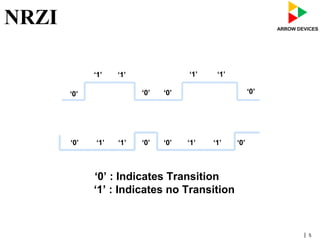
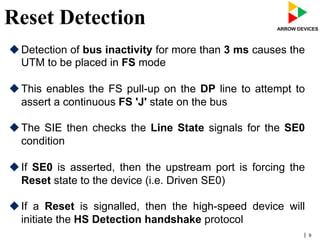
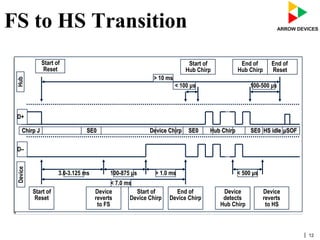
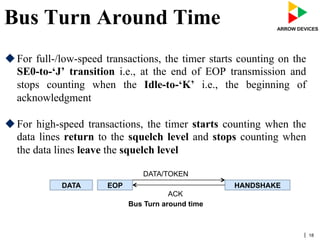
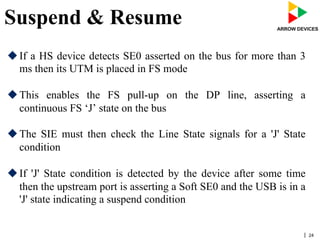
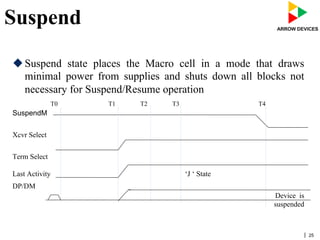
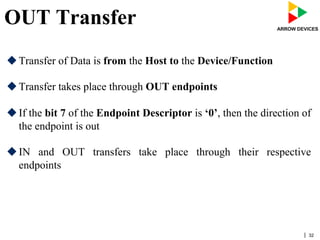
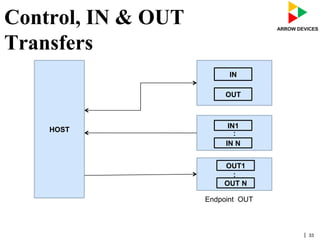
The document discusses various concepts related to USB 2.0 including chirps, squelch, NRZI encoding, bit stuffing, reset conditions, error detection, and high-speed transfers. During device enumeration, a USB 2.0 device uses chirp signals to indicate it is capable of high-speed communication. Bit stuffing and NRZI encoding are used to ensure adequate signal transitions for high-speed communication. The document also outlines the process for transitioning from full-speed to high-speed operation, as well as procedures for handling errors, suspend and resume events, and different types of high-speed transfers including control, IN, and OUT transfers.