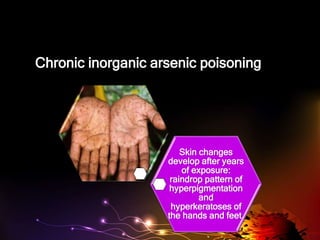
Arsenic toxicity can result from acute or chronic exposure. Acute poisoning causes gastrointestinal symptoms within hours followed by cardiovascular and neurological effects over days. Chronic low-dose exposure may cause peripheral neuropathy, skin changes, and cancer risks. Arsine gas poisoning results in massive intravascular hemolysis and potential renal failure within days. Chelation therapy with British Anti-Lewisite or dimercaprol can treat acute arsenic toxicity if given promptly, while chronic cases require ending exposure and supportive care.