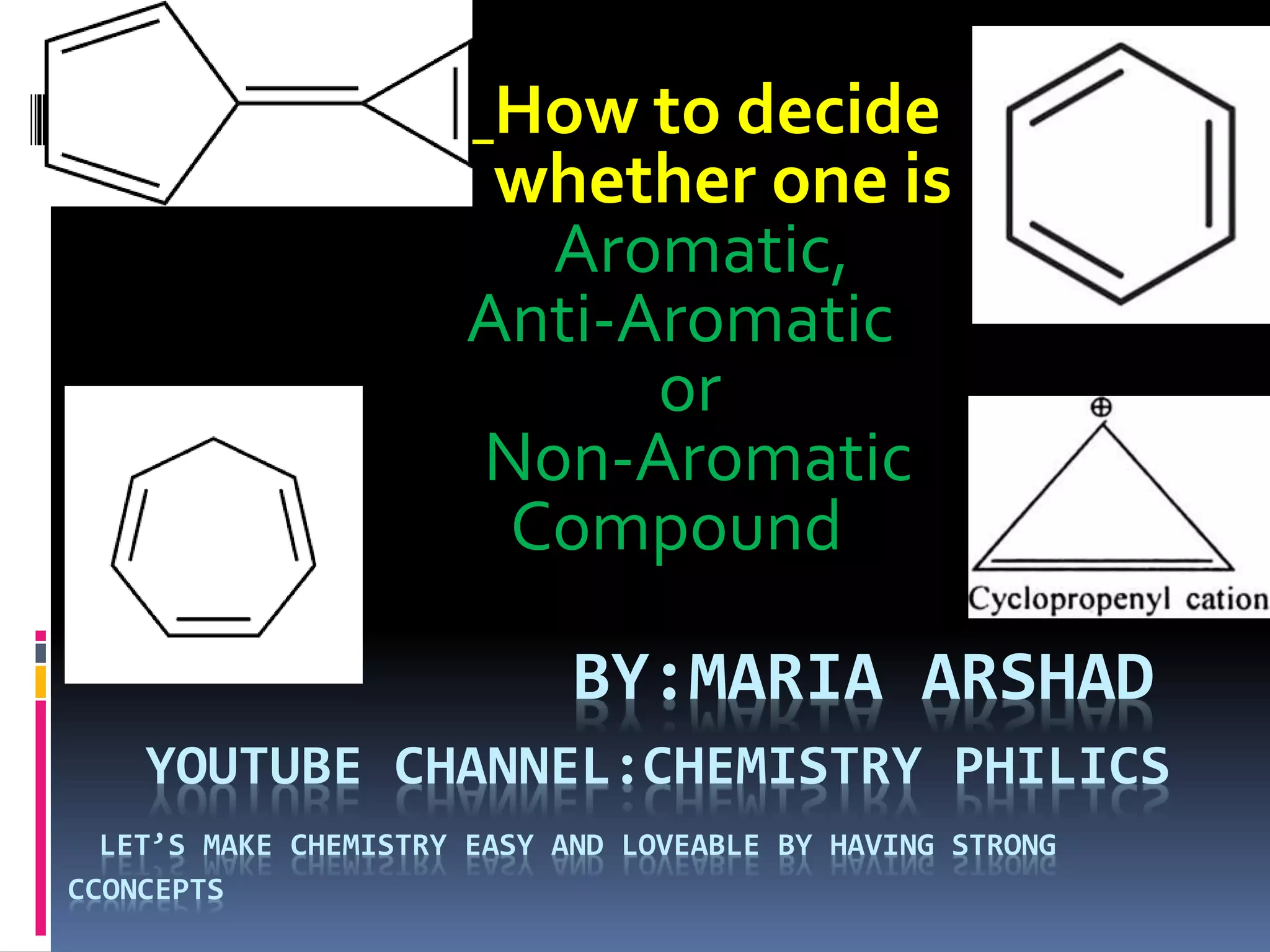
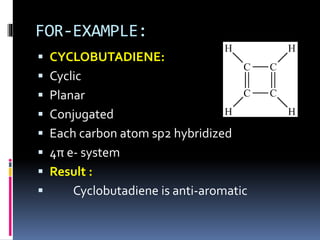
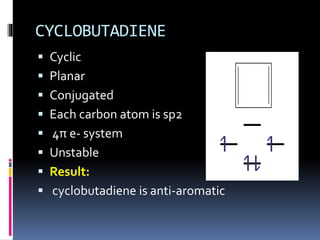
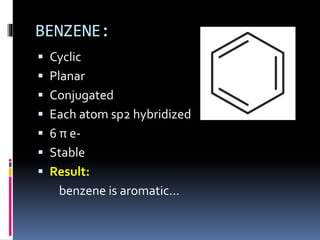
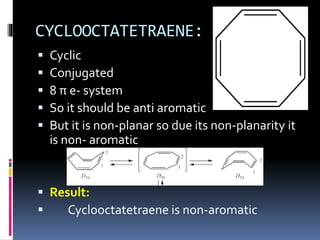
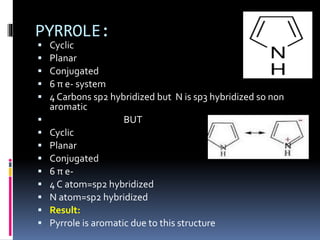
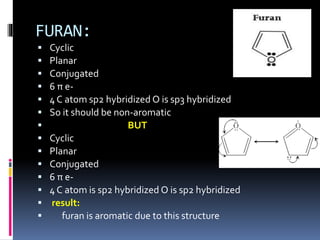
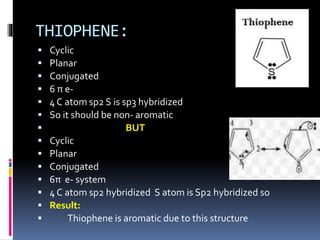
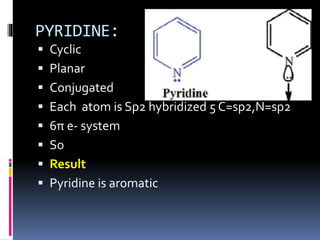
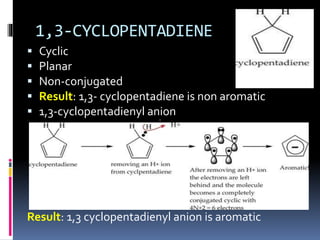
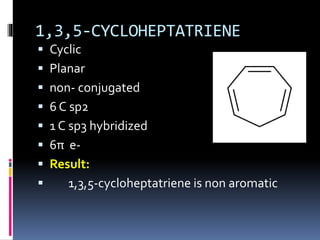
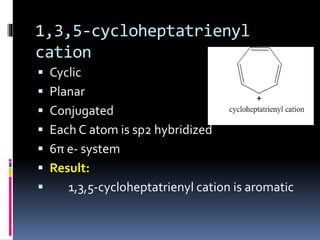
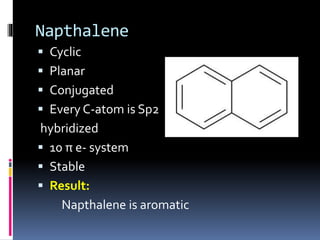
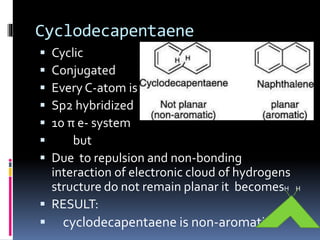
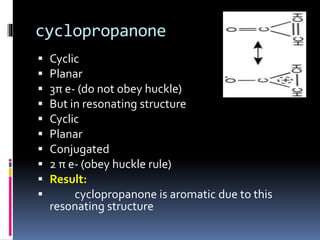
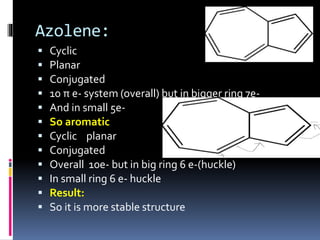
The document outlines the criteria for classifying compounds as aromatic, anti-aromatic, or non-aromatic based on their structural properties and electron configurations. Aromatic compounds must meet specific conditions, including having a cyclic, planar structure and obeying Huckel's rule, while anti-aromatic compounds contain 4n π electrons and exhibit instability. Various examples of compounds are provided to illustrate these concepts, including benzene, cyclobutadiene, and napthalene.