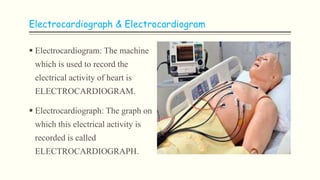
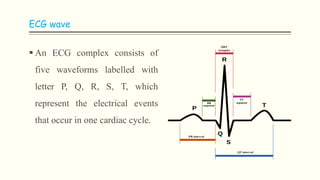
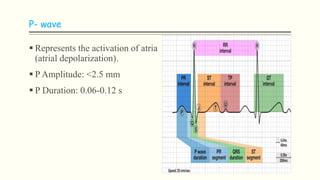
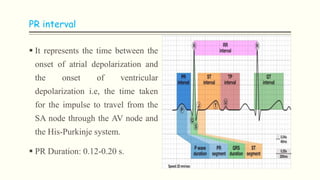
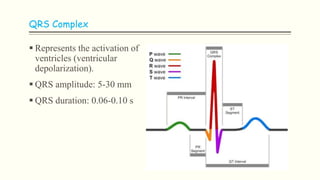
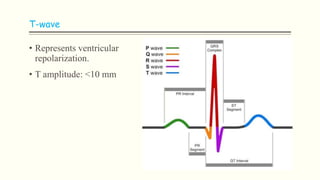
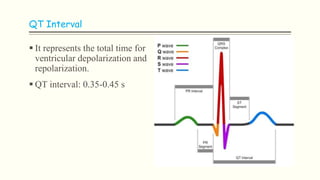
The document discusses an electrocardiogram (ECG), which detects the electrical activity of the heart during contraction and relaxation. It explains that the sinoatrial node initiates the heart's electrical impulse, which travels through the atrioventricular node and bundle of His before causing the heart to contract. An ECG records this electrical activity through different waves that represent events in the cardiac cycle, such as atrial depolarization (P wave), ventricular depolarization (QRS complex), and repolarization (T wave). The ECG provides information to diagnose various heart conditions by analyzing features like rate, rhythm, and time intervals between waves.