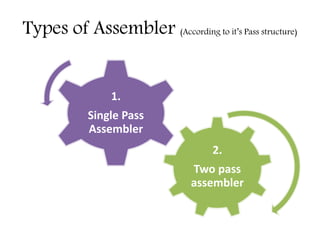
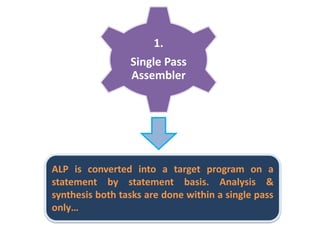
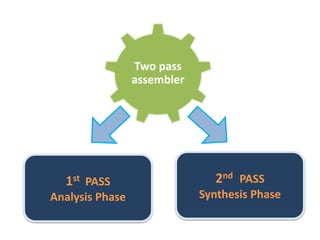
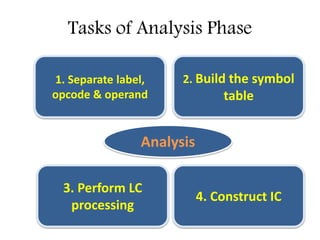
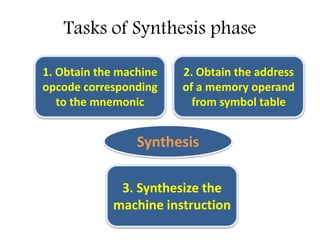
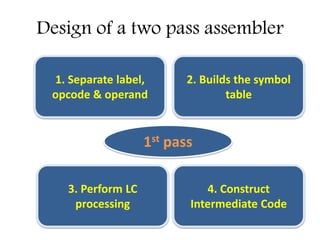
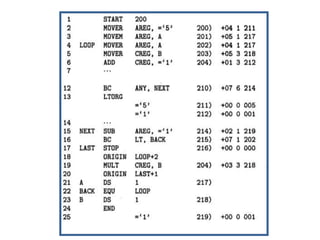
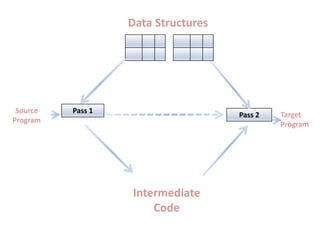
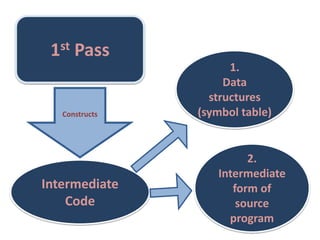
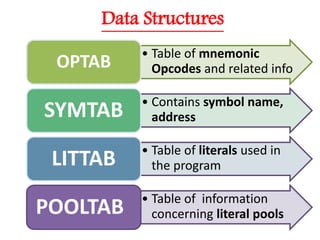
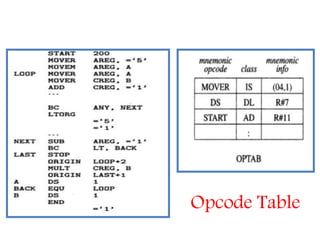
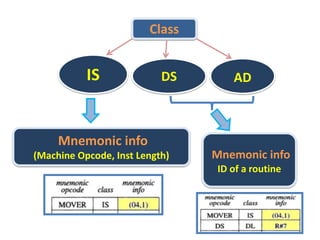
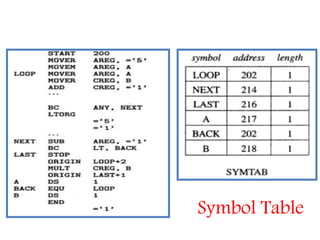
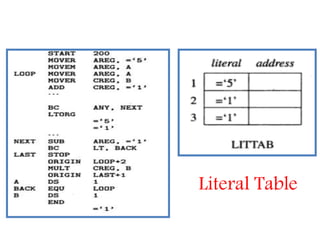
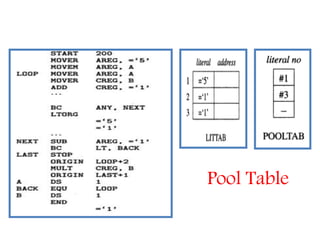
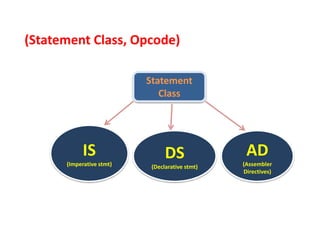
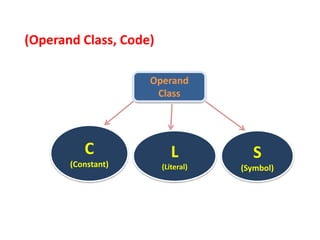
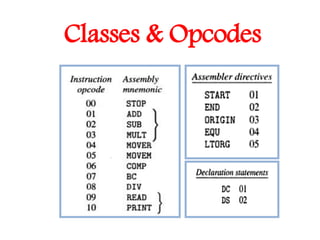
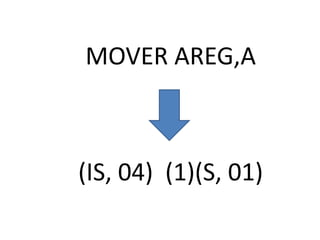
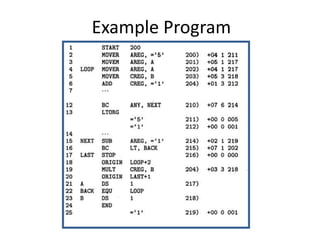
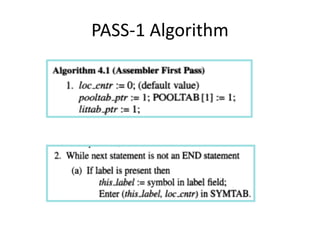
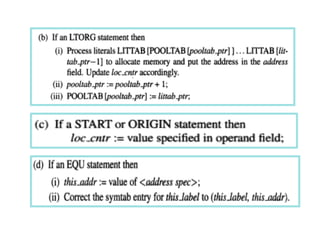
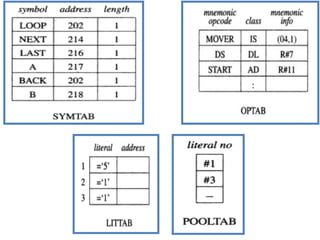
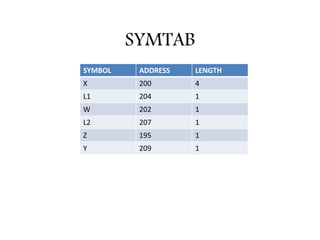
This document discusses the first pass of an assembler. It begins by defining an assembler as a language processor that converts assembly language to machine language. It then describes the different types of assemblers, focusing on single-pass and two-pass assemblers. For two-pass assemblers, it outlines the tasks of the analysis and synthesis phases in the first and second passes respectively. These include separating symbols, building symbol tables, performing label and literal processing, and constructing intermediate code in the first pass and then generating the target program in the second pass. The document provides an example of intermediate code format and walks through converting an example assembly program to intermediate code using the first pass of a two-pass assembler.