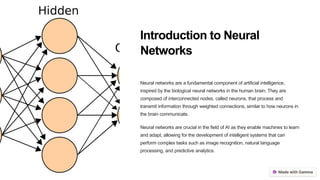
The document discusses neural networks, which are brain-inspired models essential to advancements in artificial intelligence. It covers key components, operation methods, applications in various fields, advantages, challenges, and future trends of neural networks. The presentation concludes by emphasizing their transformative potential in diverse industries and invites questions for further clarification.