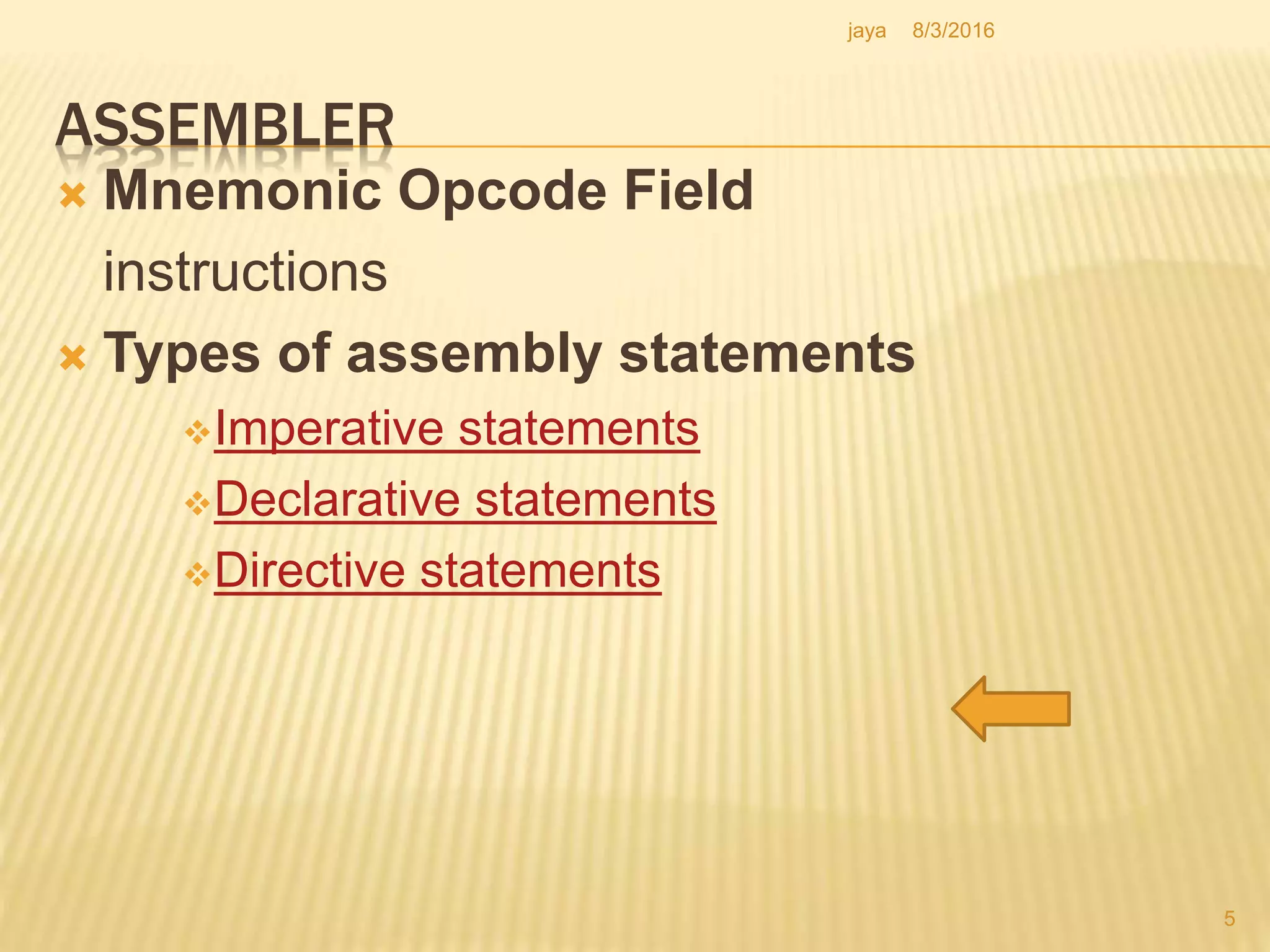
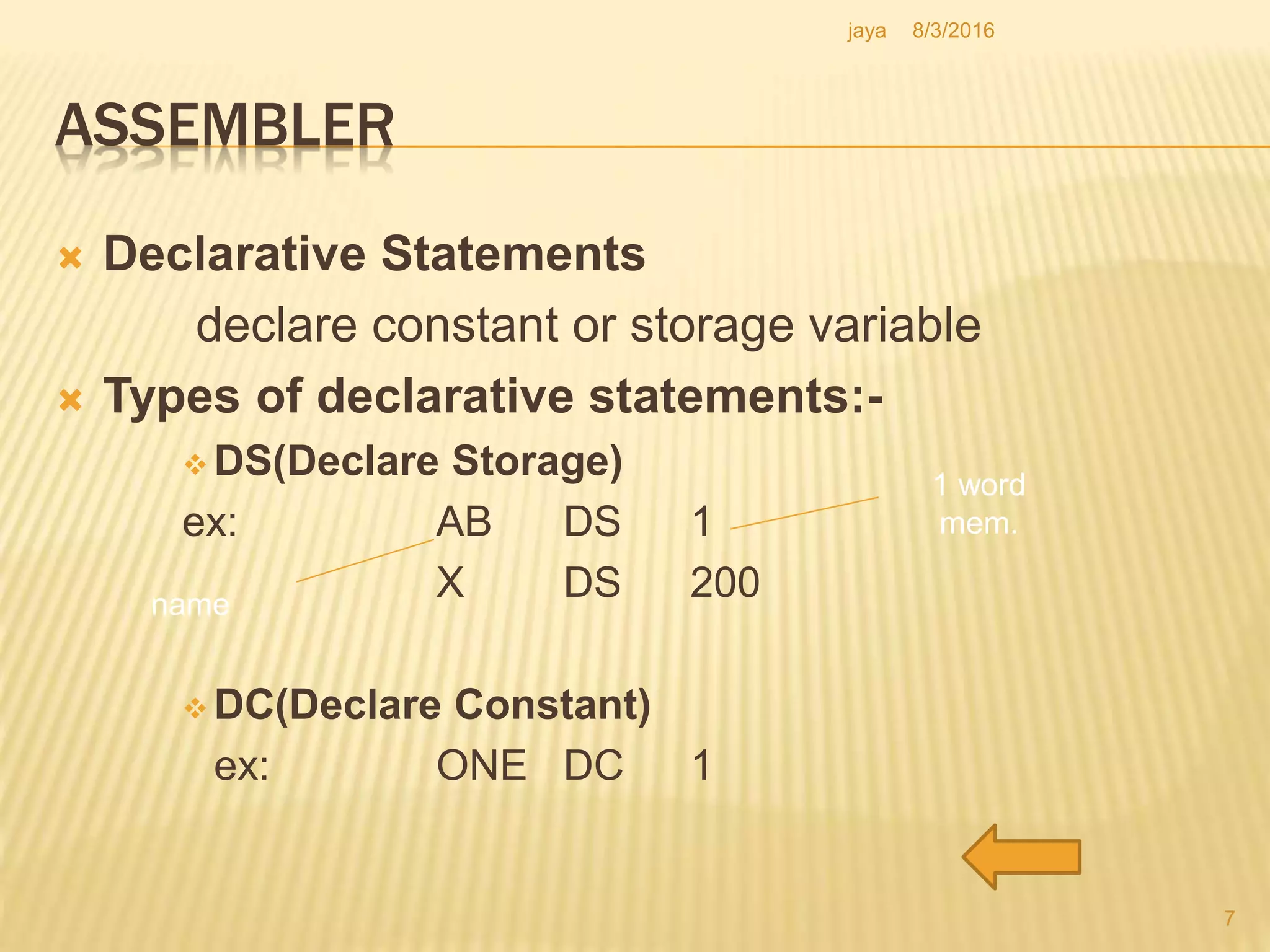
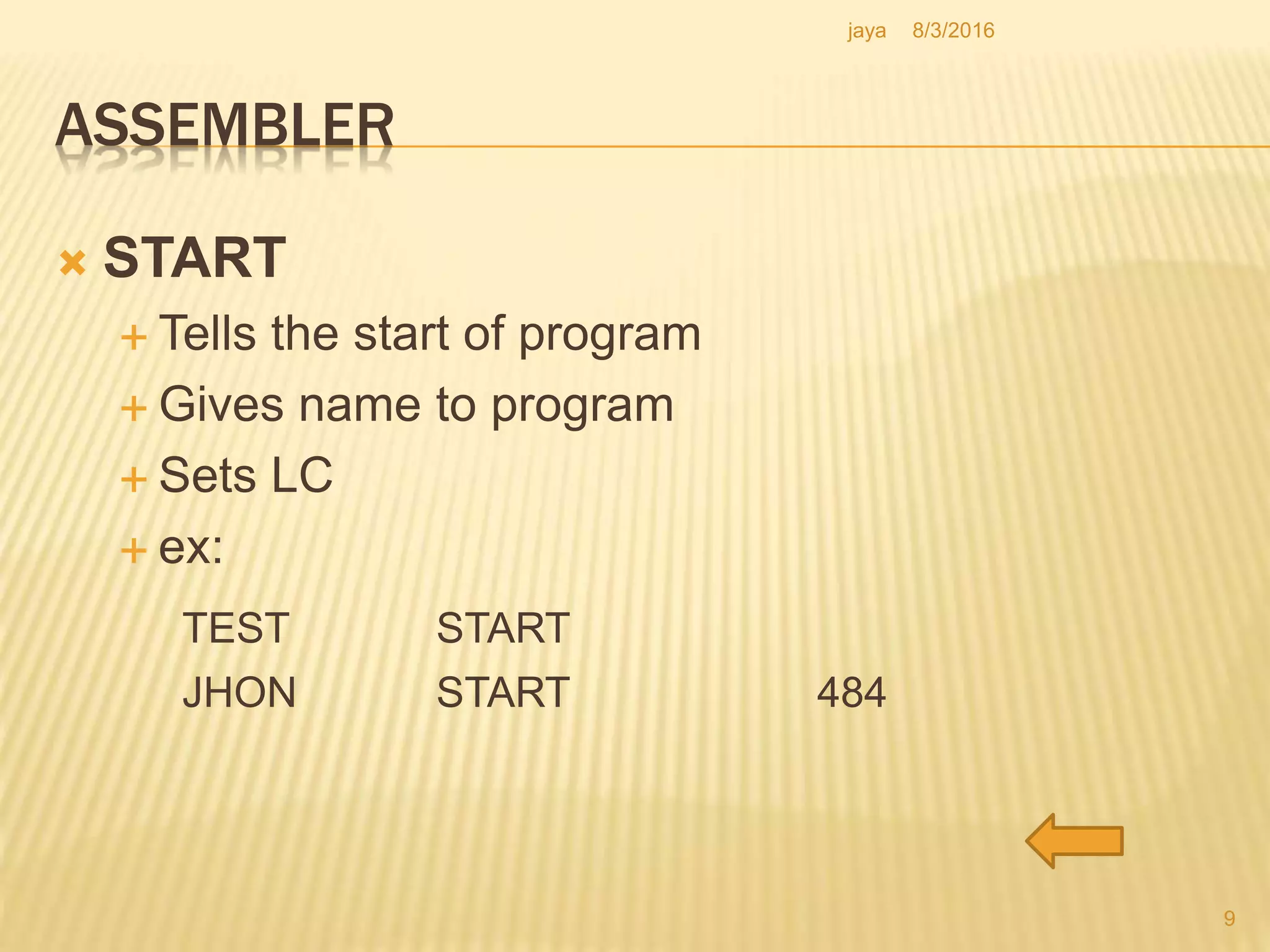
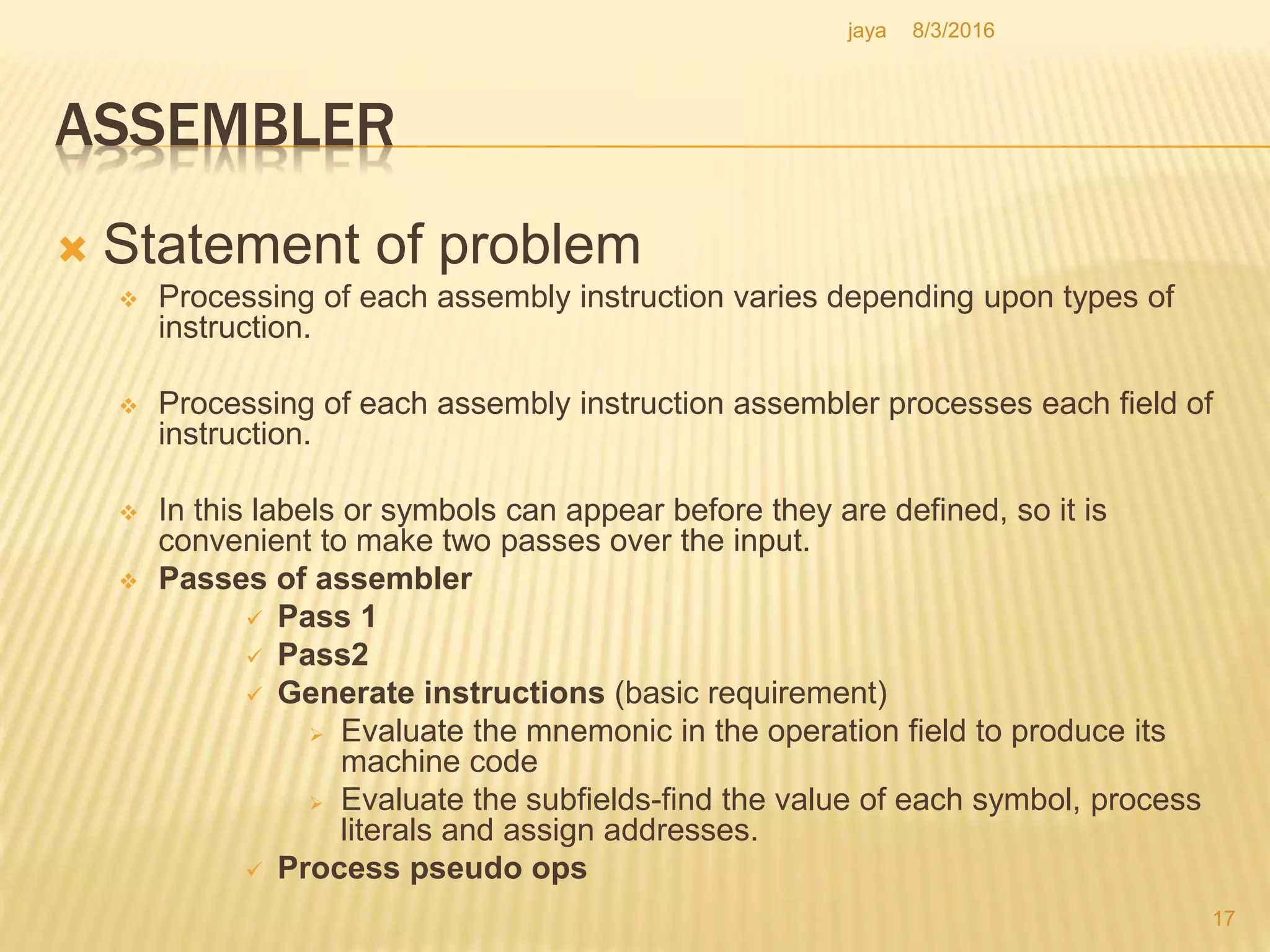
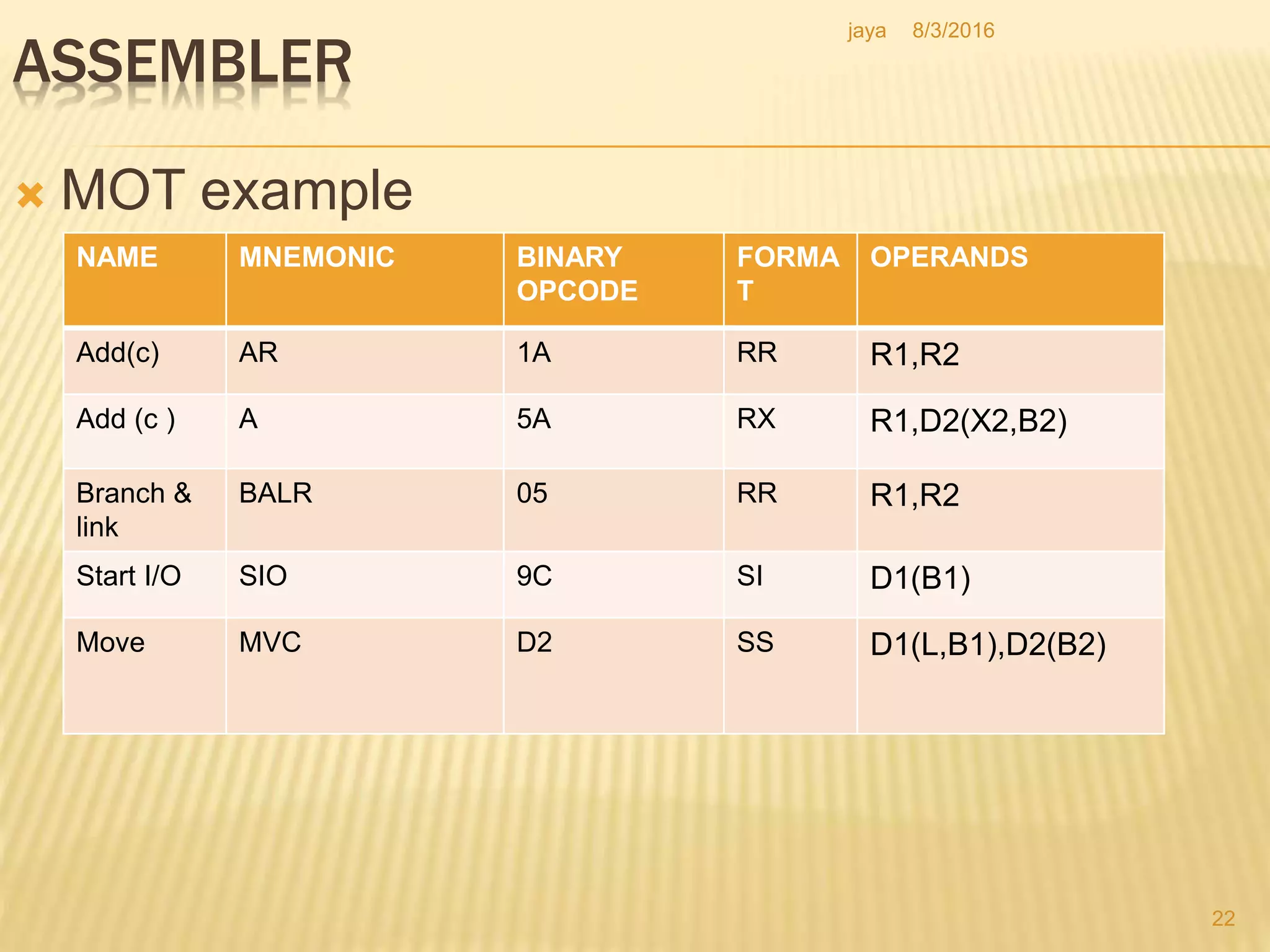
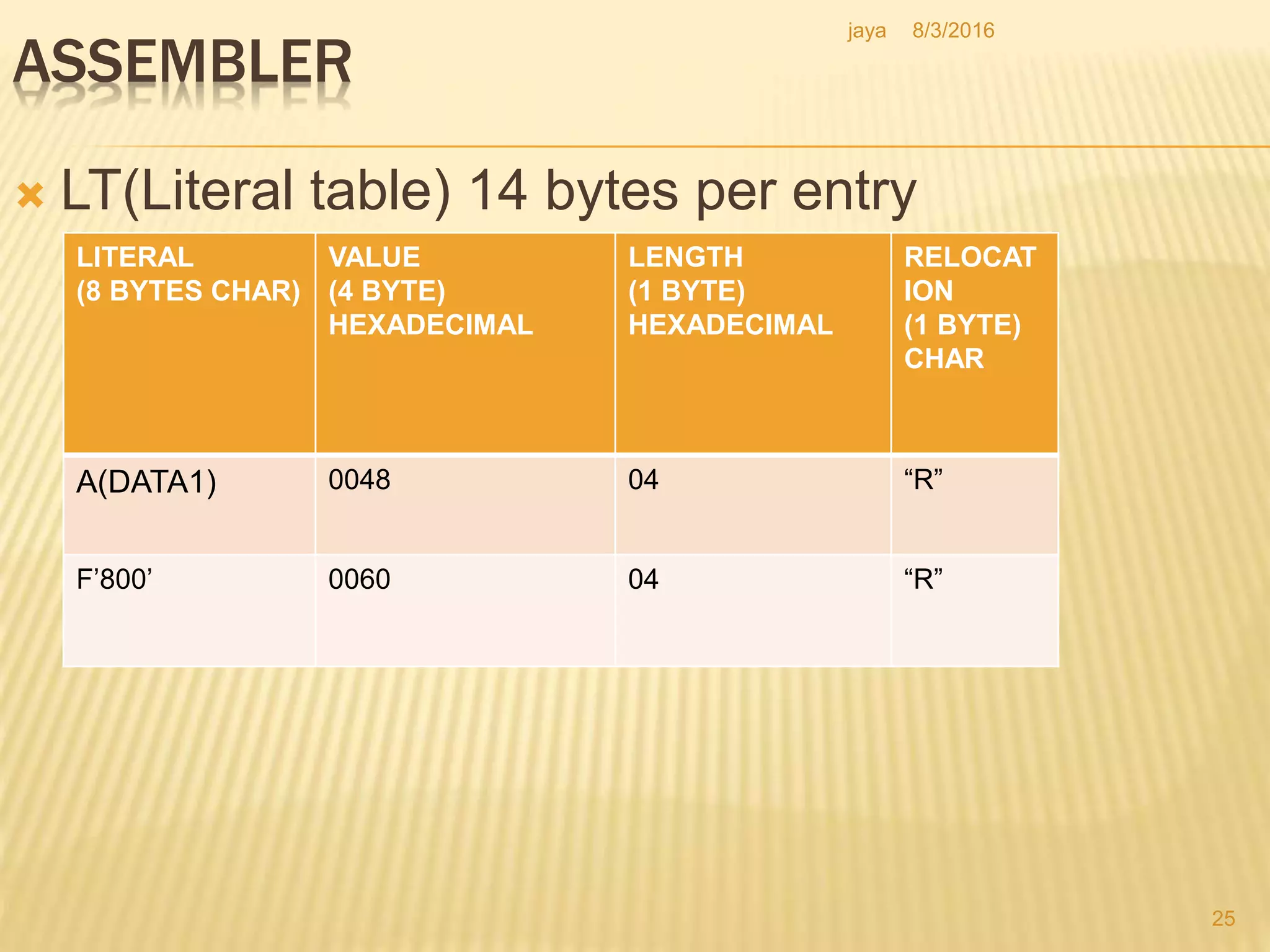
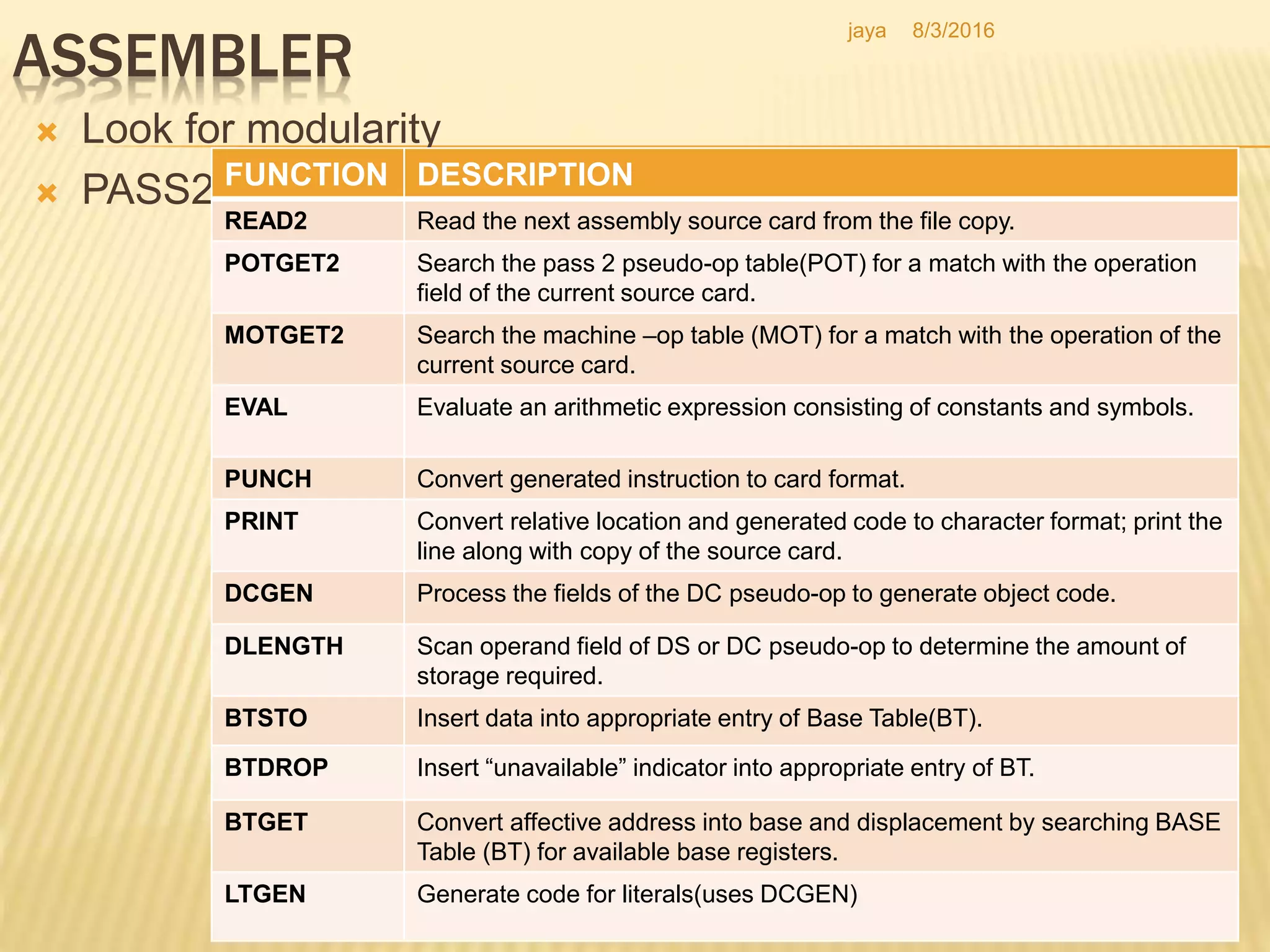
The document discusses the functions of an assembler. An assembler takes an assembly language program as input and produces a machine language program and additional information as output. It performs two passes over the input source program. In the first pass, it processes directives and defines symbols. In the second pass, it generates the machine language program. The assembler uses tables like the symbol table, machine opcode table, and pseudo opcode table to process instructions and directives. It also uses data structures like the location counter, literal table, and base table to track information during the assembly process.

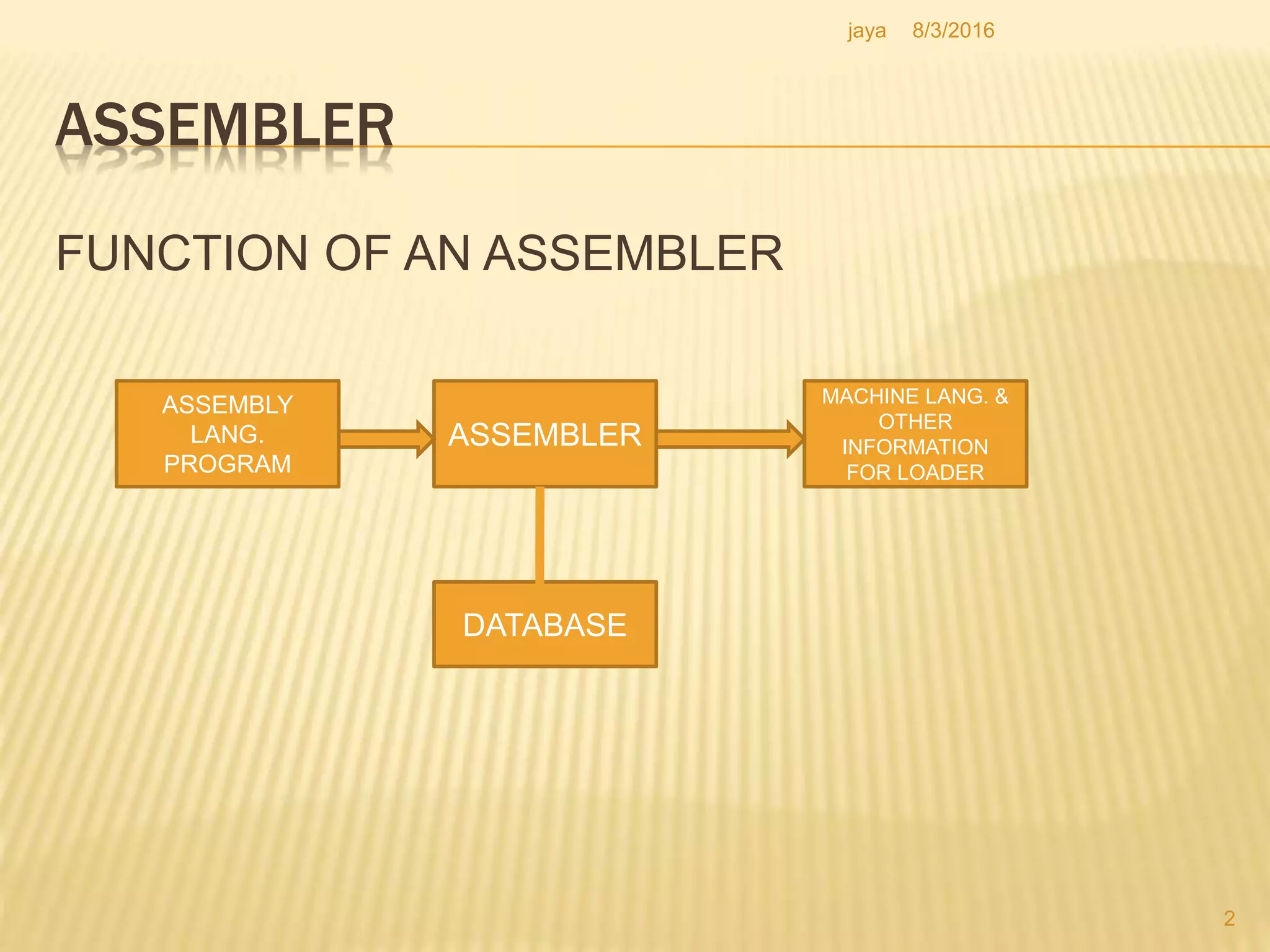
![ASSEMBLER
General format for assembly language statement
Example:
JOHN START 0
FOUR DC F’4’
A 2,FOUR
Opcode ------- 1 digit
Register operand ---------- 1 digit
Memory operand ---------- 3 digits
[Label *] [opcode] [operand1]*, [operand2]*
3
8/3/2016jaya](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assembler1-160803095033/75/Assembler1-3-2048.jpg)