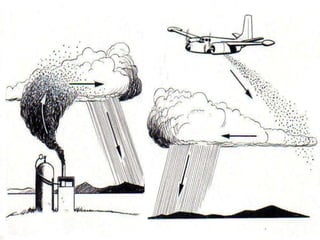
This document discusses artificially induced precipitation and methods for measuring rainfall intensity. It describes cloud seeding as dispersing substances into clouds like silver iodide or dry ice to alter microphysical processes and change the type or amount of precipitation. Rainfall intensity is defined as the ratio of total rainfall to duration and can be light, moderate, or heavy. Common rain gauges used to measure rainfall amounts include standard rain gauges, tipping bucket rain gauges, natural siphon rain gauges, and weight bucket rain gauges.