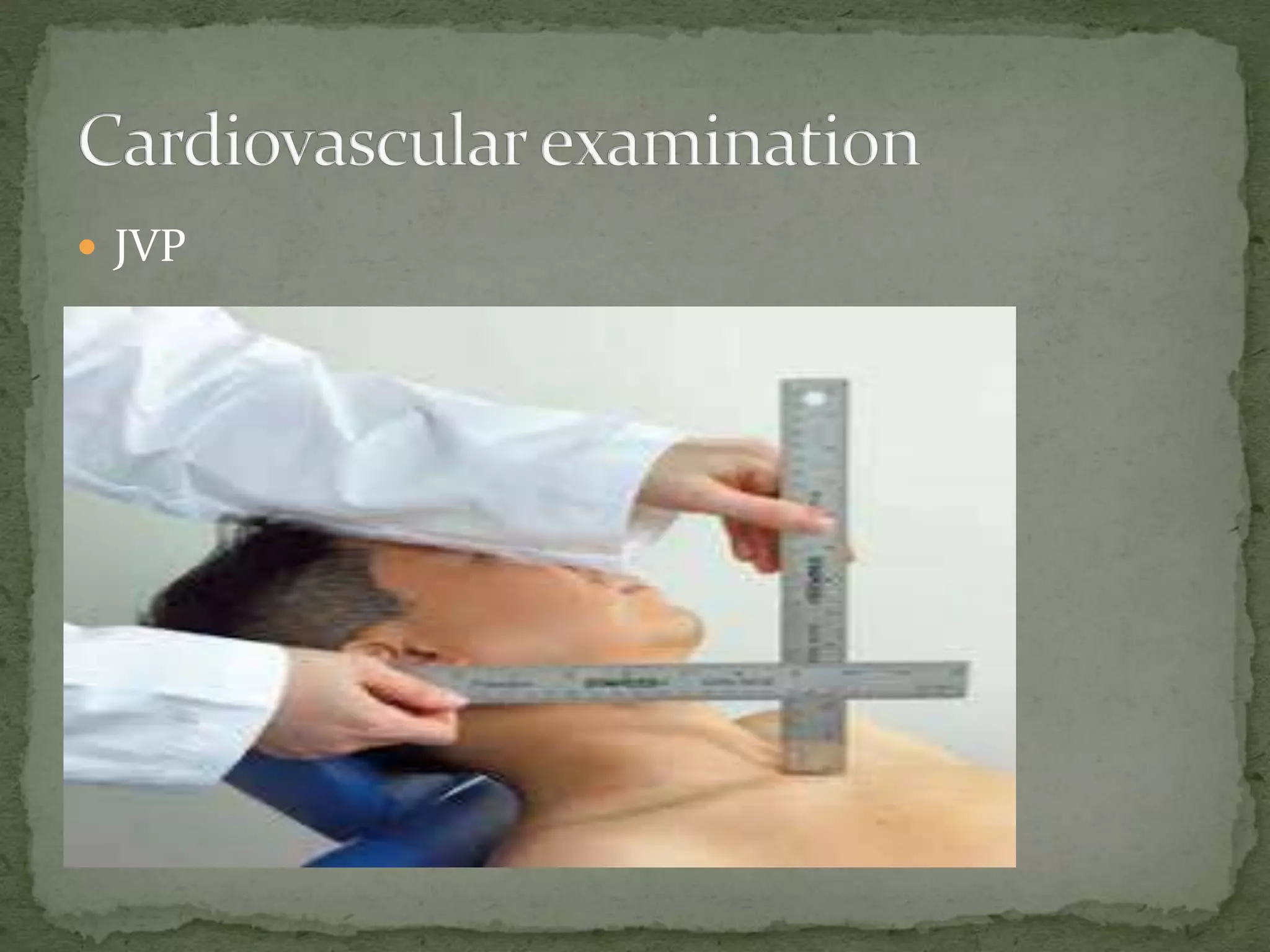
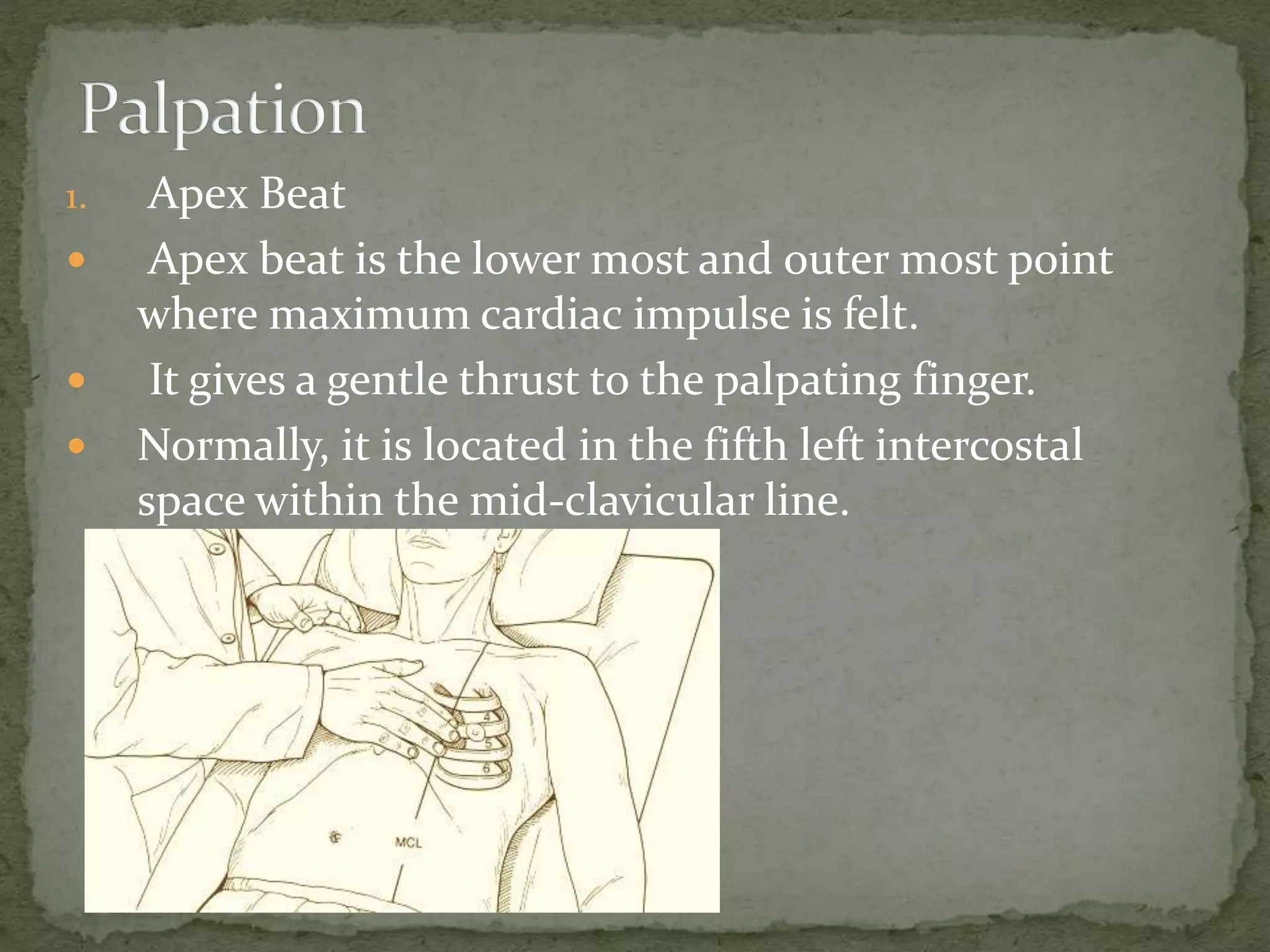
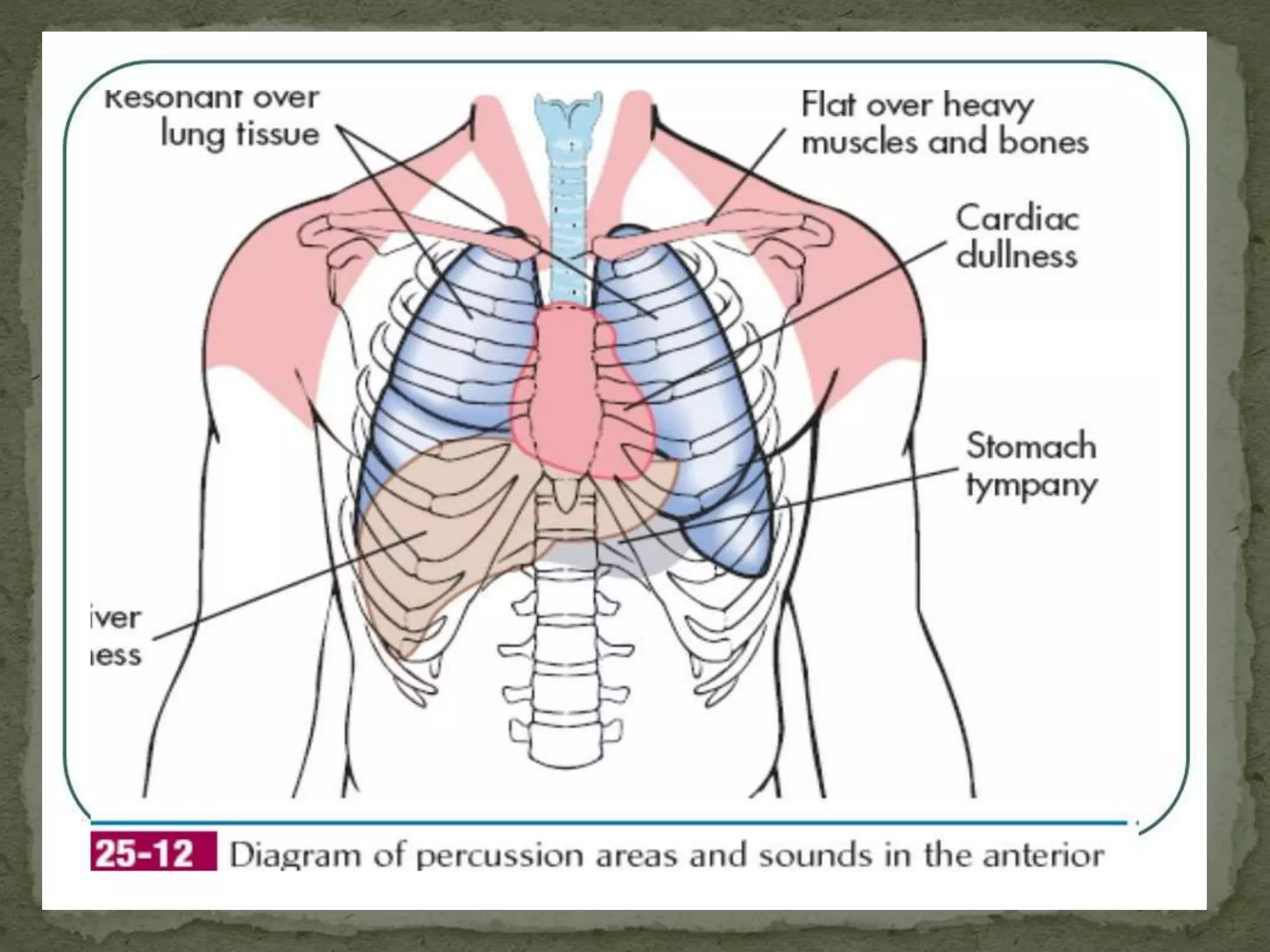
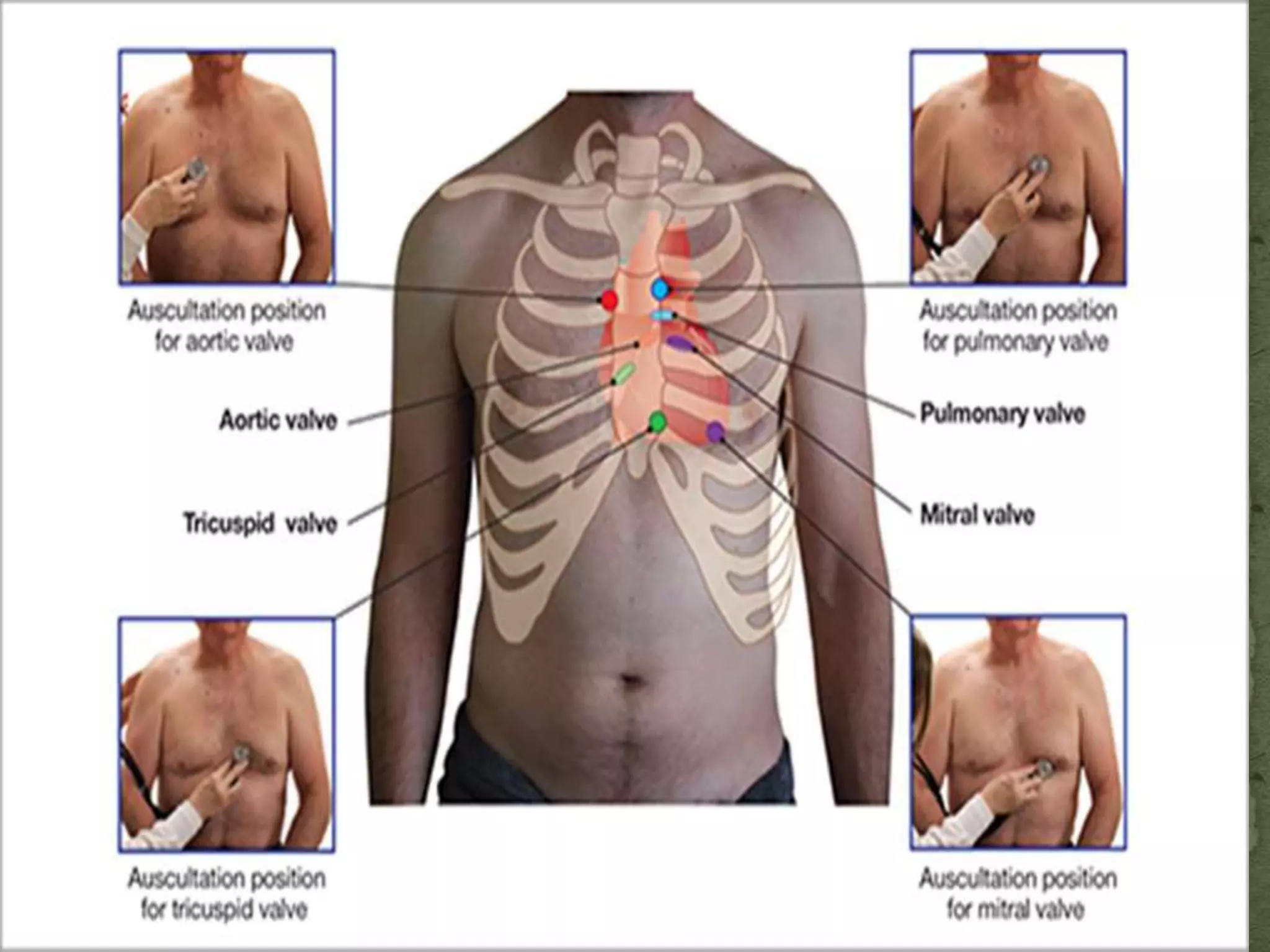
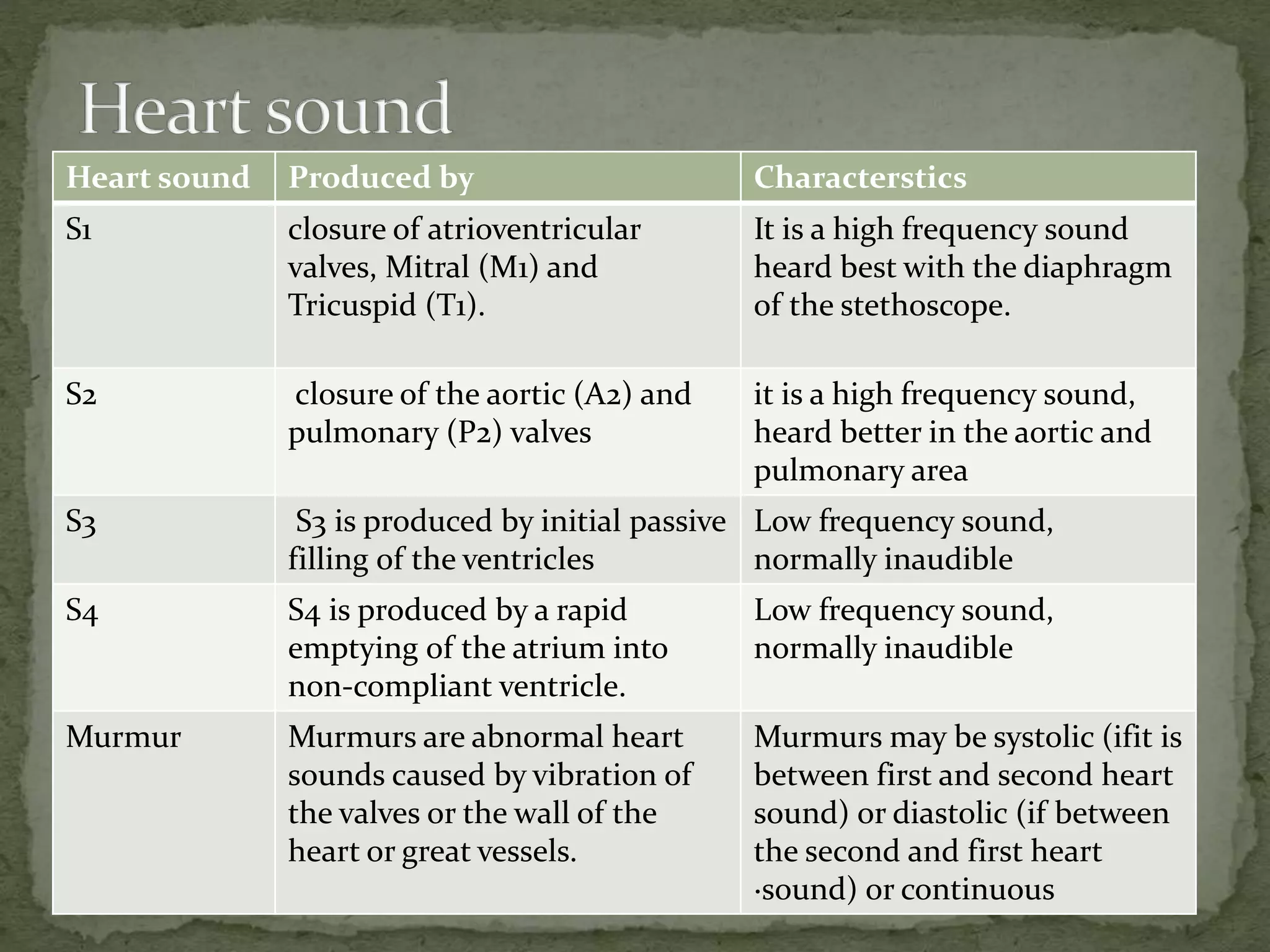
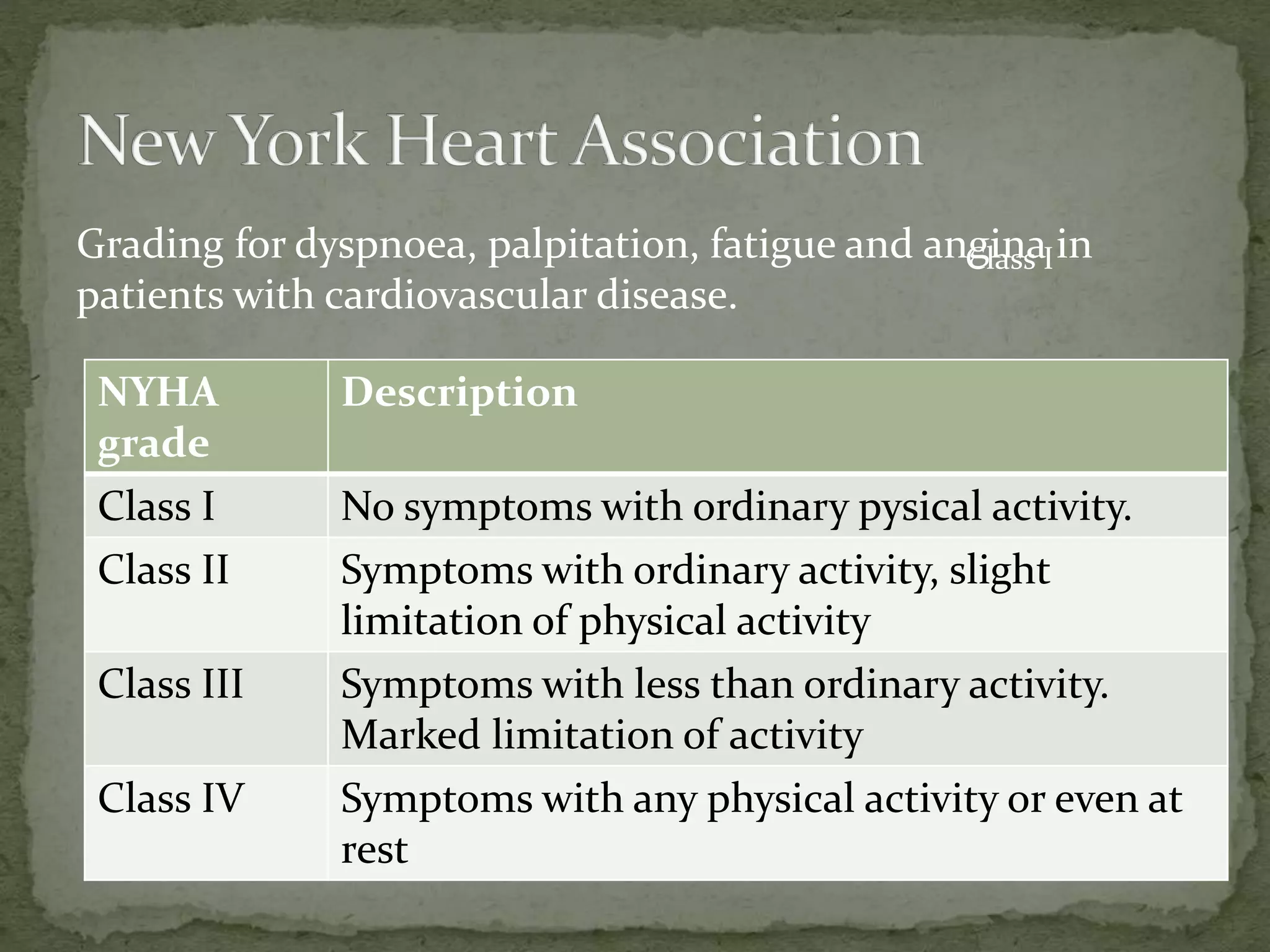
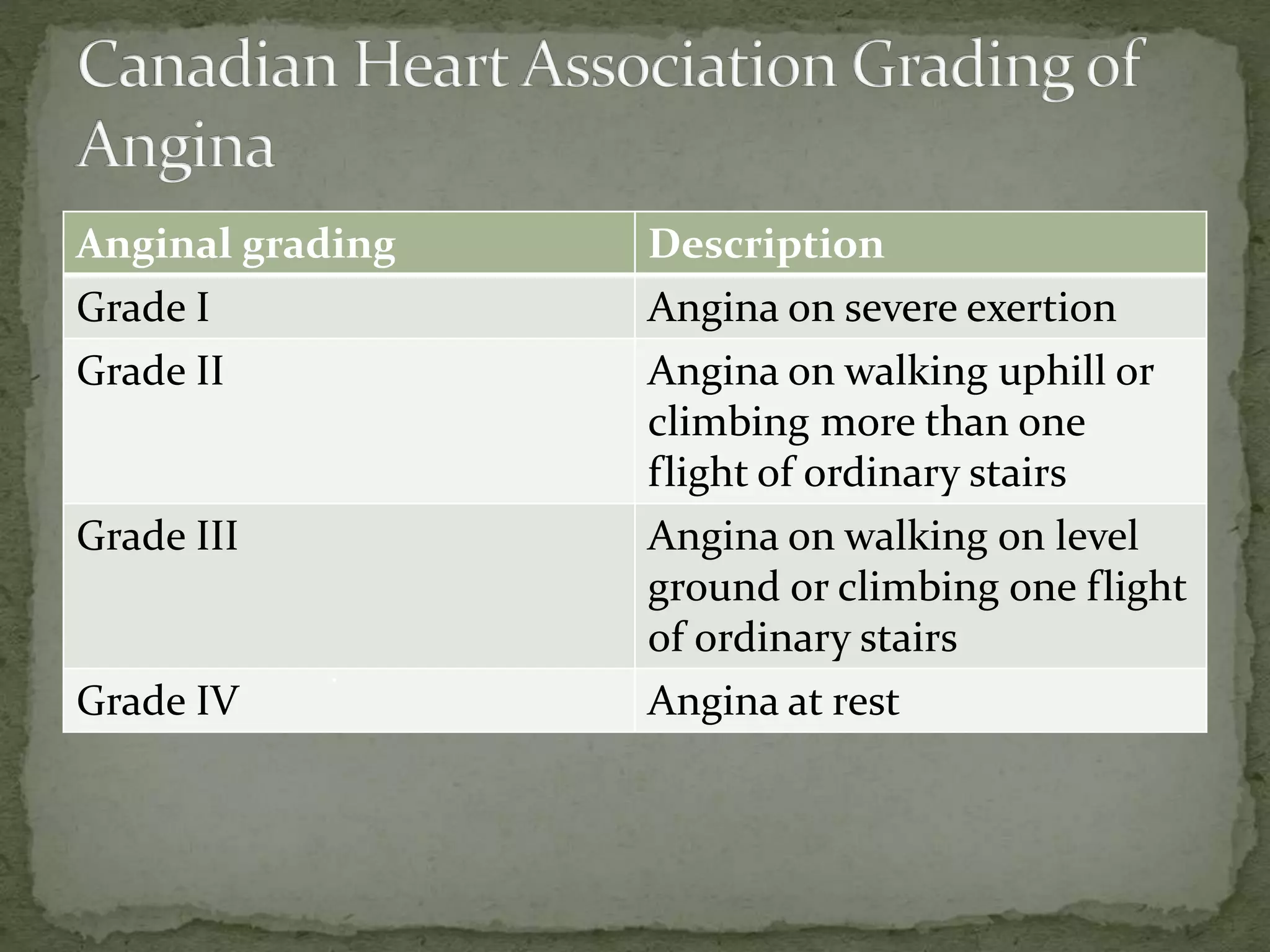
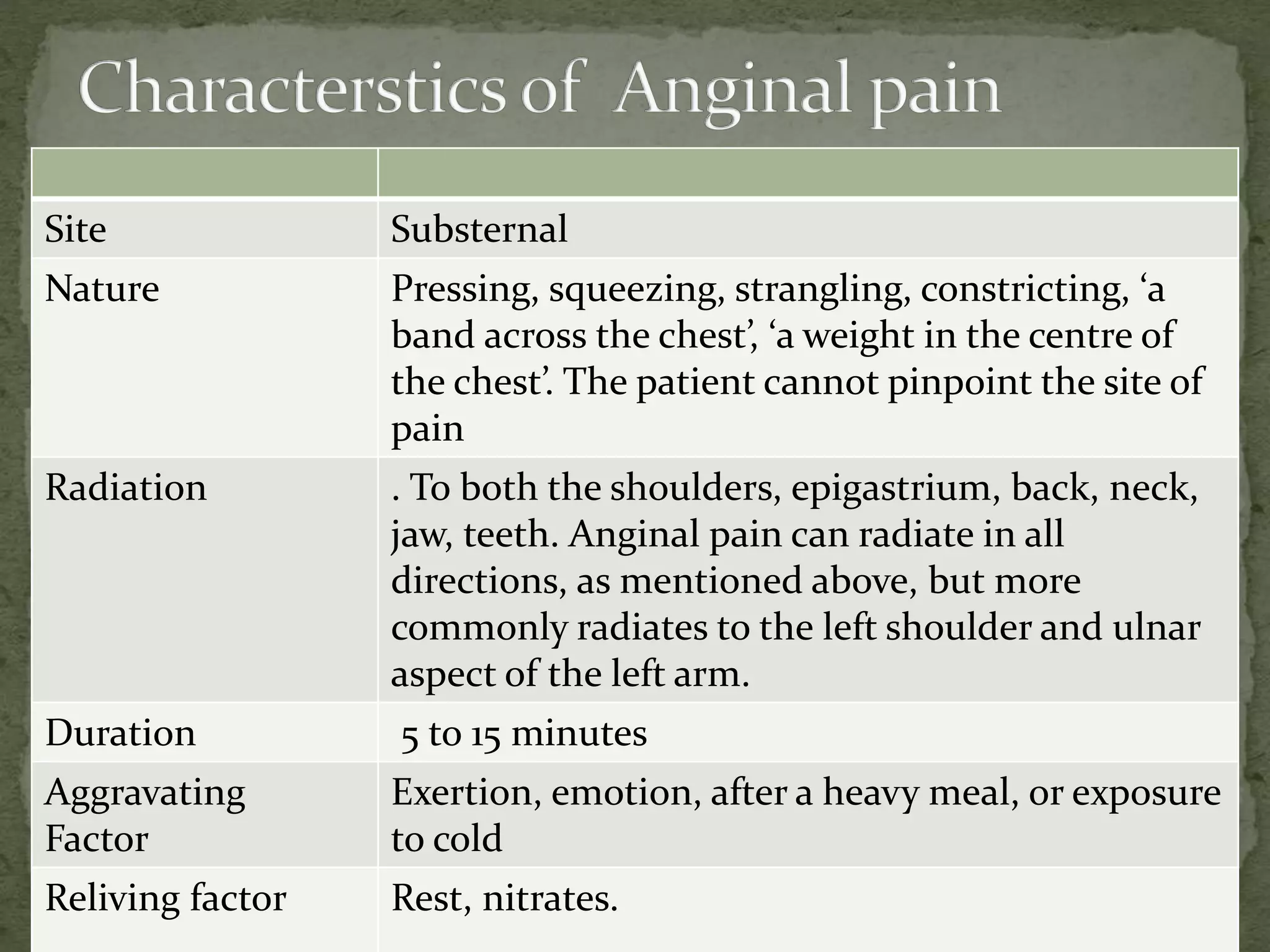
This document provides information on the history, physical examination, investigations, signs and symptoms, grading scales, and causes of various cardiorespiratory conditions. The physical examination section describes examination of the precordium, heart sounds, murmurs, jugular venous pressure, and cardiac borders determined by percussion and auscultation. Common symptoms discussed include dyspnea, chest pain, cough, hemoptysis, palpitations, and syncope. Investigations mentioned are chest X-ray, ECG, echocardiogram, angiography and biomarkers. References cited are practical cardiology textbooks.

![ History [ sign and symptoms]
Physical Examination
1. General examination
2. Examination [ inspection, palpation, percussion and
auscultation]
Investigations for confirmatory diagnosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assessmentofcardiovascularsystem-210407104818/75/Assessment-of-cardiovascular-system-2-2048.jpg)















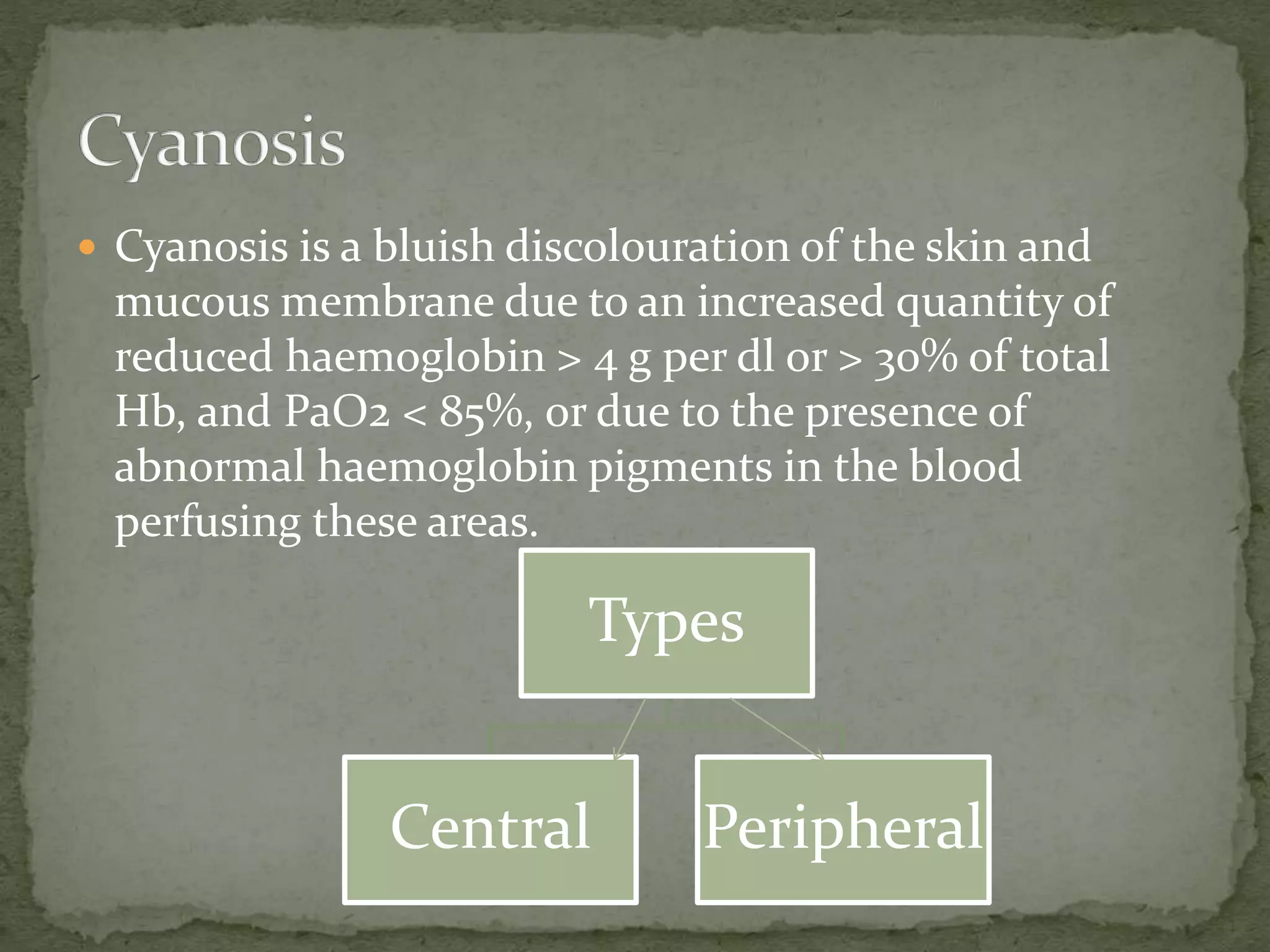
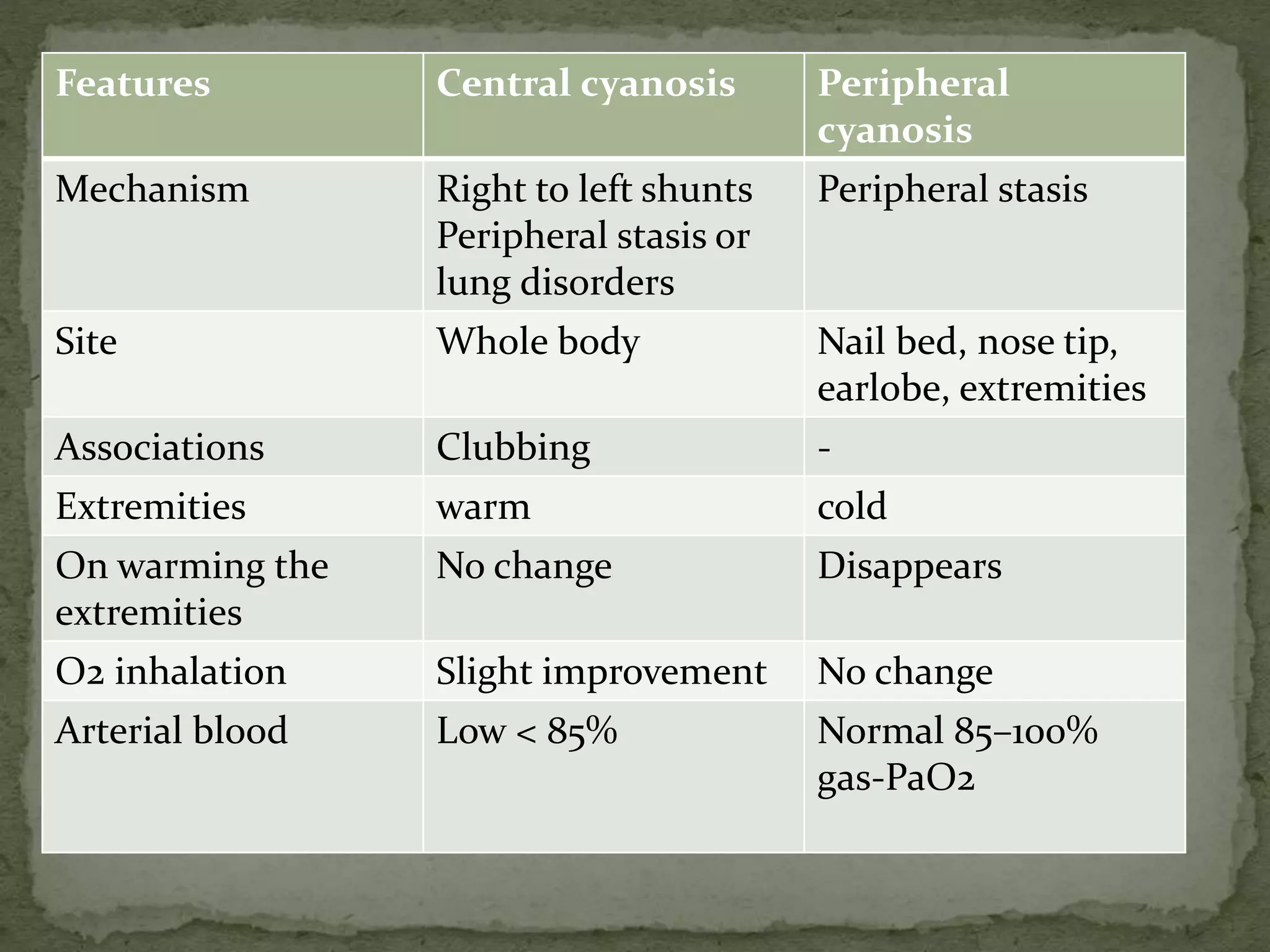

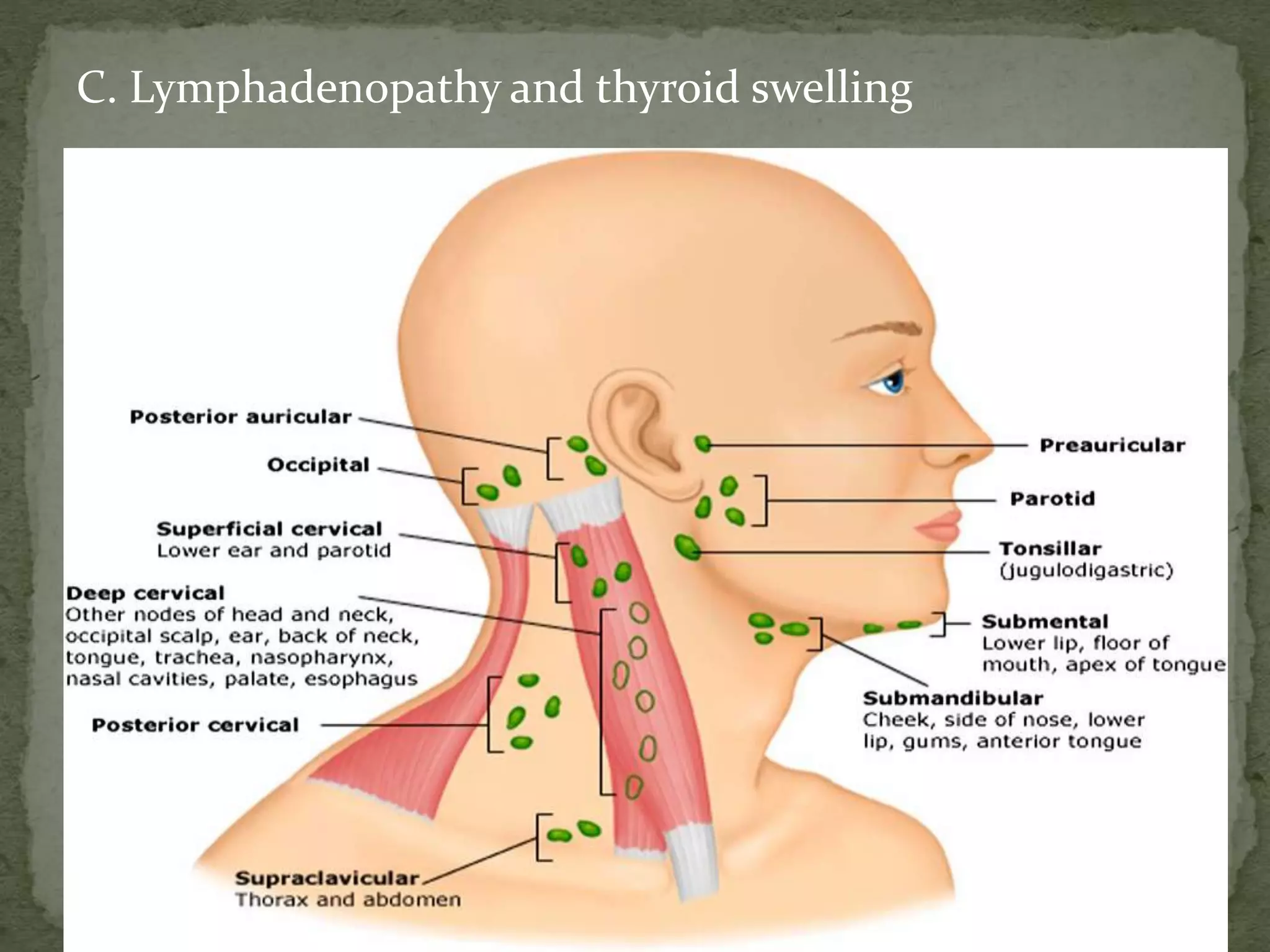
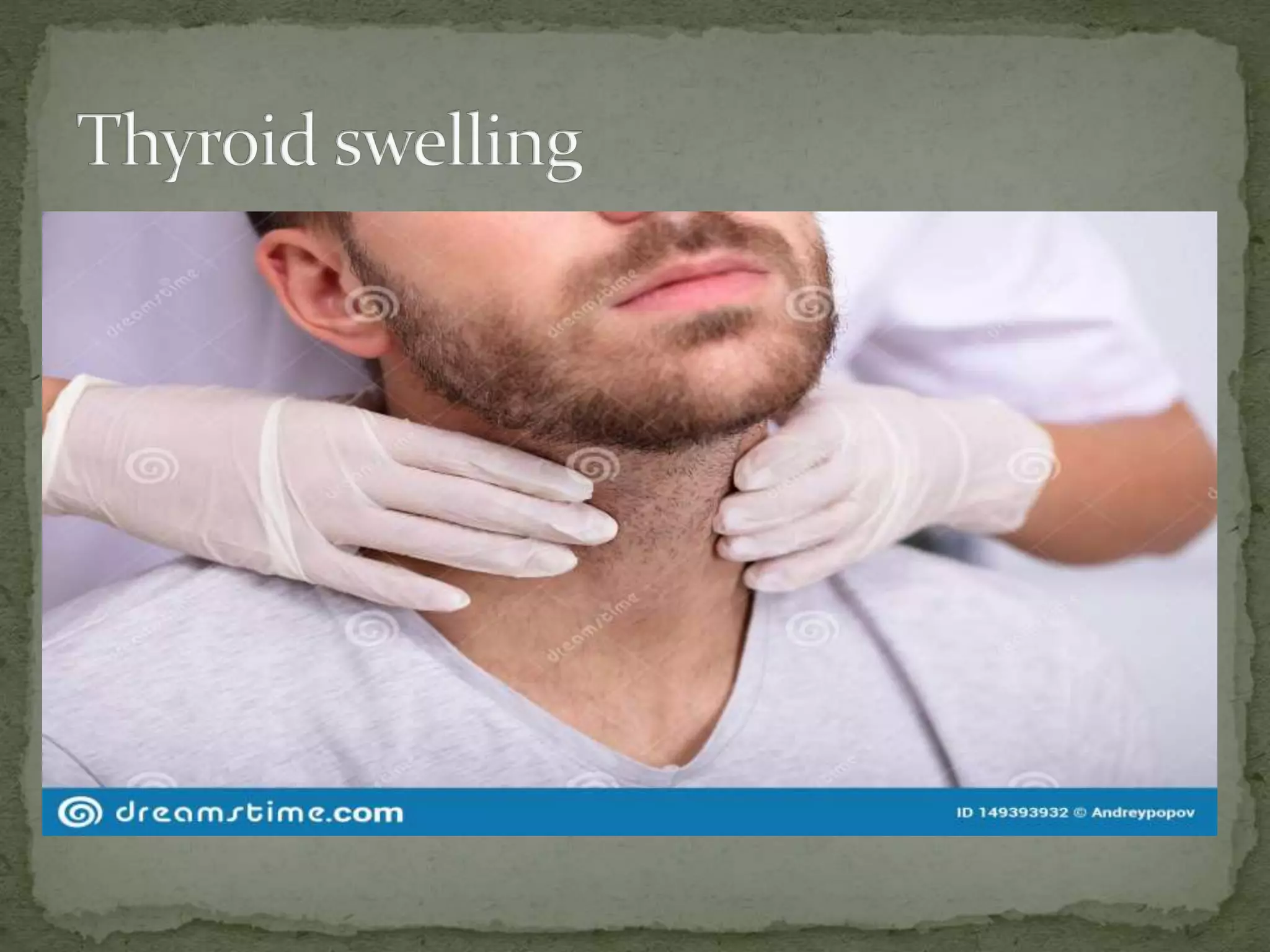
![B. Nails and conjunctiva for pallor [mucus membrane of
lower eye lid],
icterus, clubbing, cyanosis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assessmentofcardiovascularsystem-210407104818/75/Assessment-of-cardiovascular-system-28-2048.jpg)
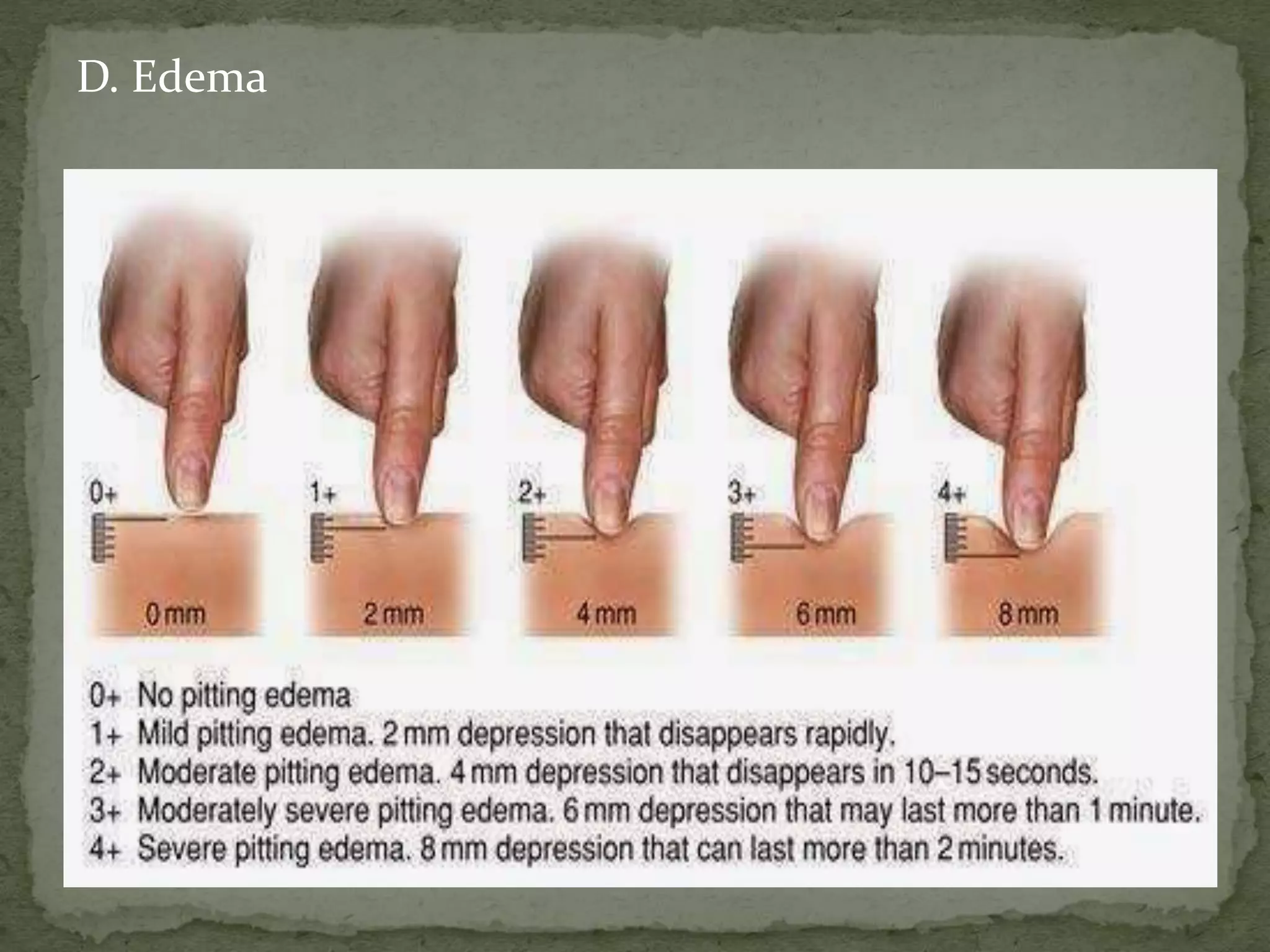
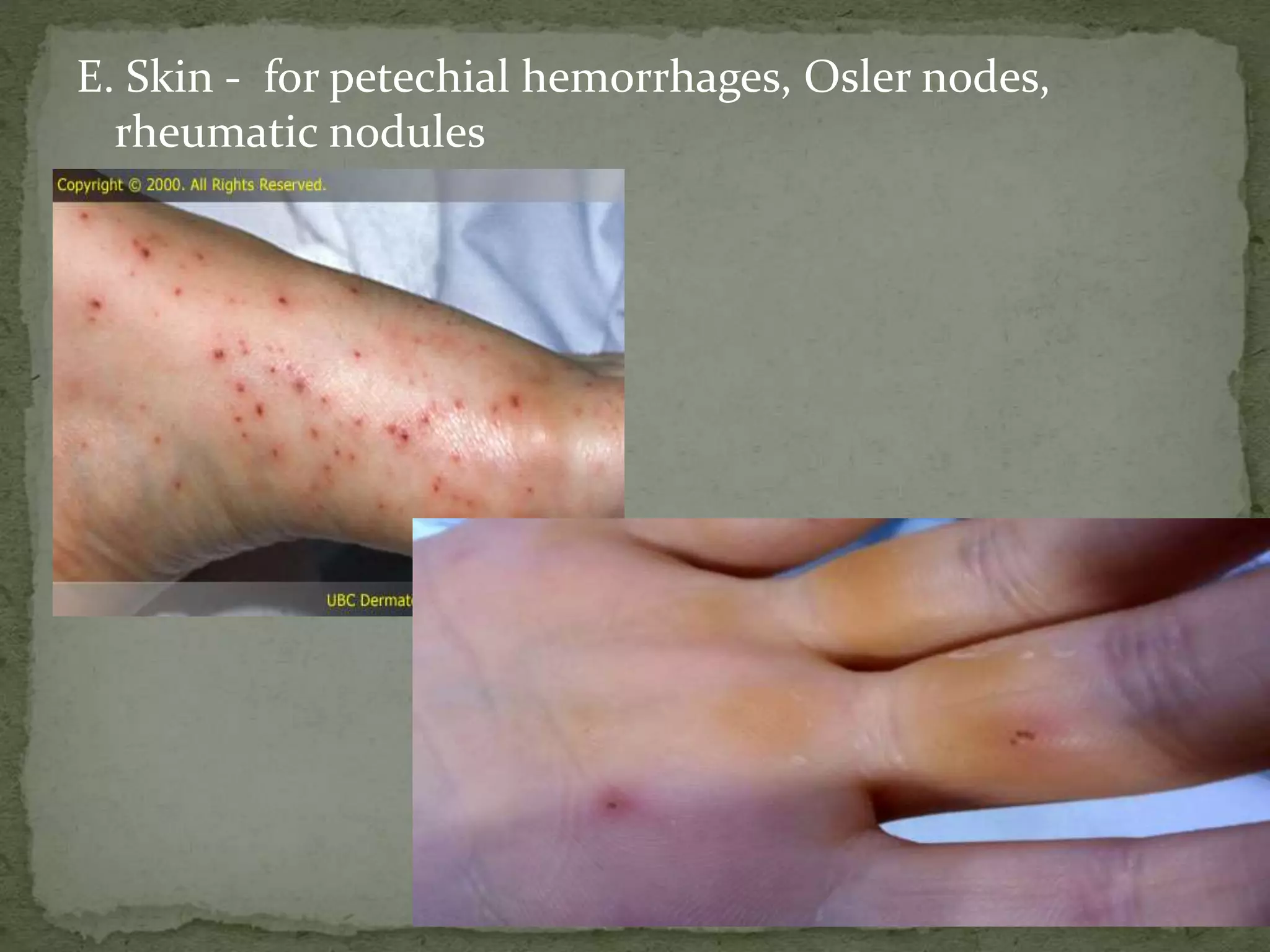
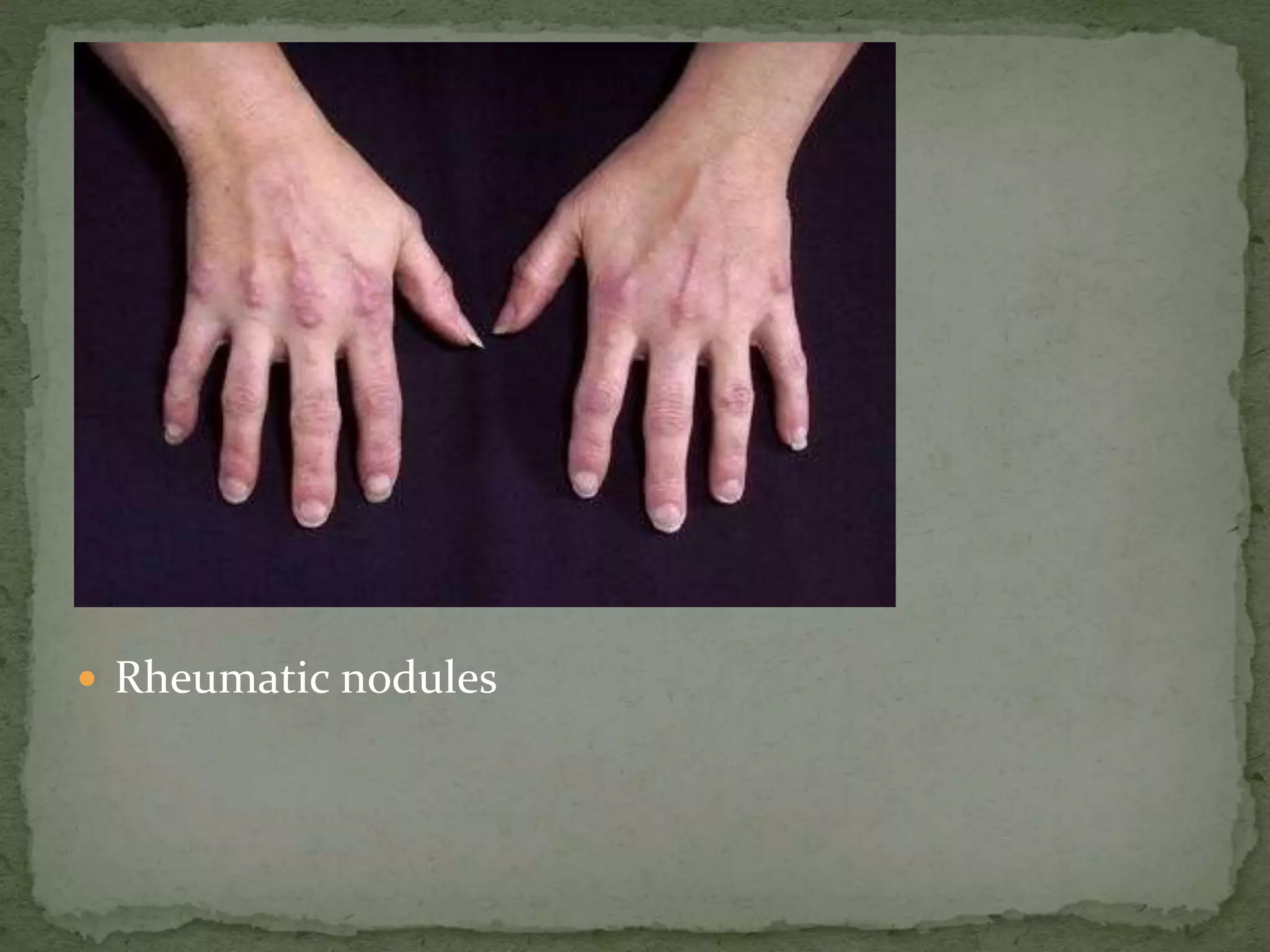
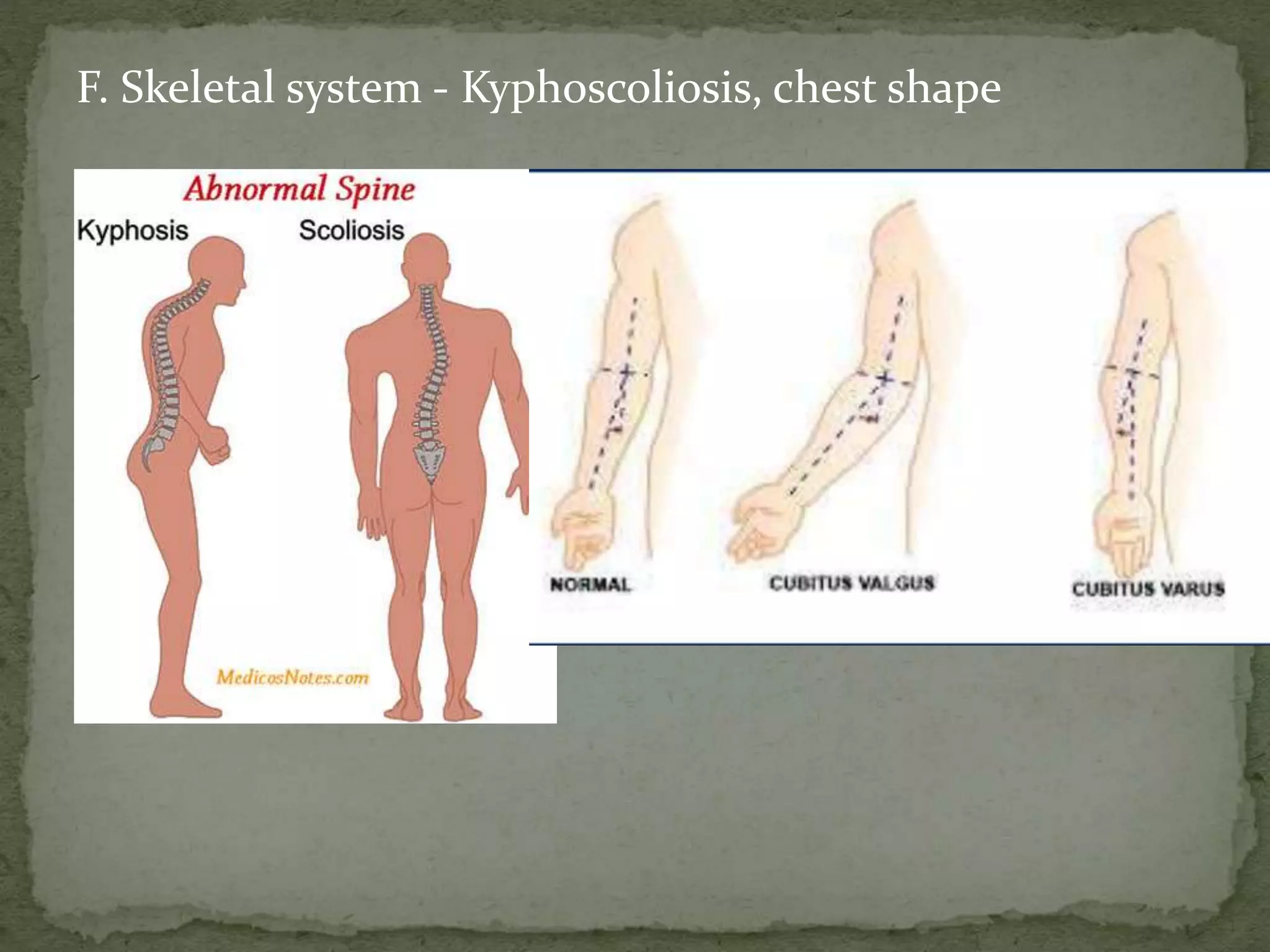
![ G. TPR, BP
T- temperature [36.5-37.5 degree Celsius or 97.7 – 99.5
degree frenite]
P- pulse
R- respiratory Rate
BP- Blood Pressure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assessmentofcardiovascularsystem-210407104818/75/Assessment-of-cardiovascular-system-35-2048.jpg)