Embed presentation
Downloaded 442 times





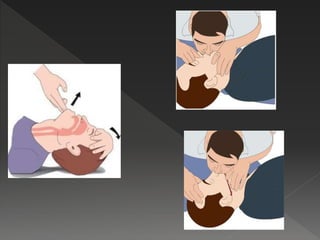





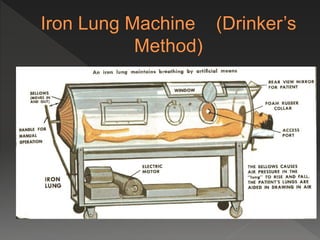



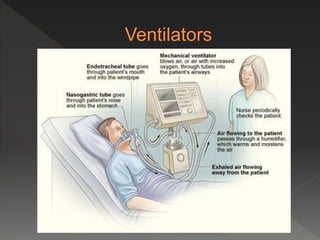

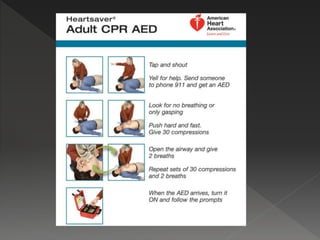

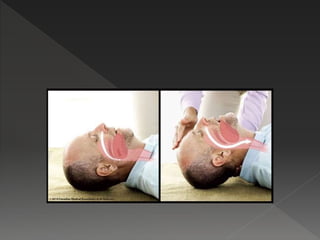


This document provides instructions for performing manual cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and lists causes of respiratory failure that may require CPR, including drowning, electrocution, anesthesia, carbon monoxide poisoning, polio, myasthenia gravis, and certain drugs. It describes how to perform manual CPR by placing the patient supine, clearing the airway, extending the neck, exhaling forcefully into the mouth and nostrils, and repeating at a rate of 10-15 breaths per minute until normal breathing resumes or the patient can be transferred to a hospital.






















