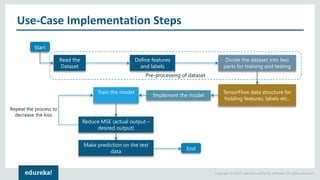
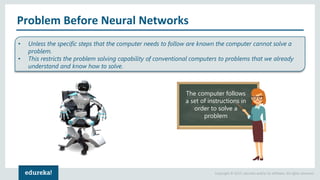
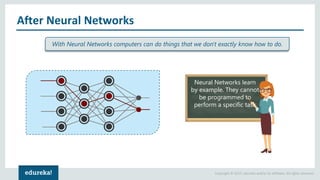
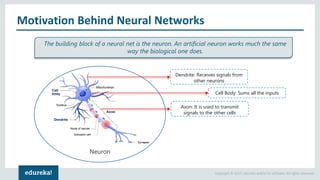
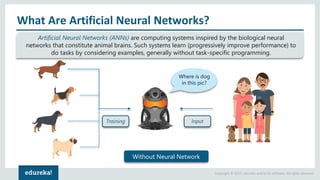
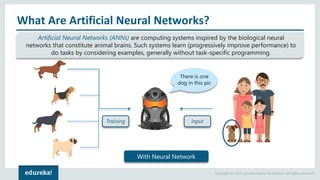
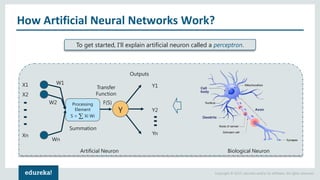
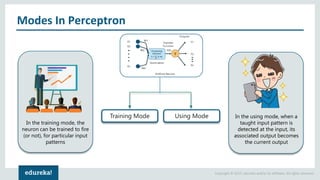
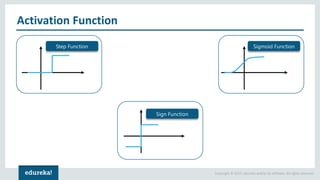
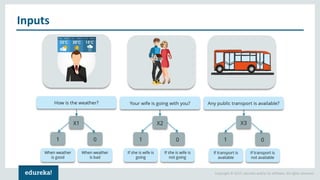
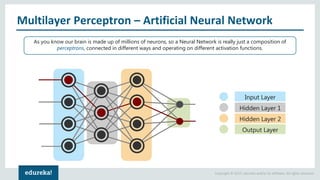
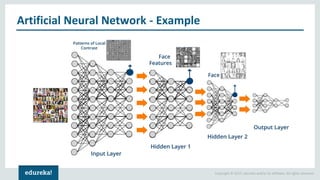
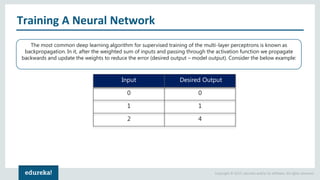
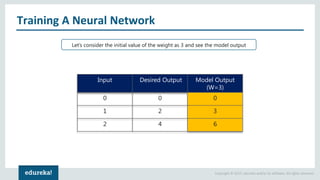
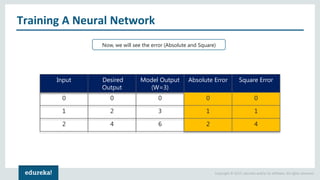
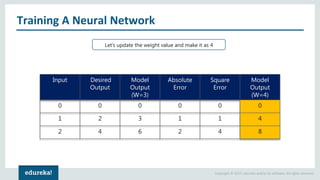
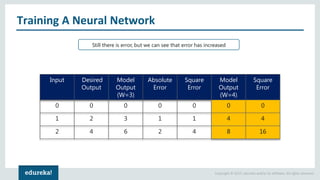
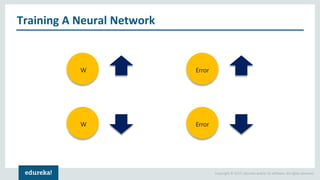
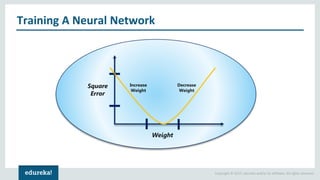
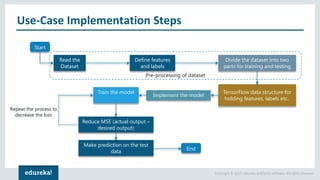
The document discusses the use of artificial neural networks (ANNs) to determine the authenticity of bank notes using a dataset of images of real and forged notes. It outlines the implementation steps, including dataset preparation, model training, and applications of ANNs in various fields. Additionally, it covers the motivation behind using neural networks, their operational principles, and training methodologies like backpropagation.