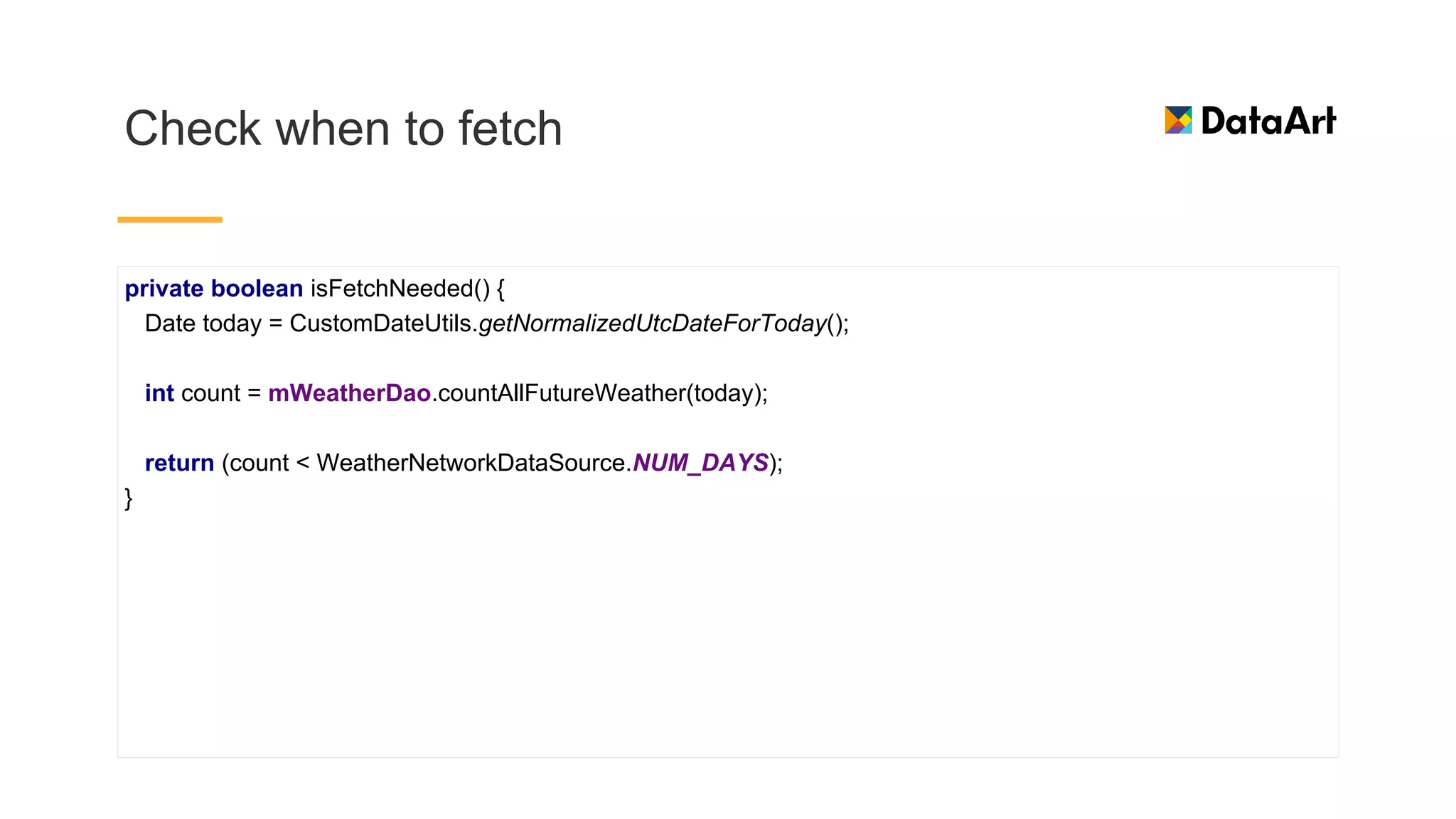
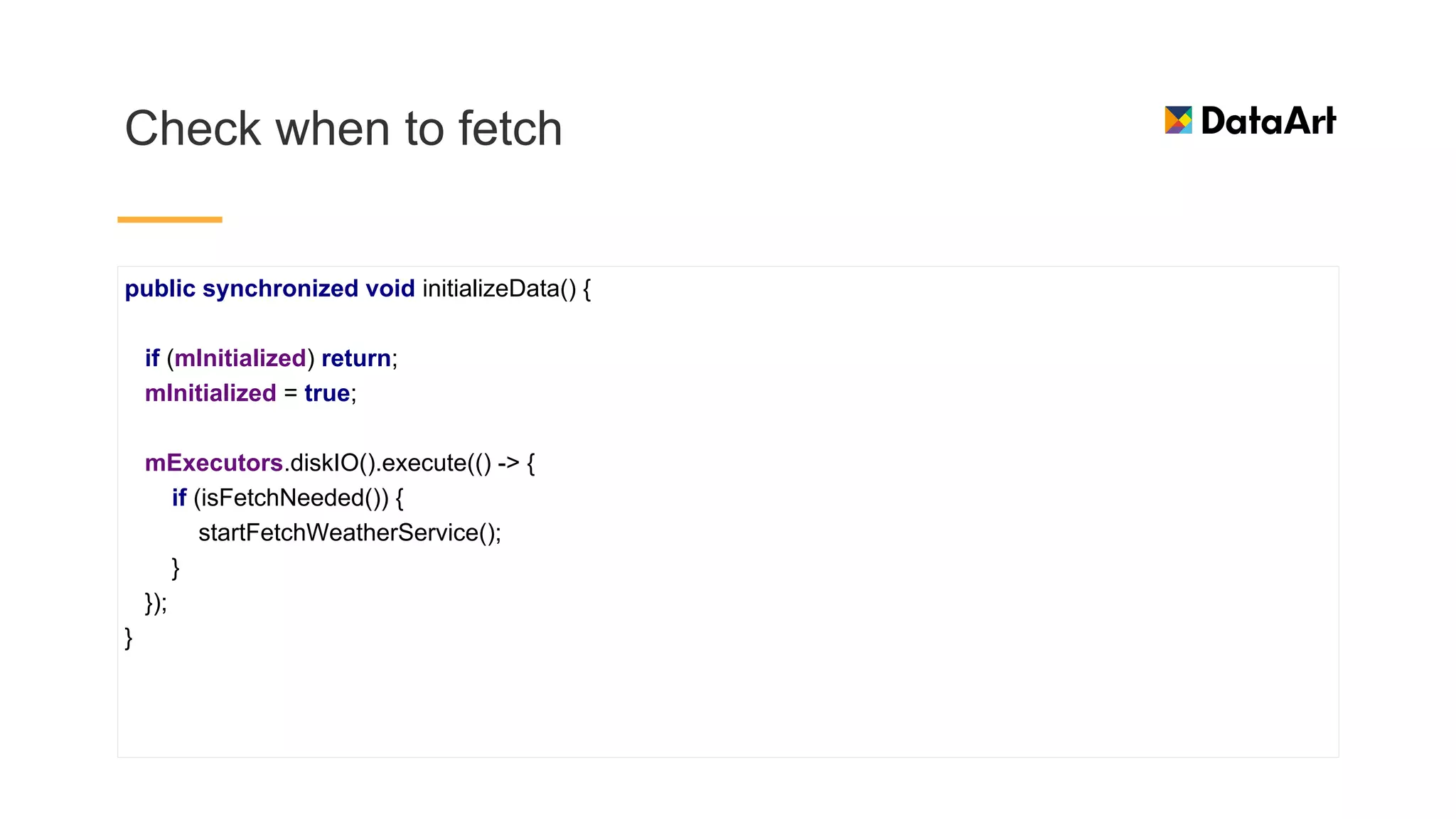
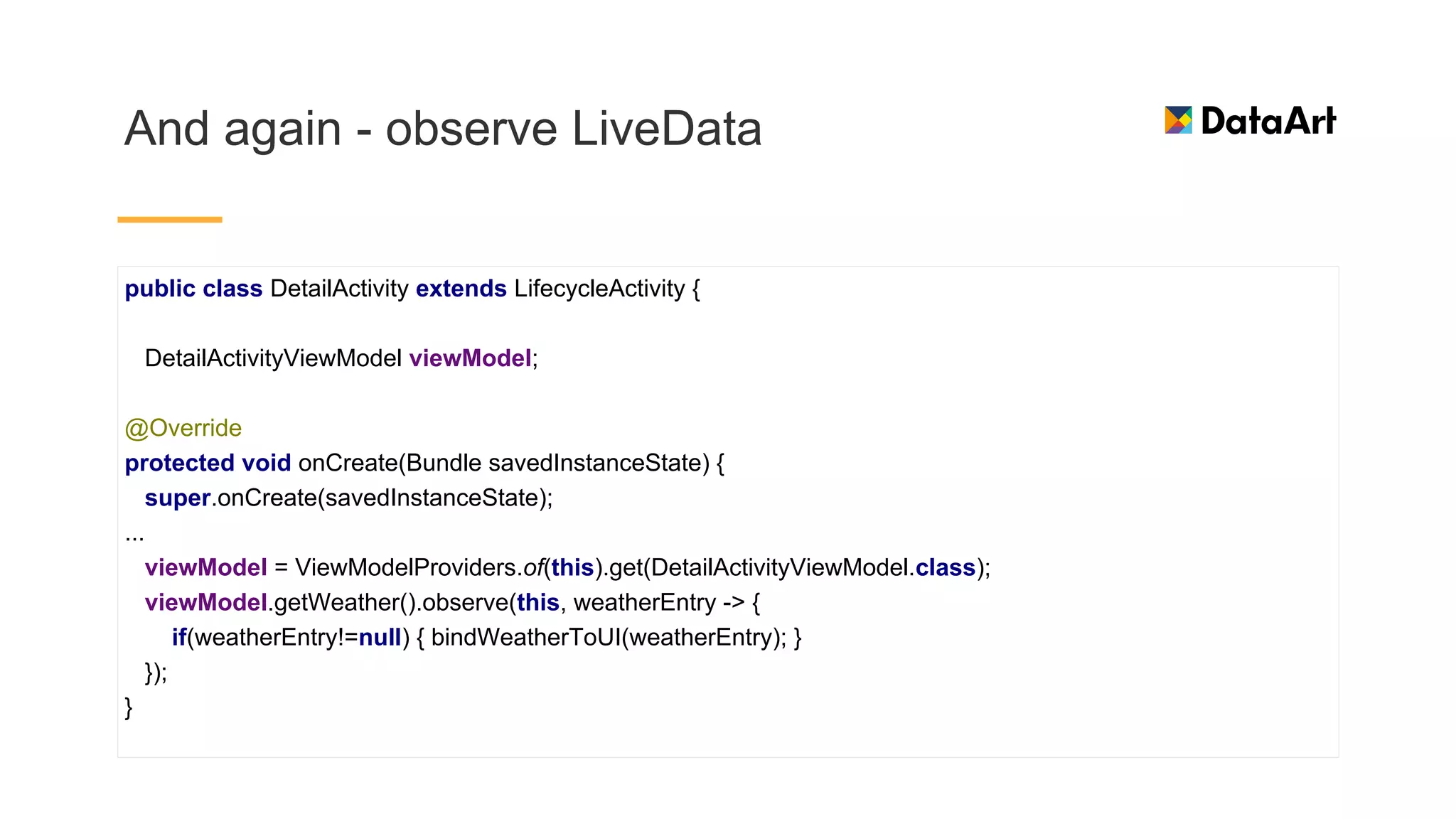
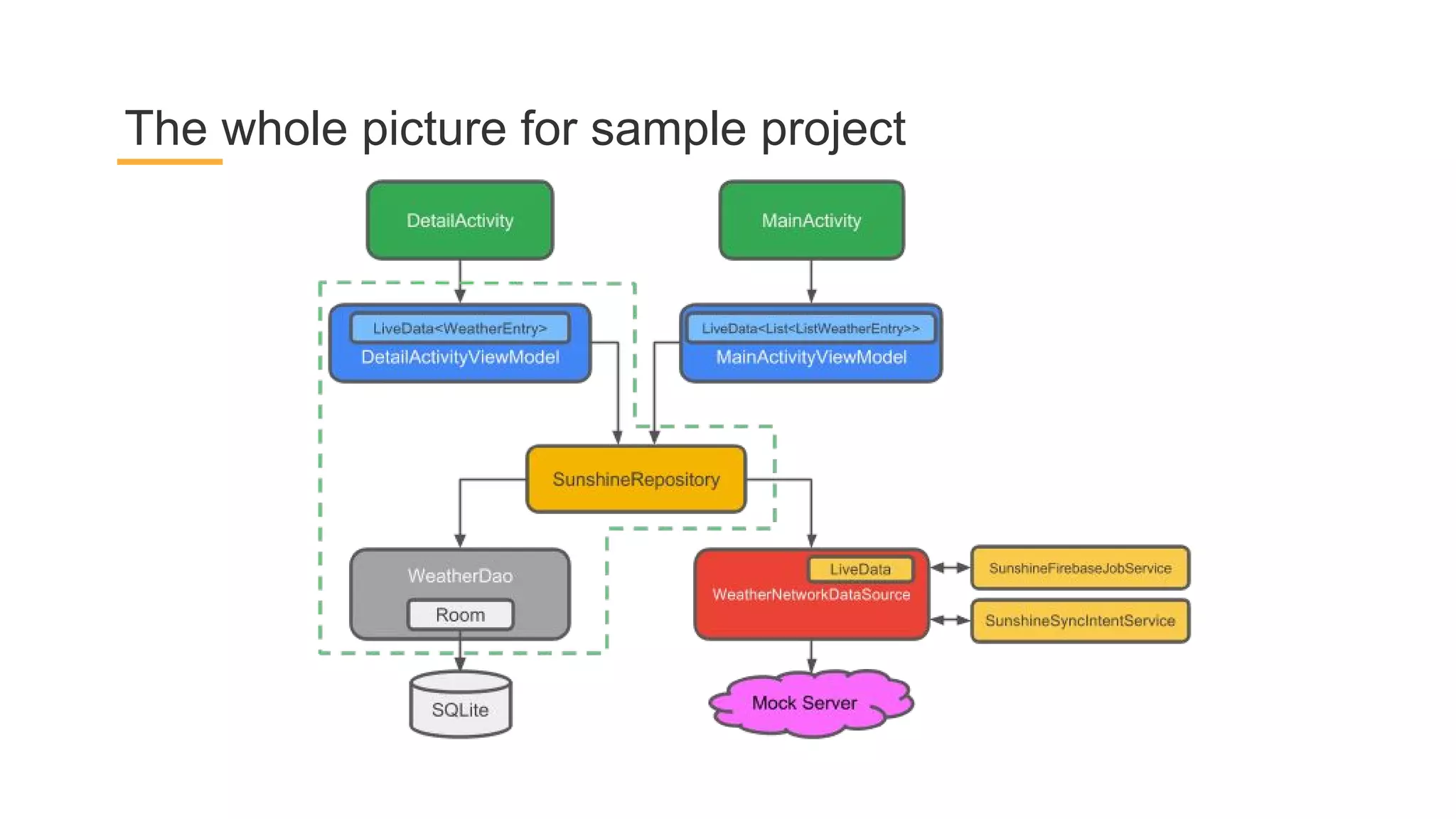
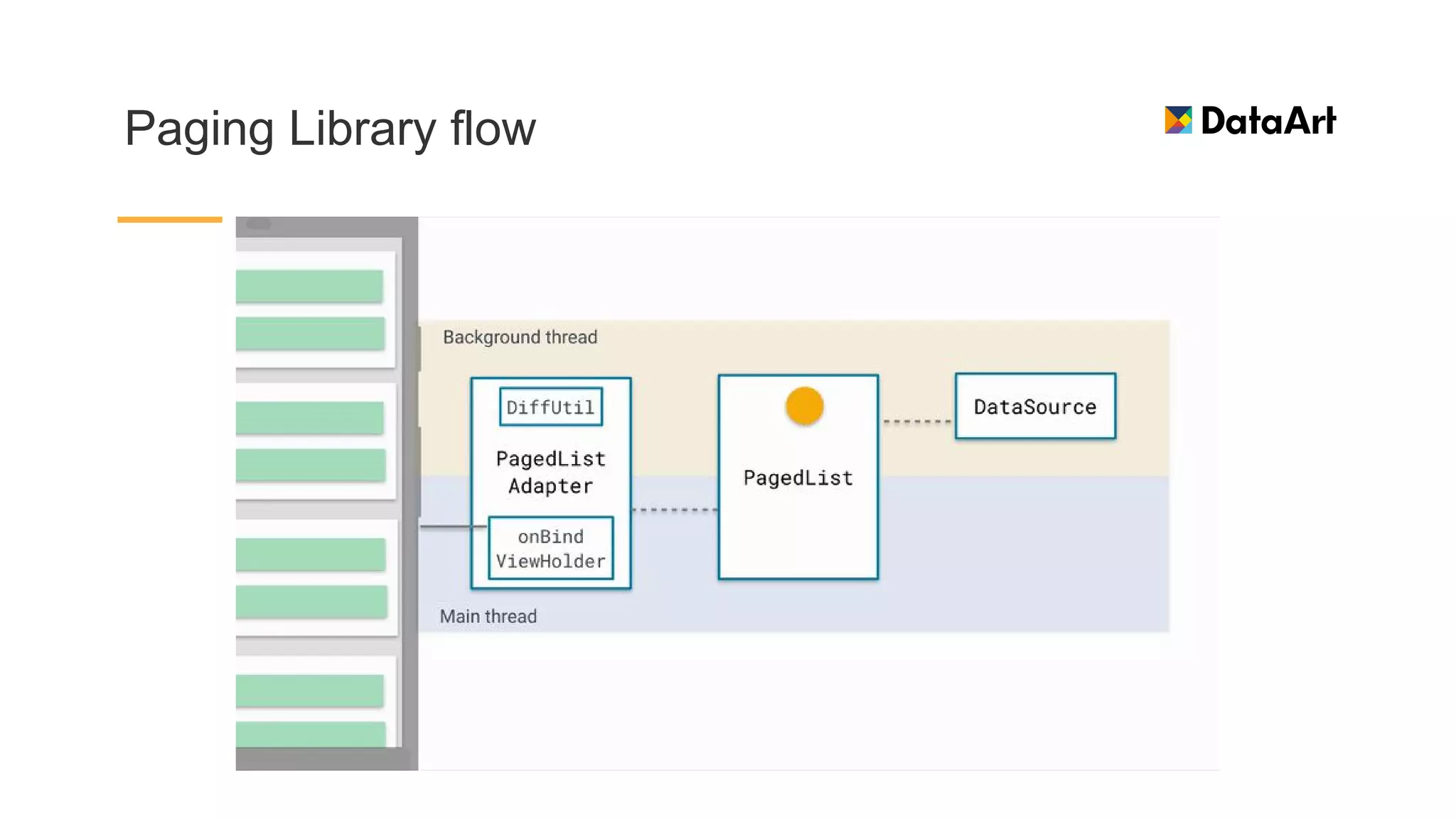
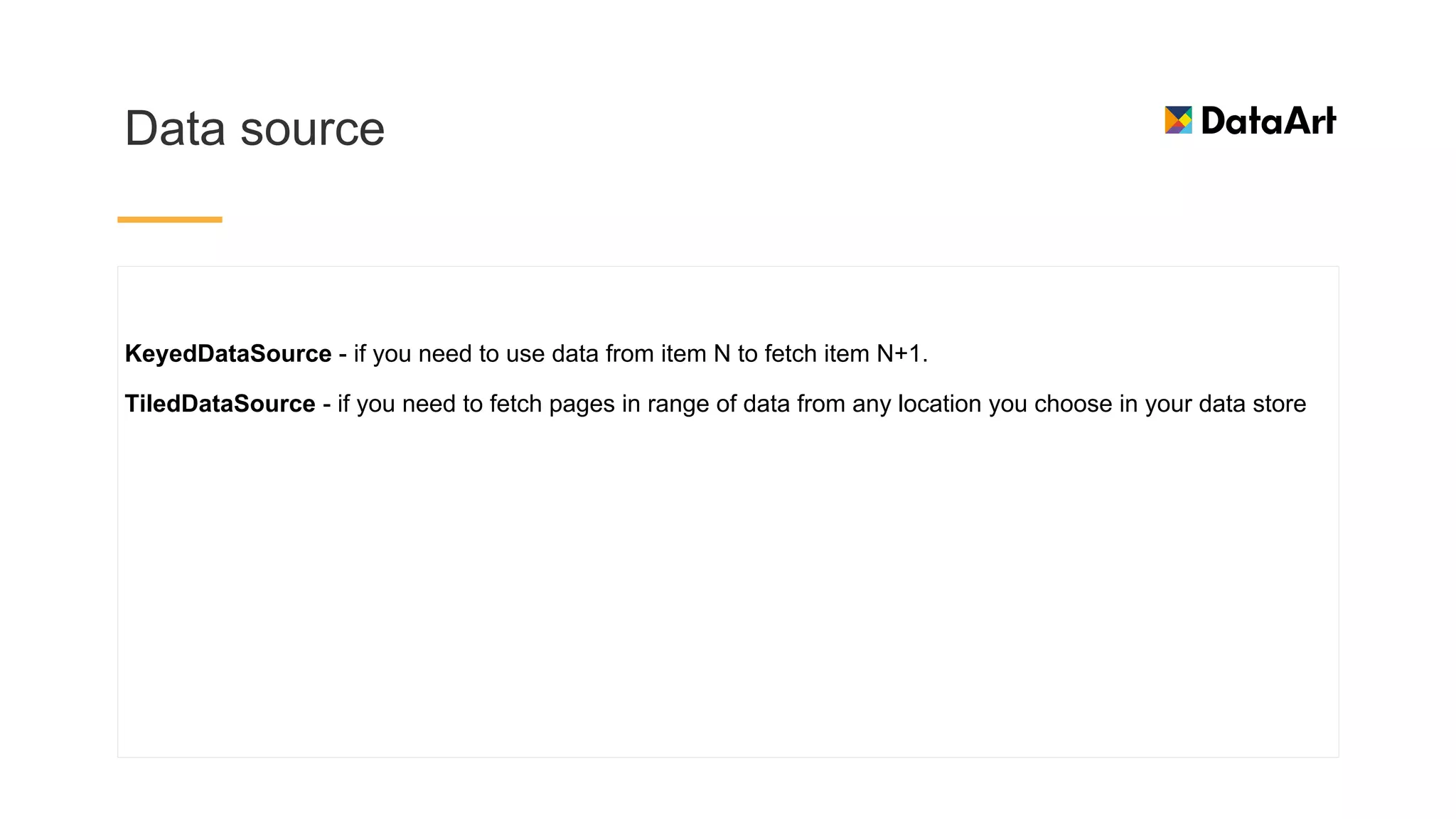
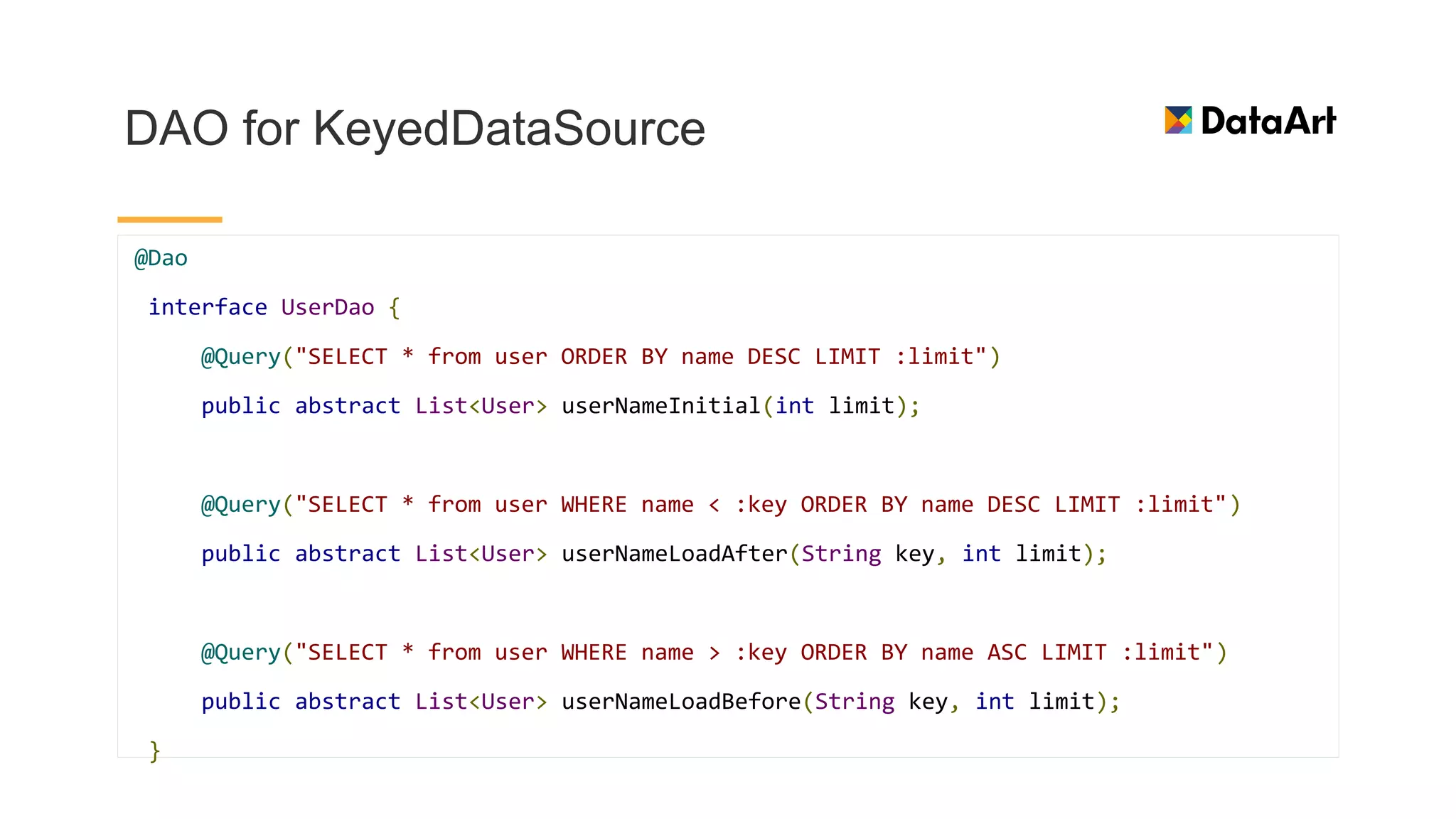
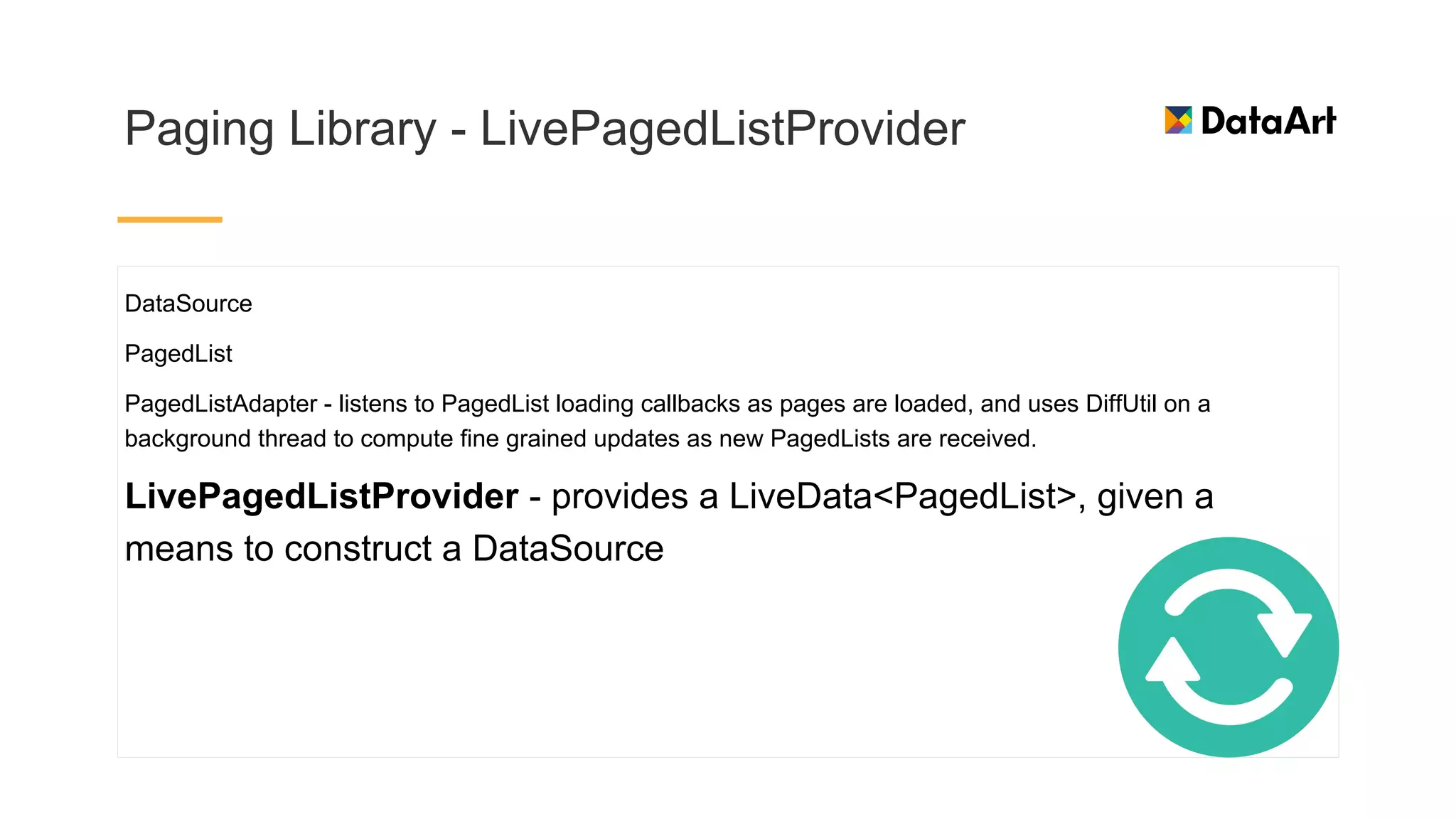
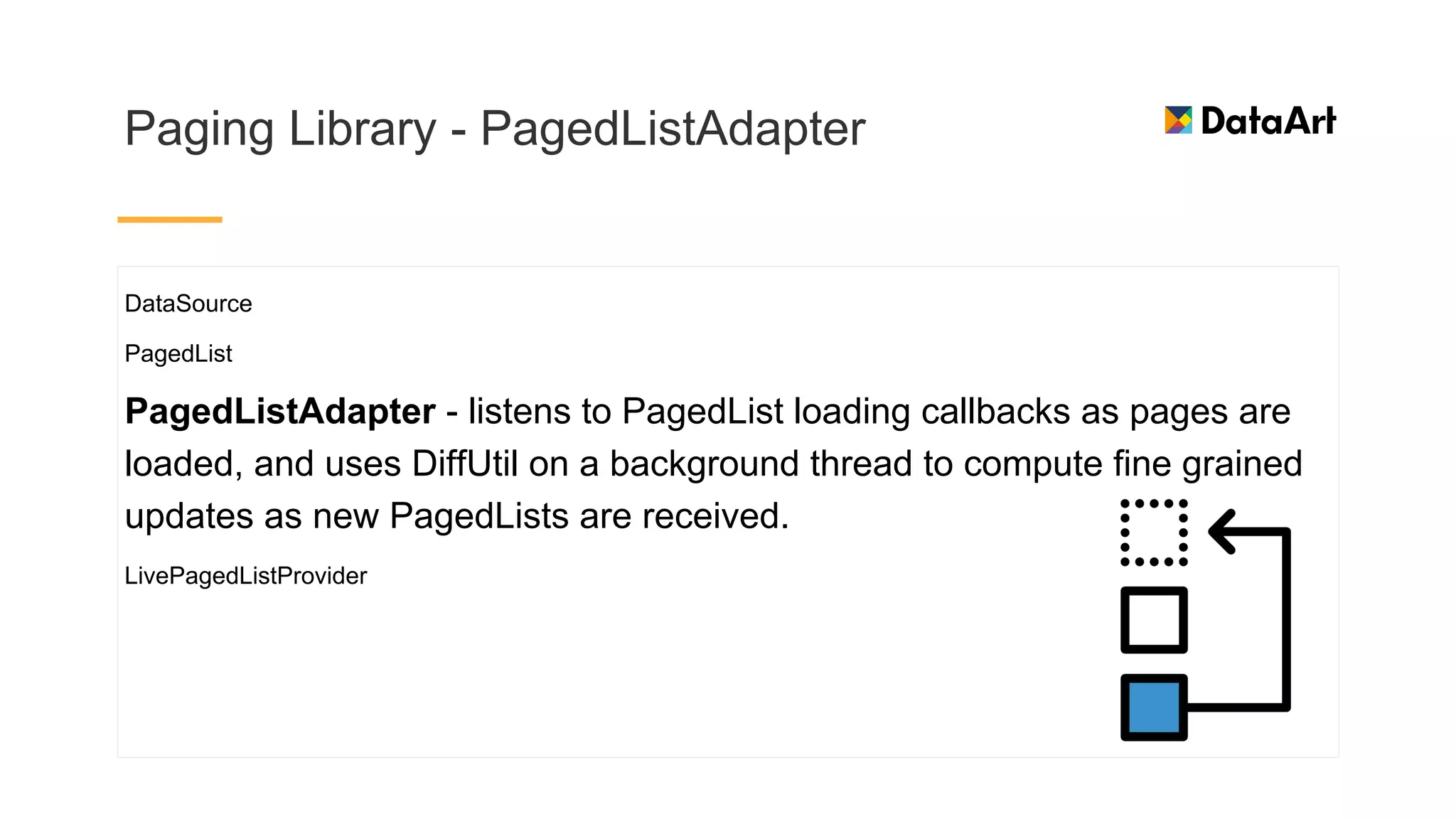
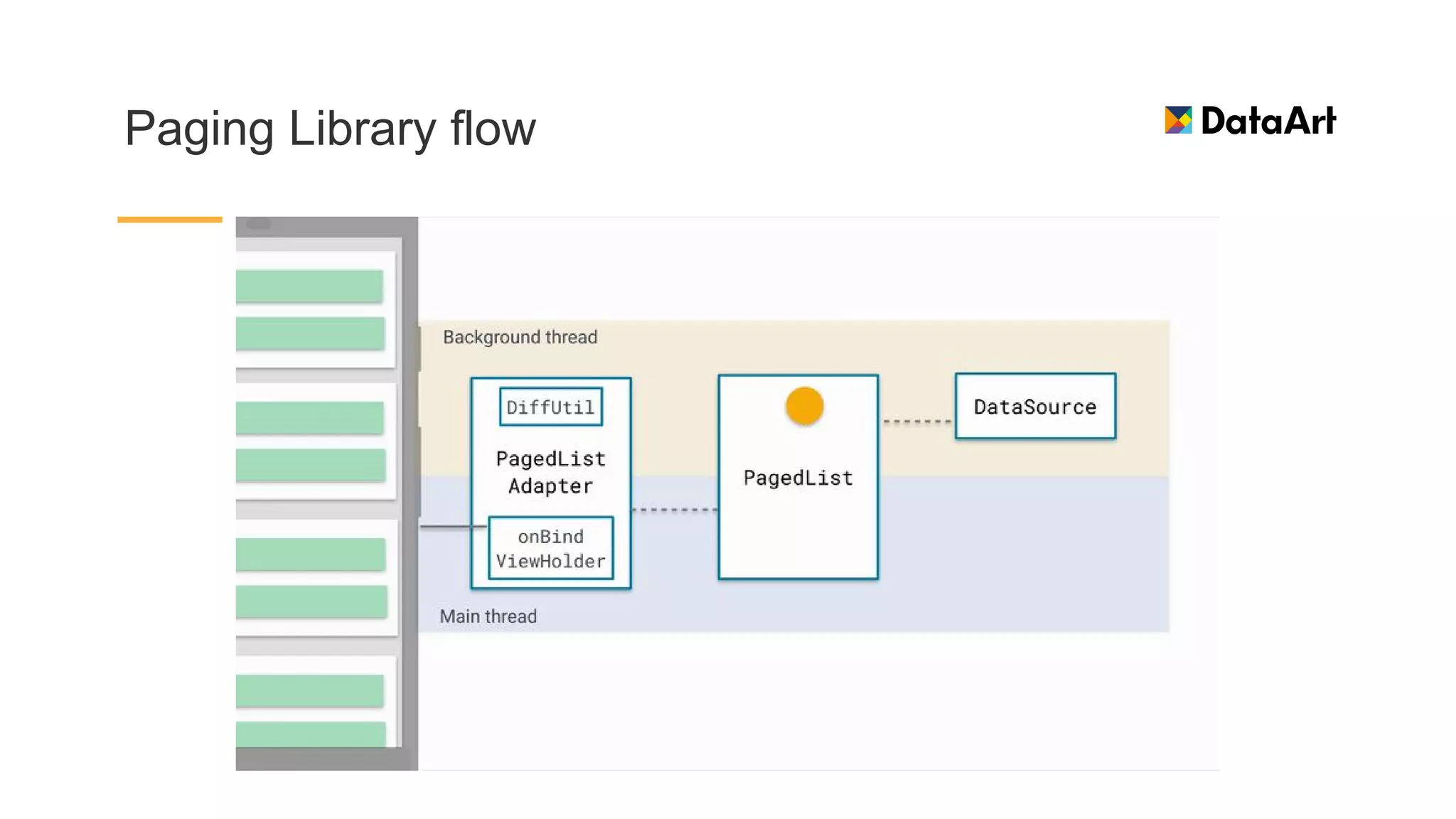
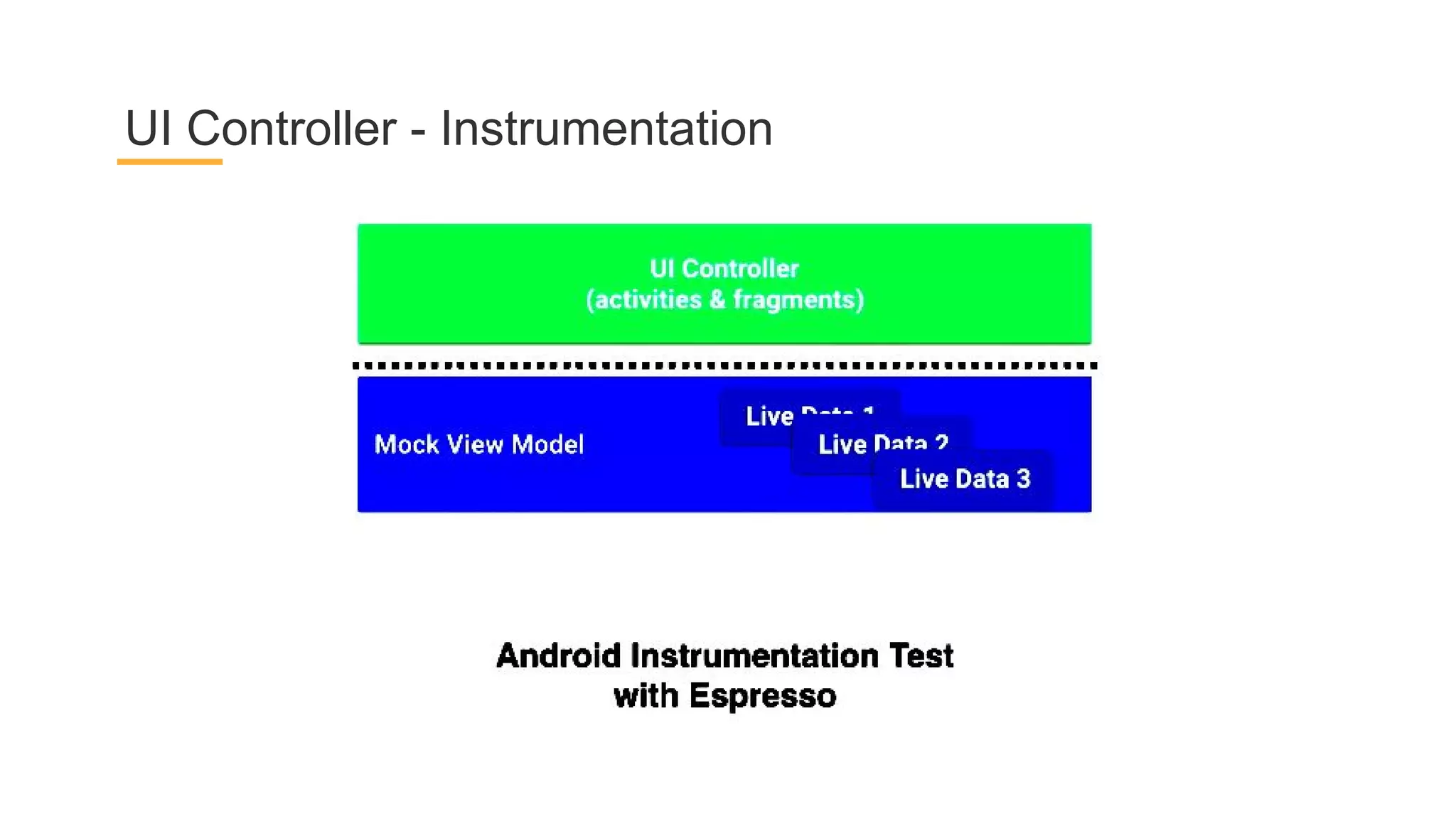
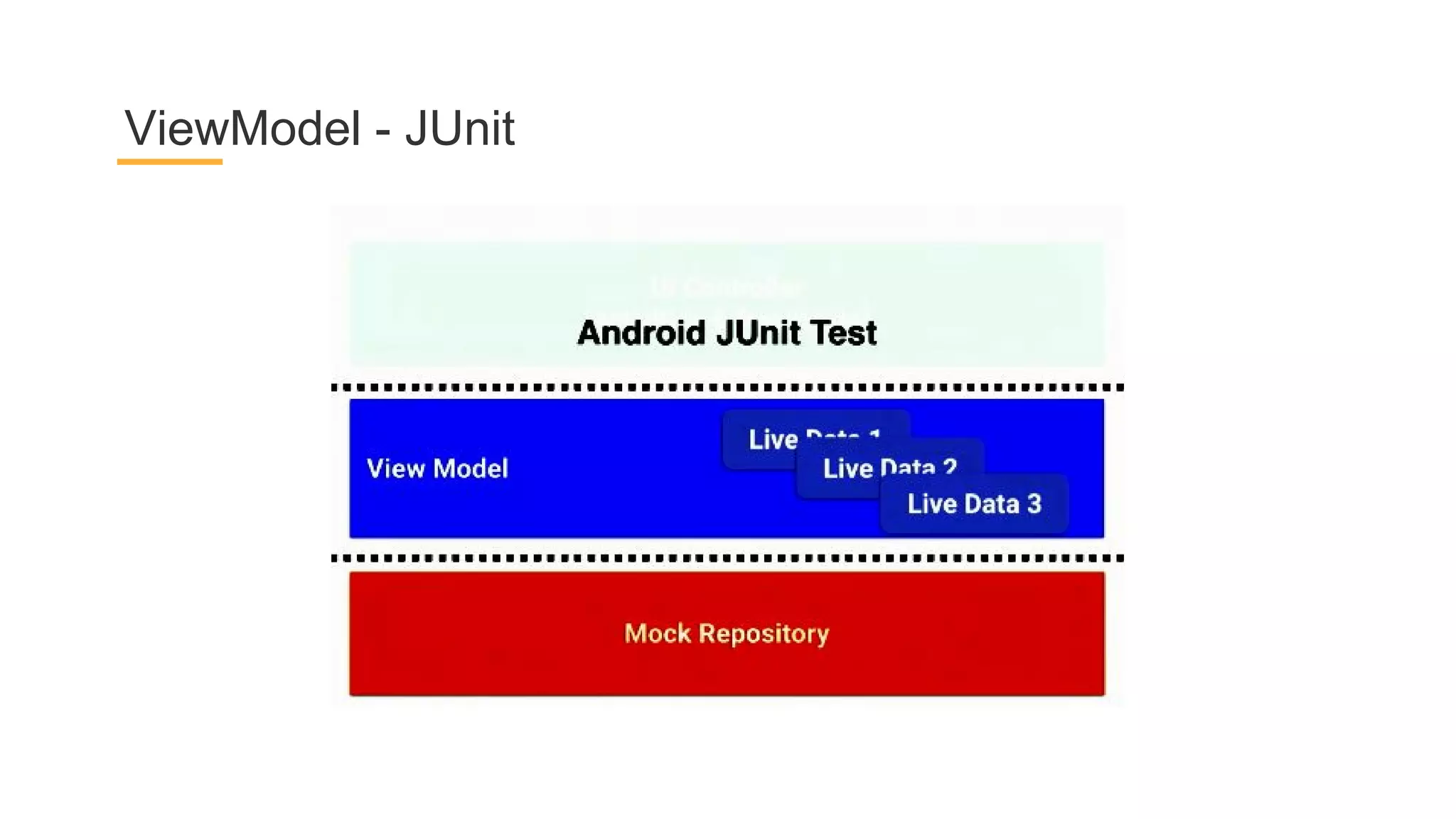
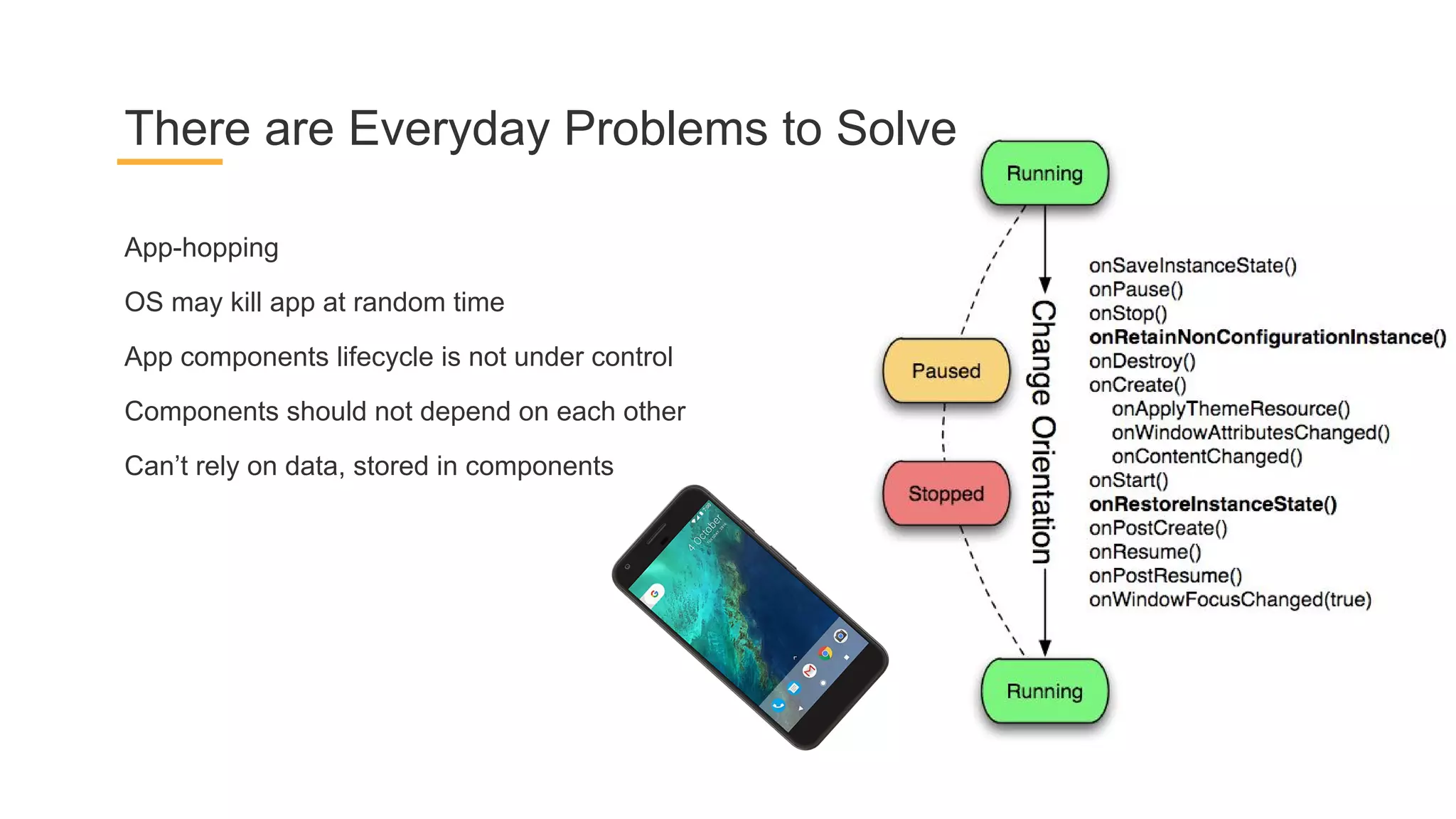
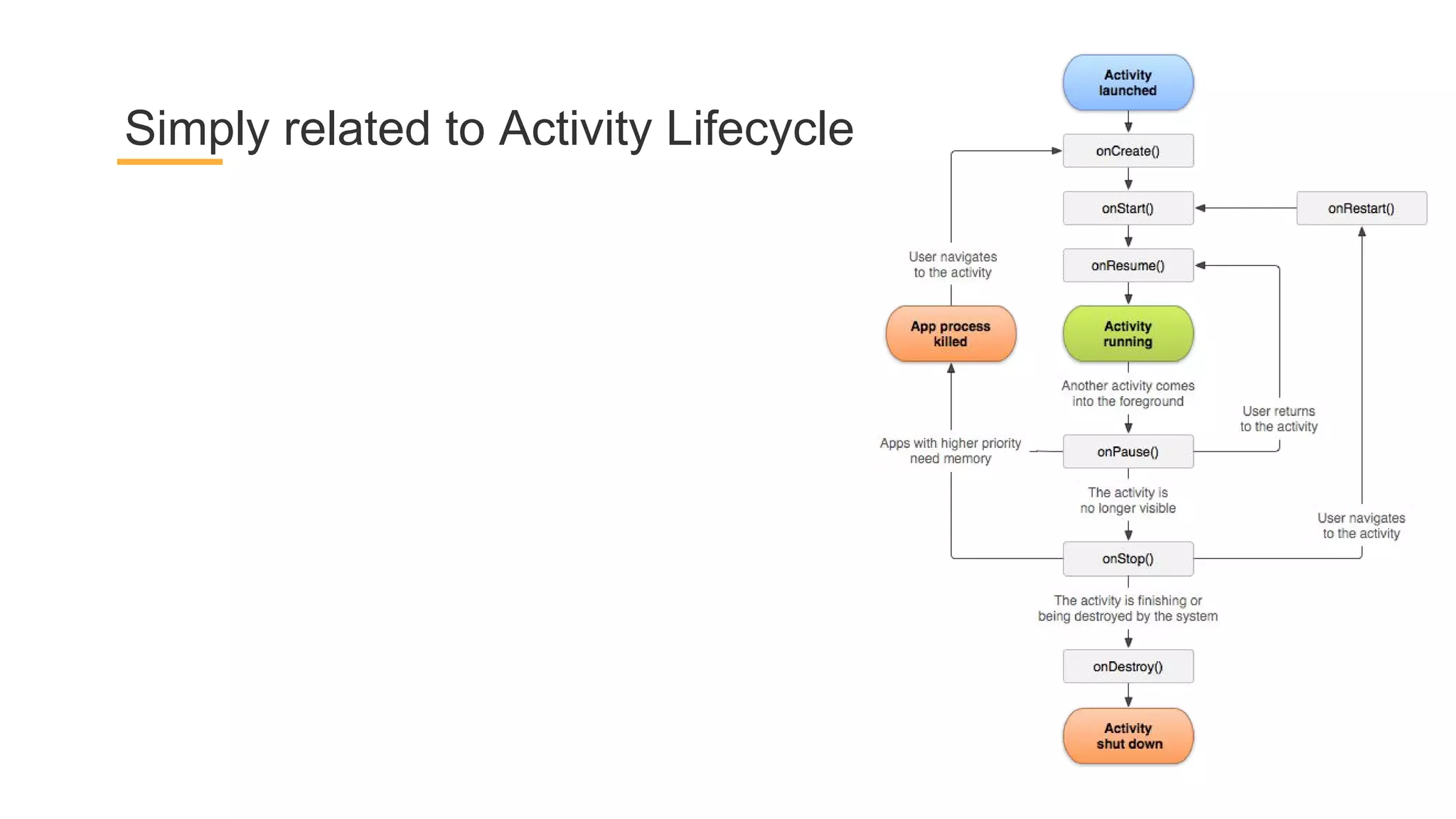
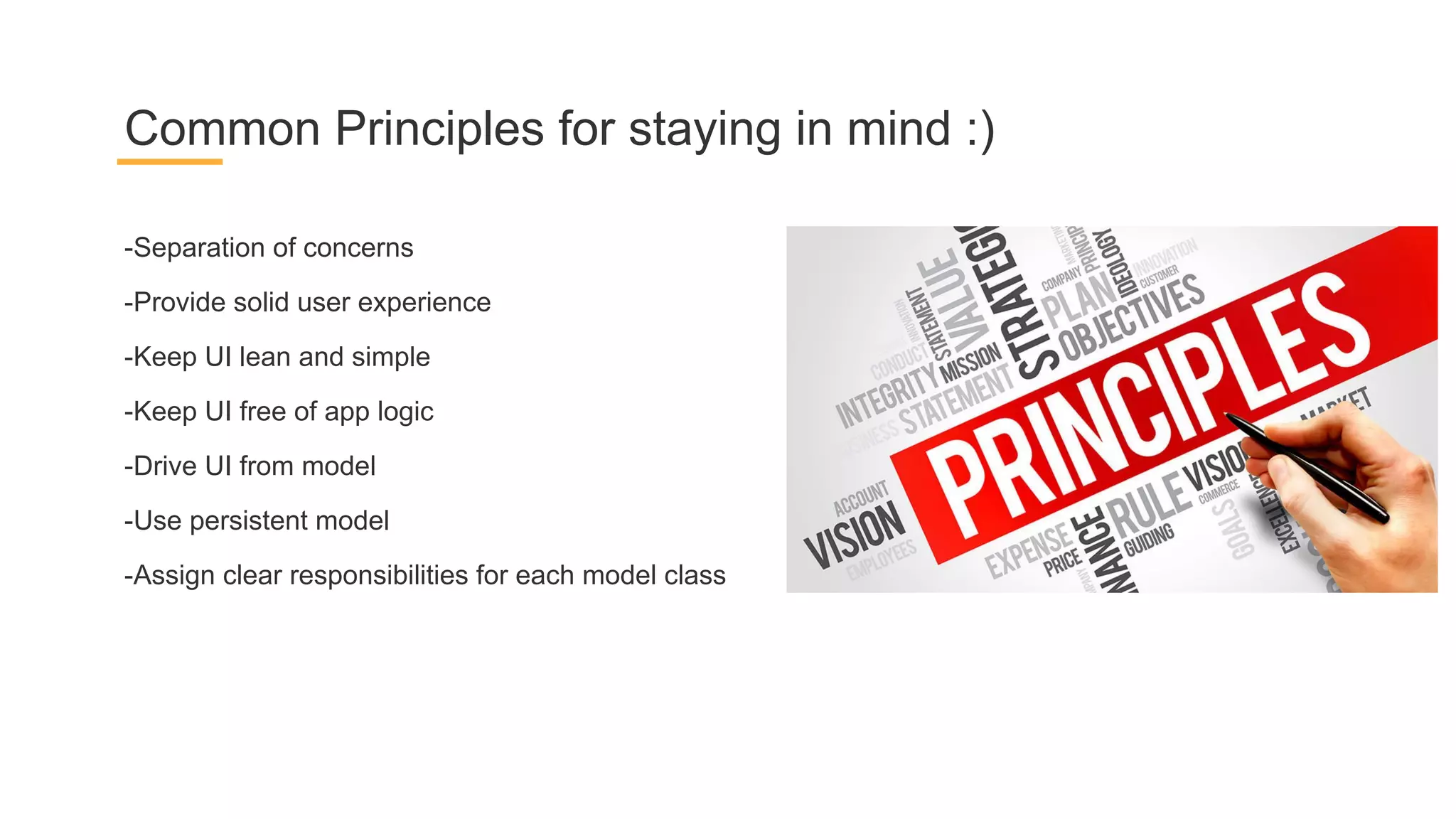
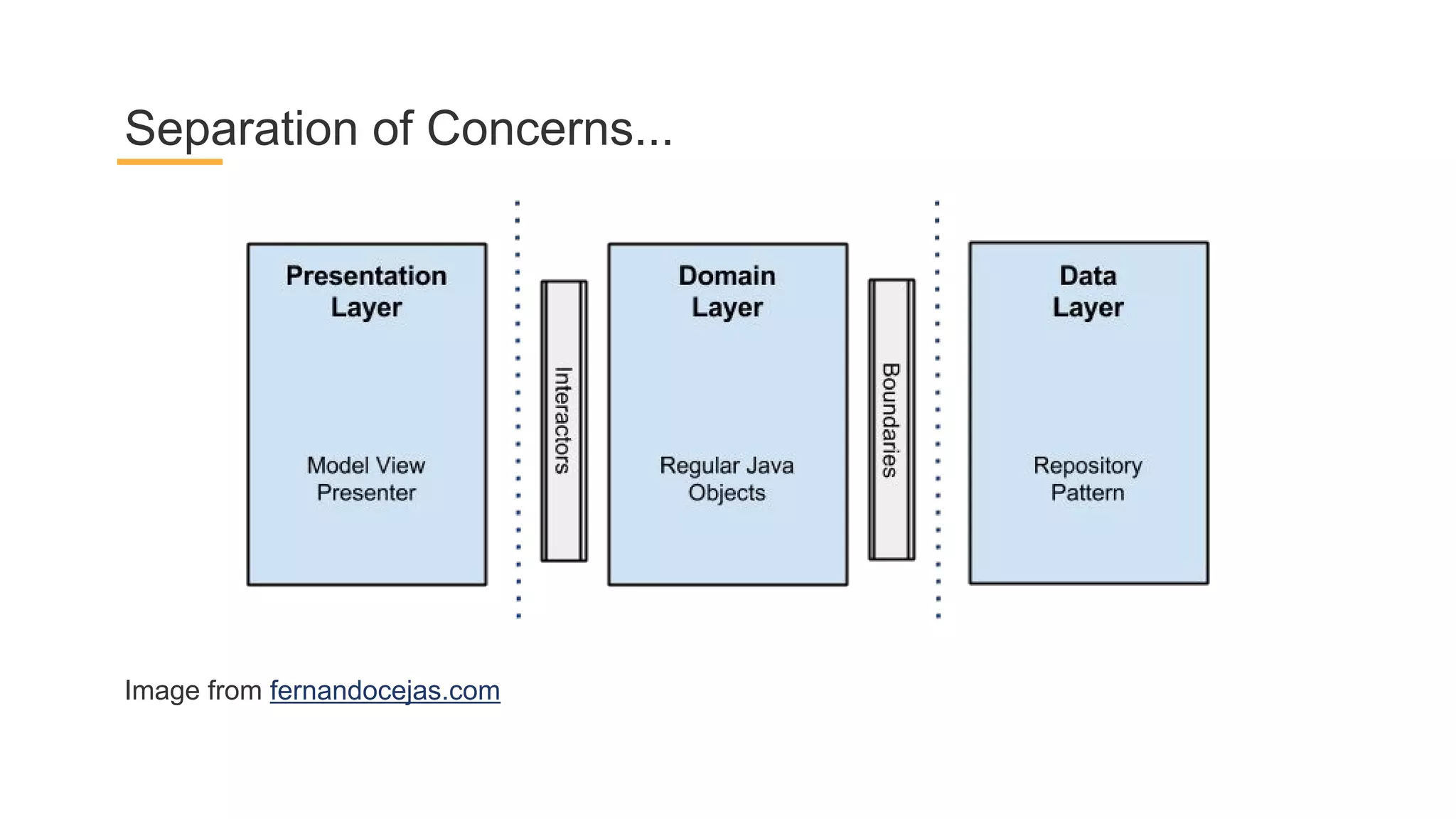
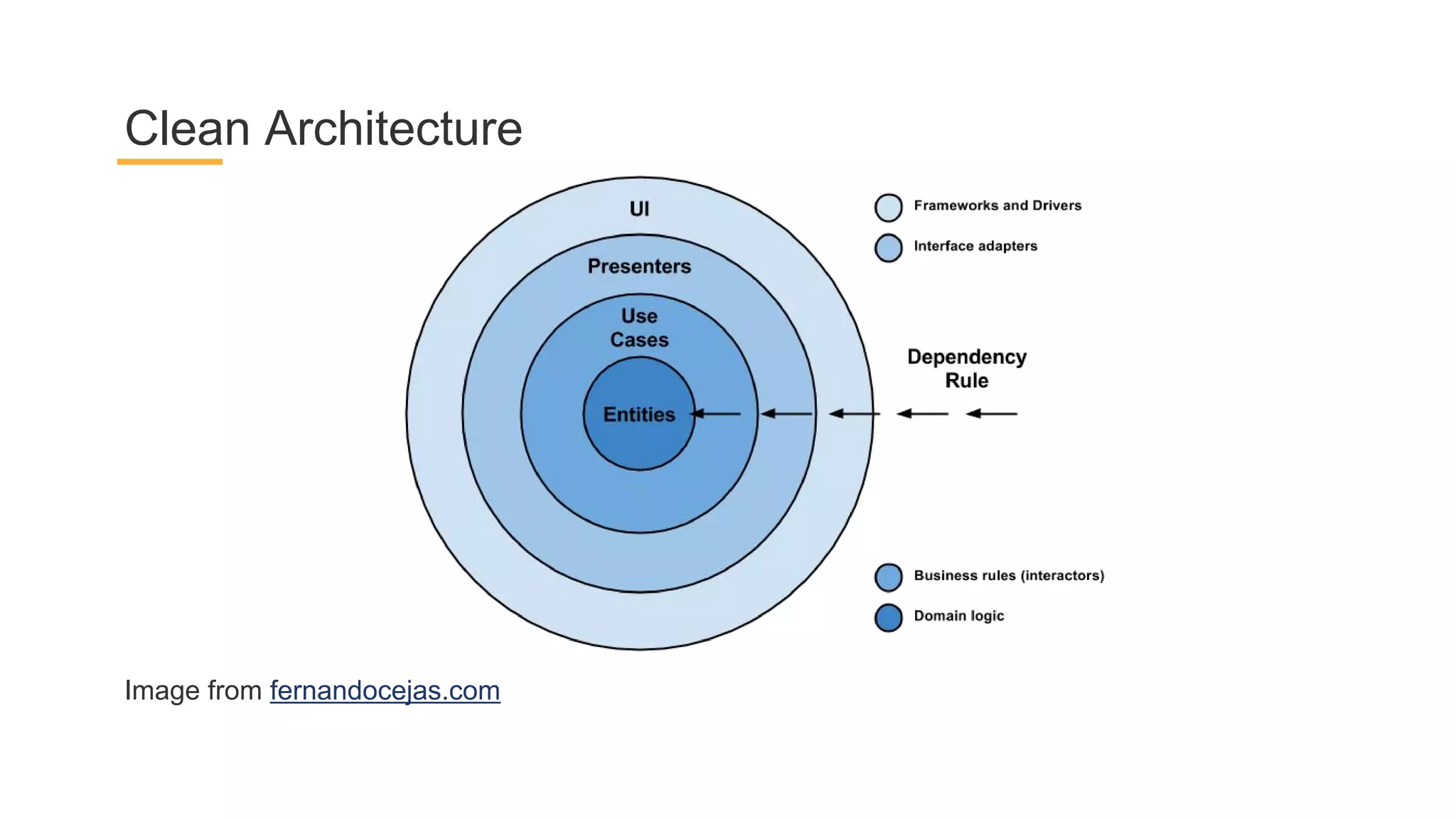
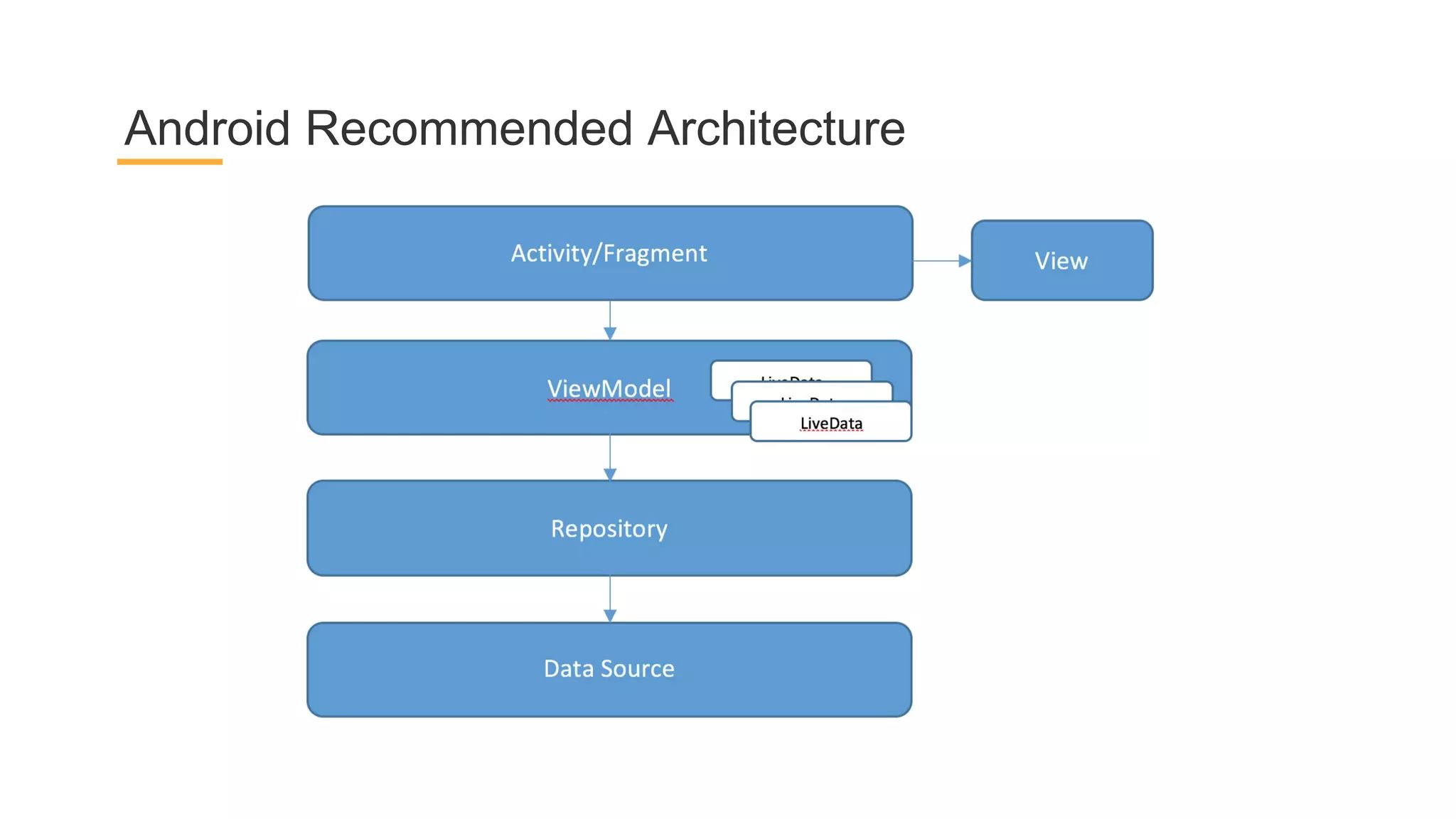
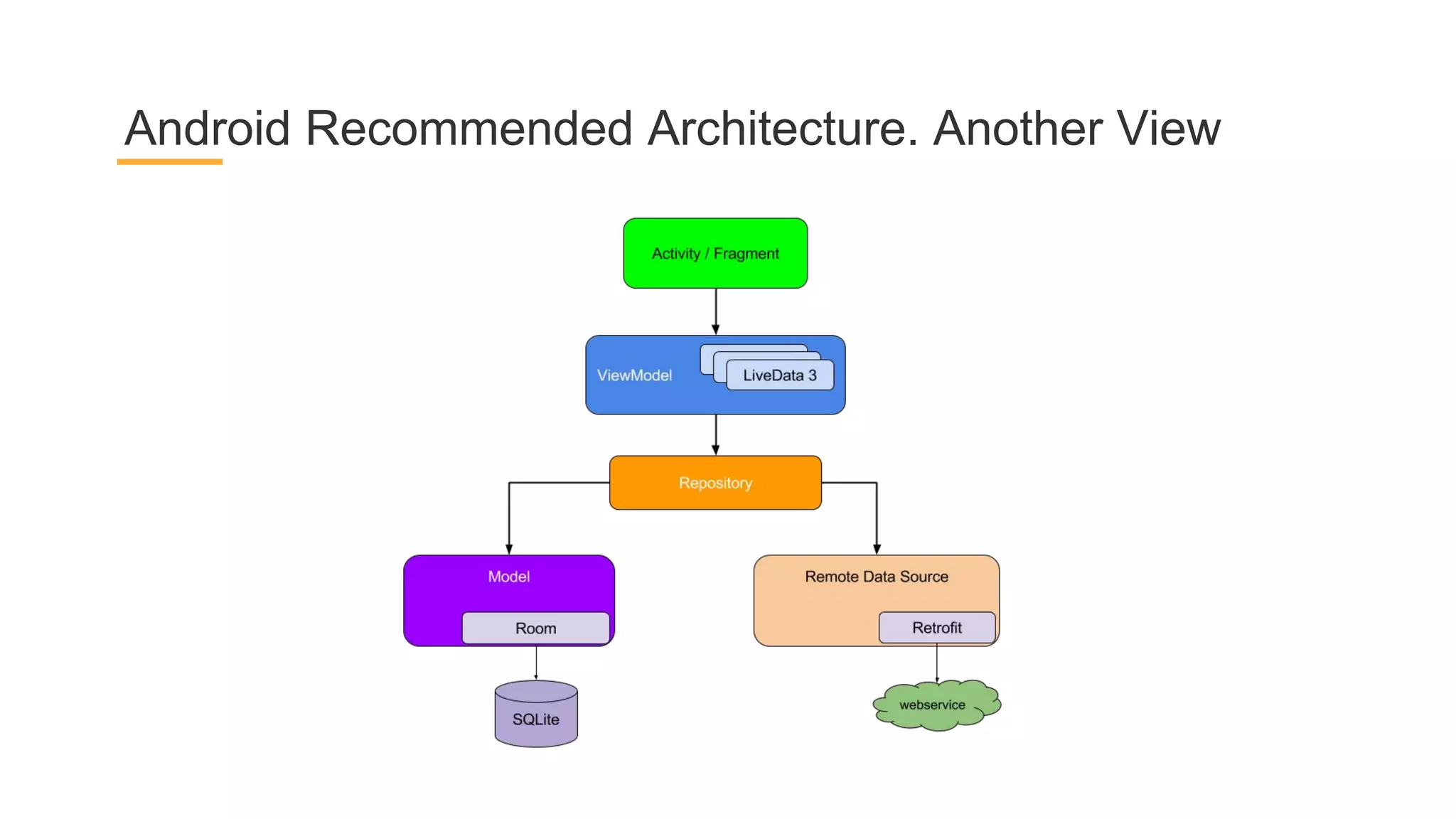
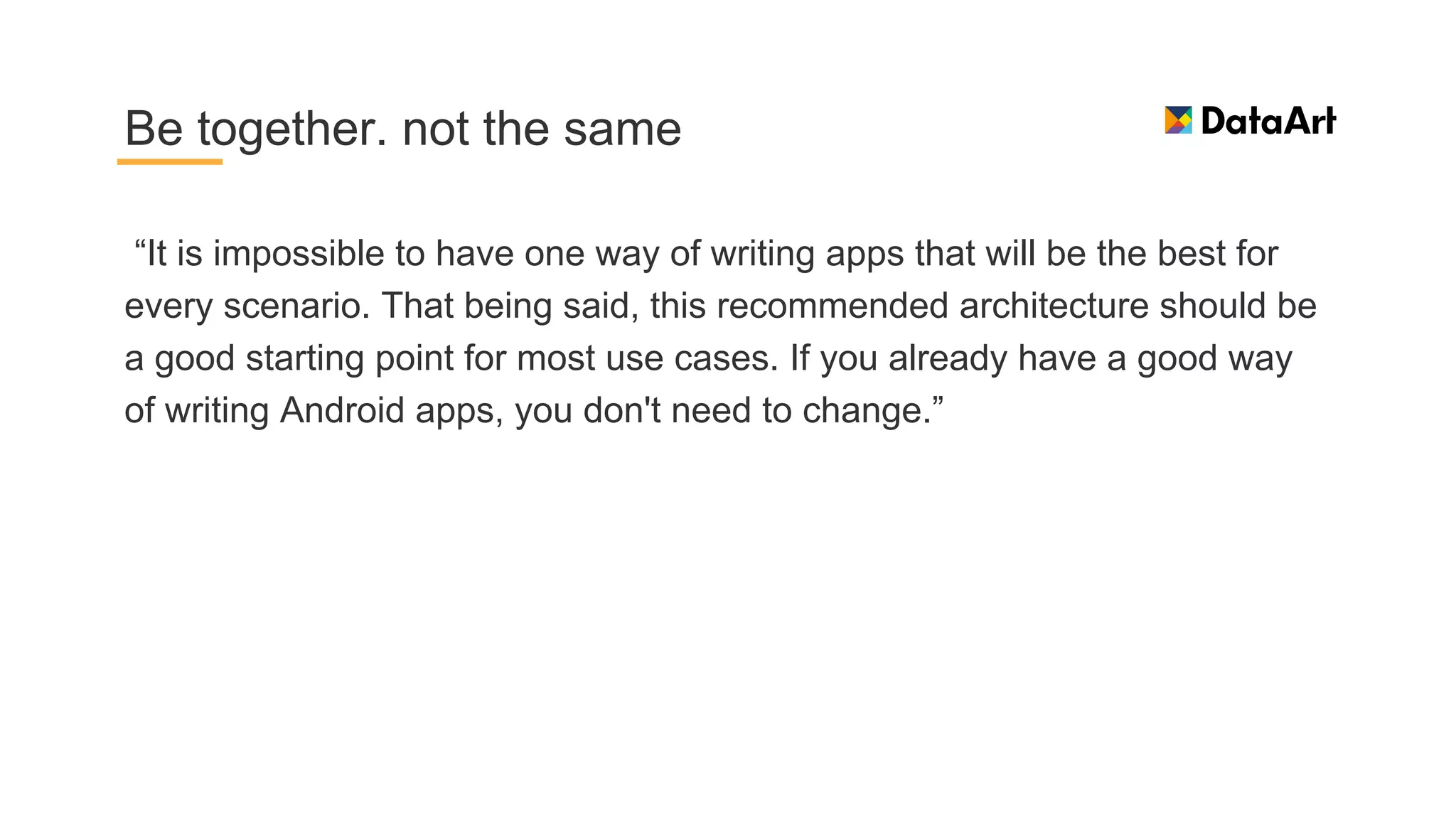
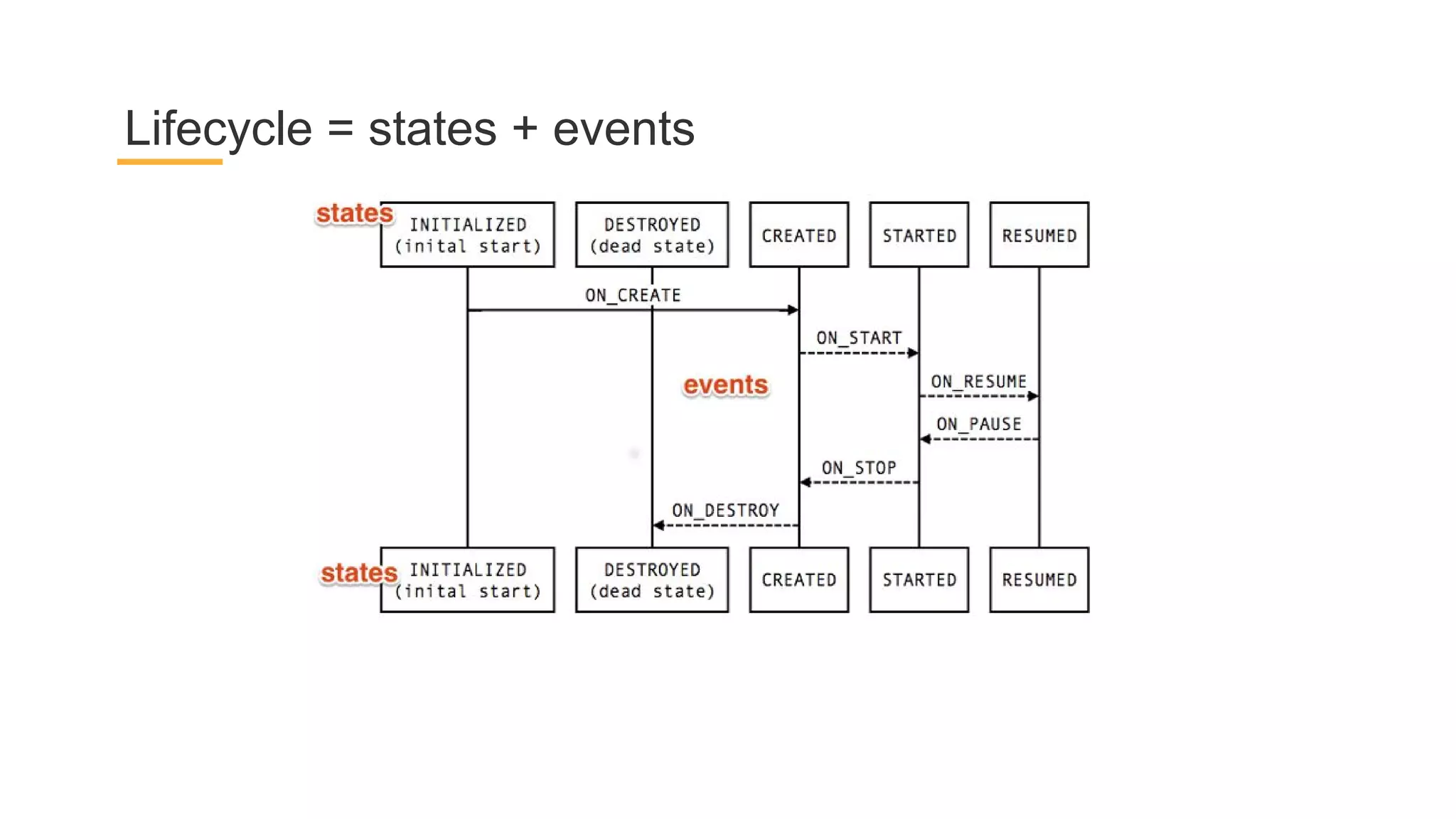
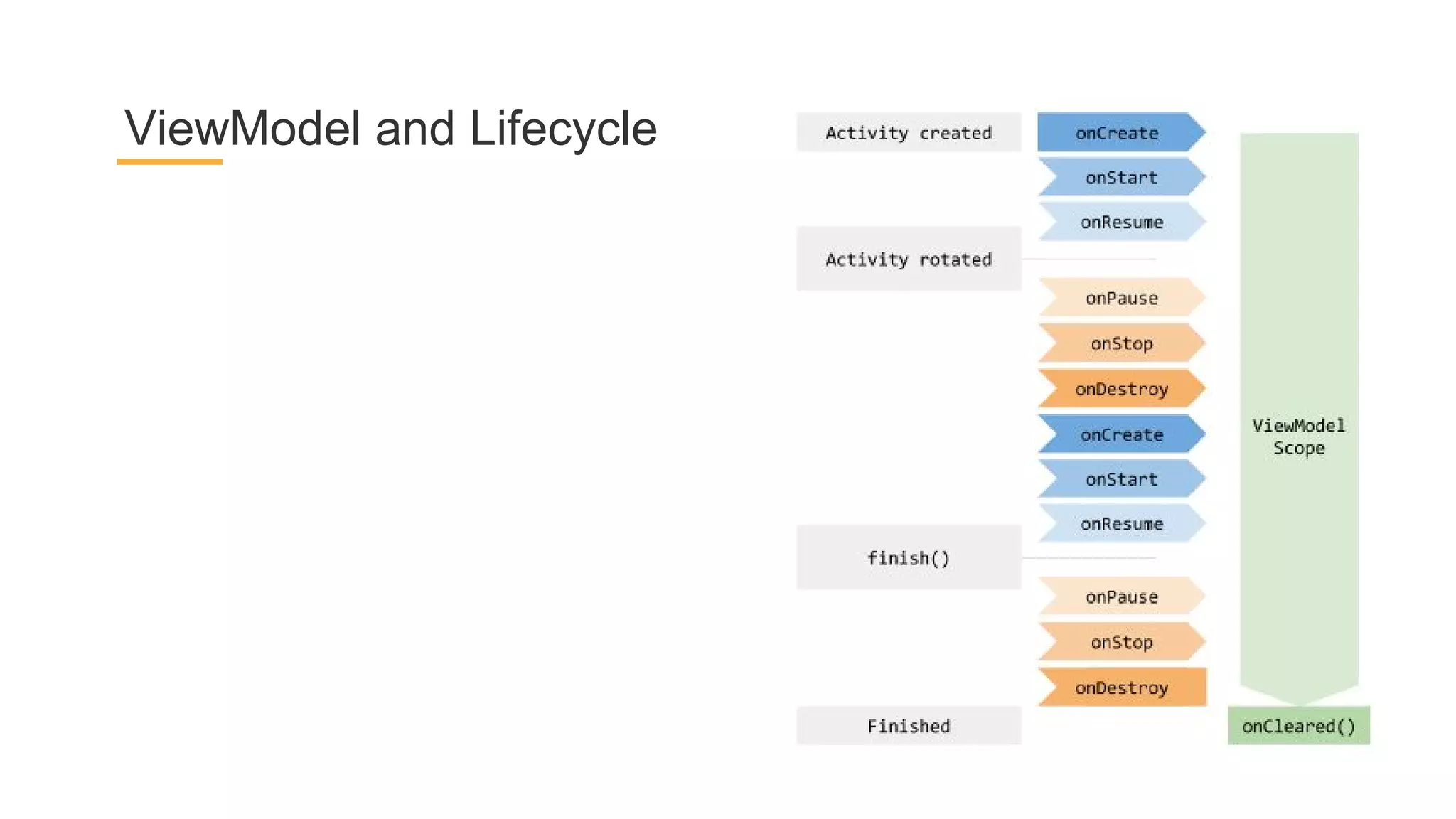
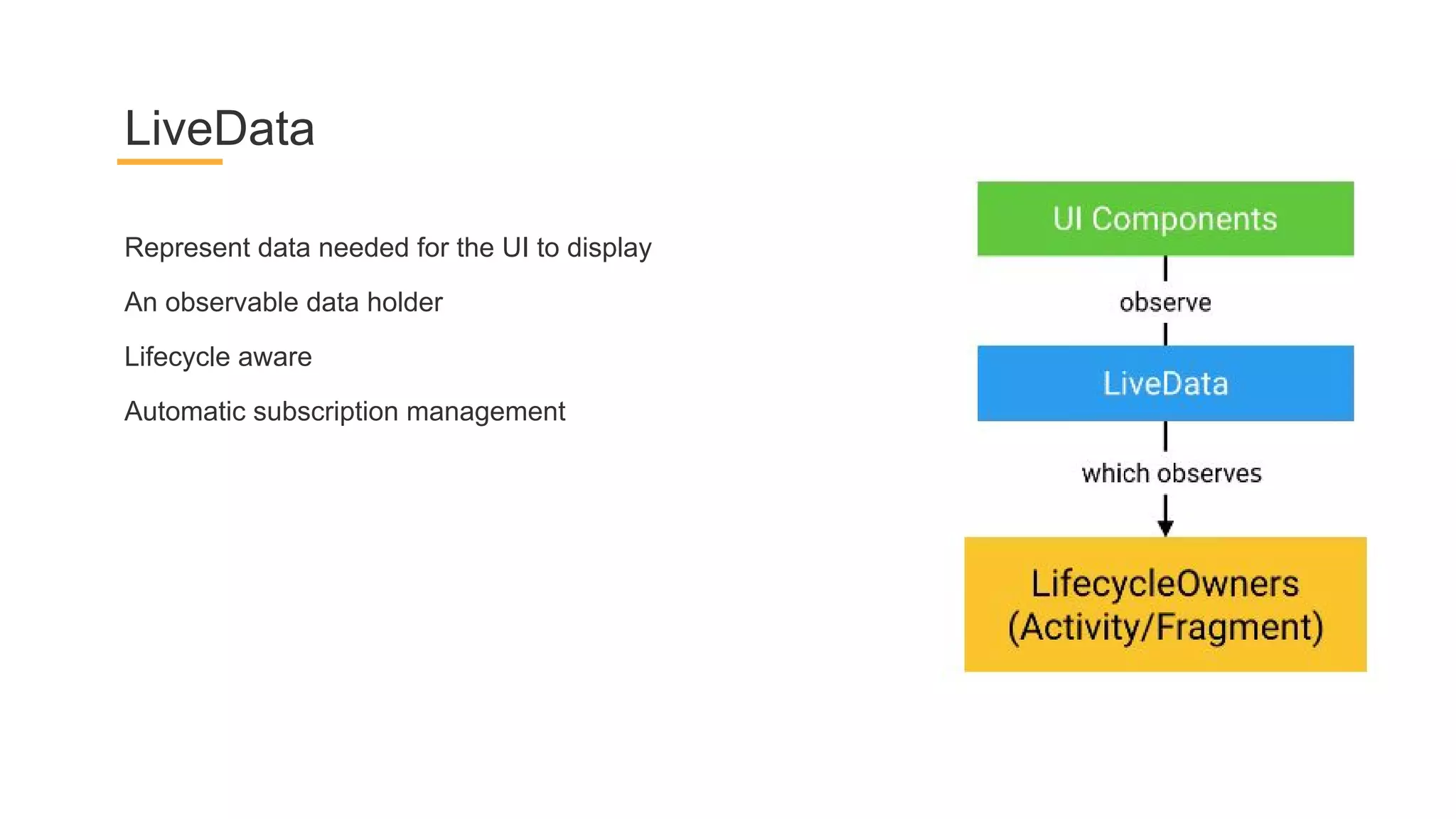
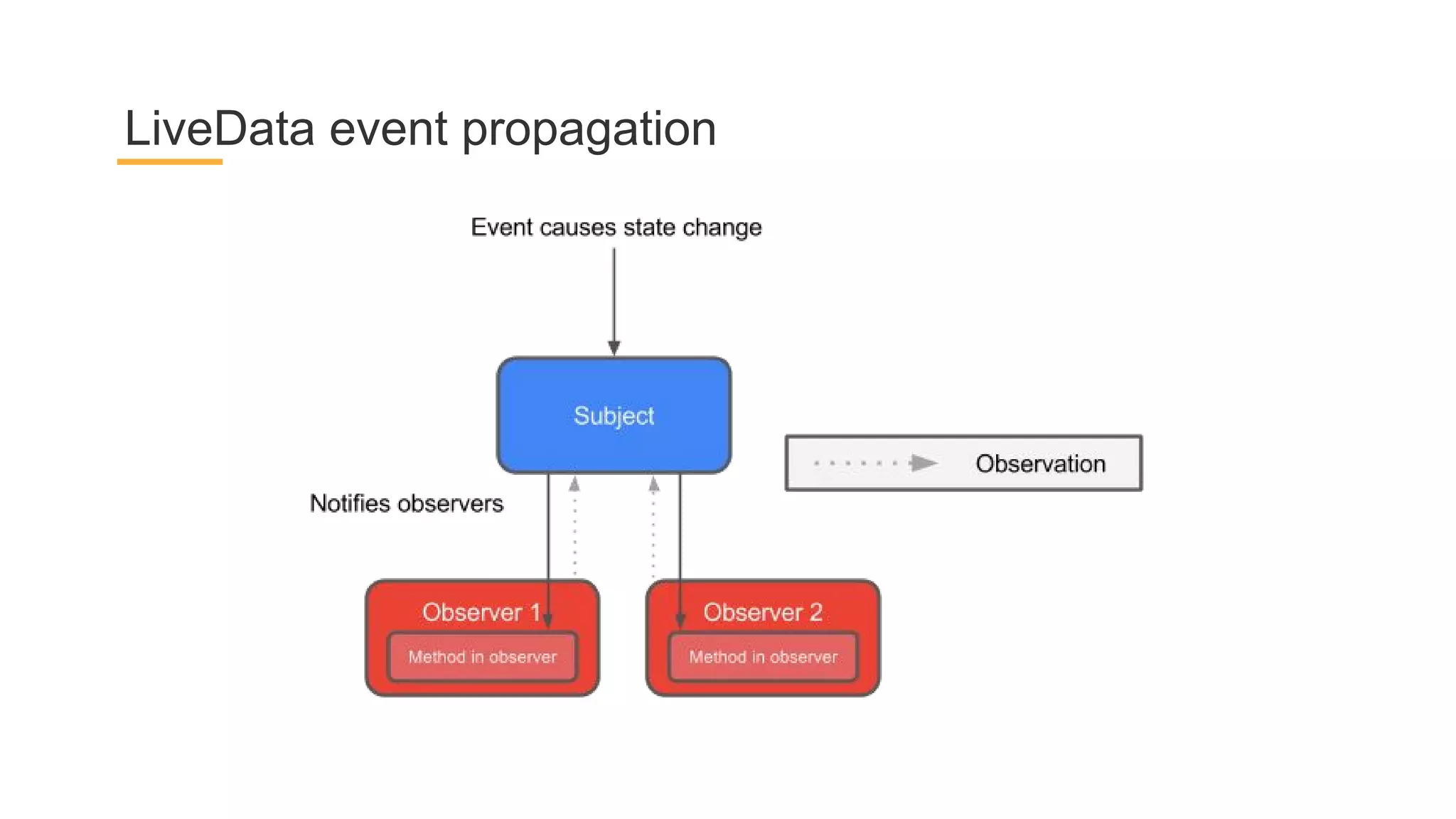
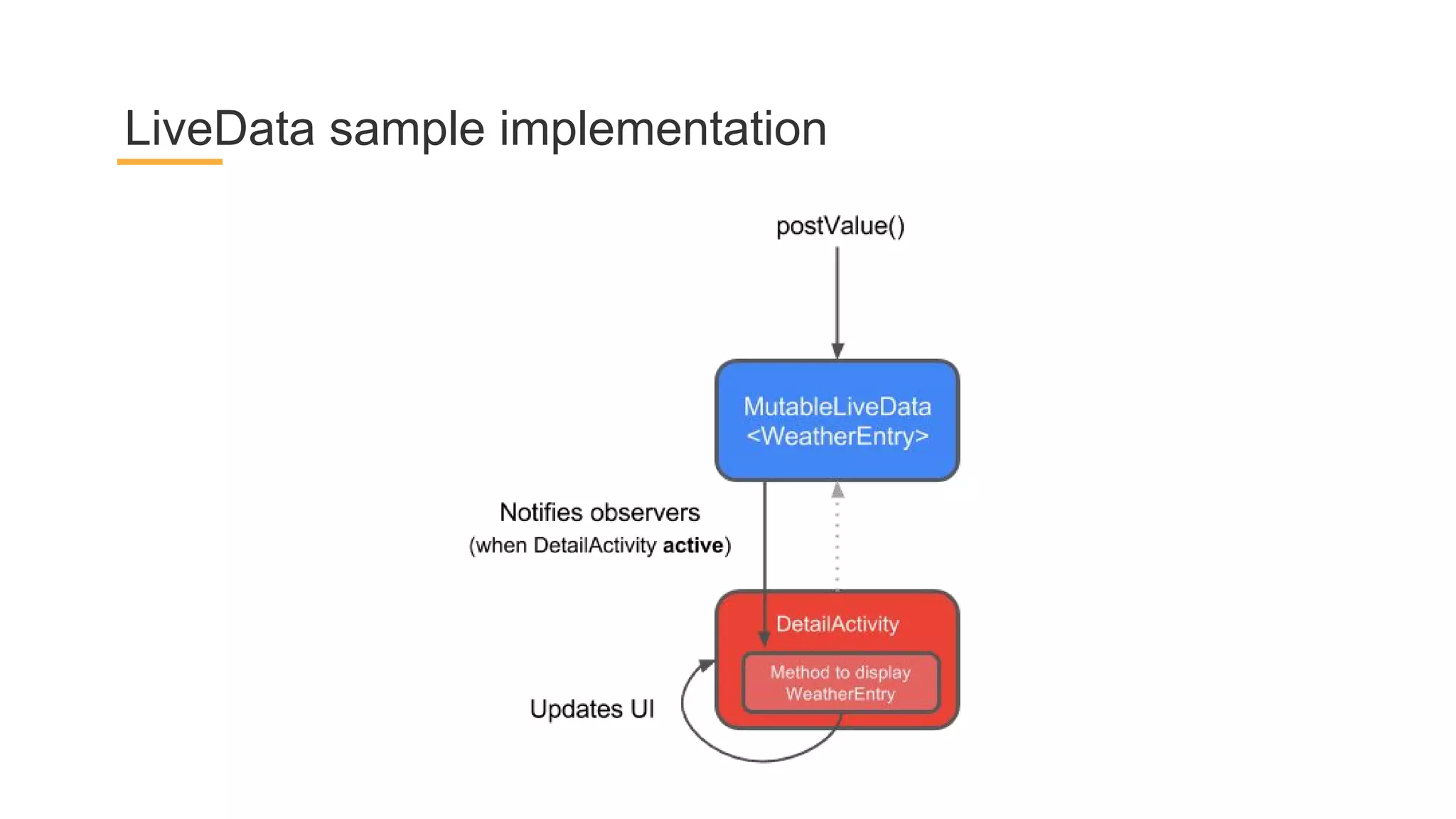
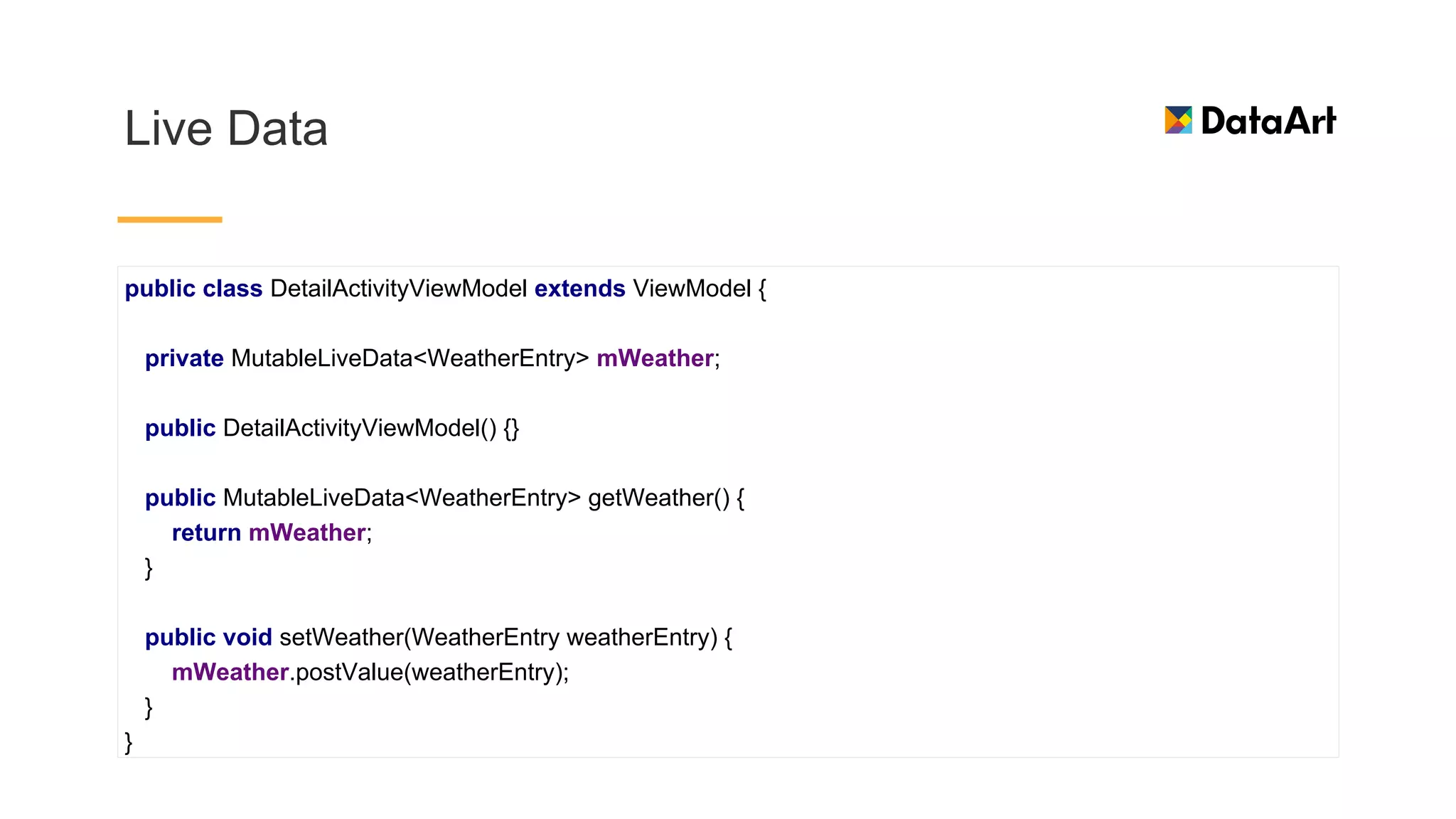
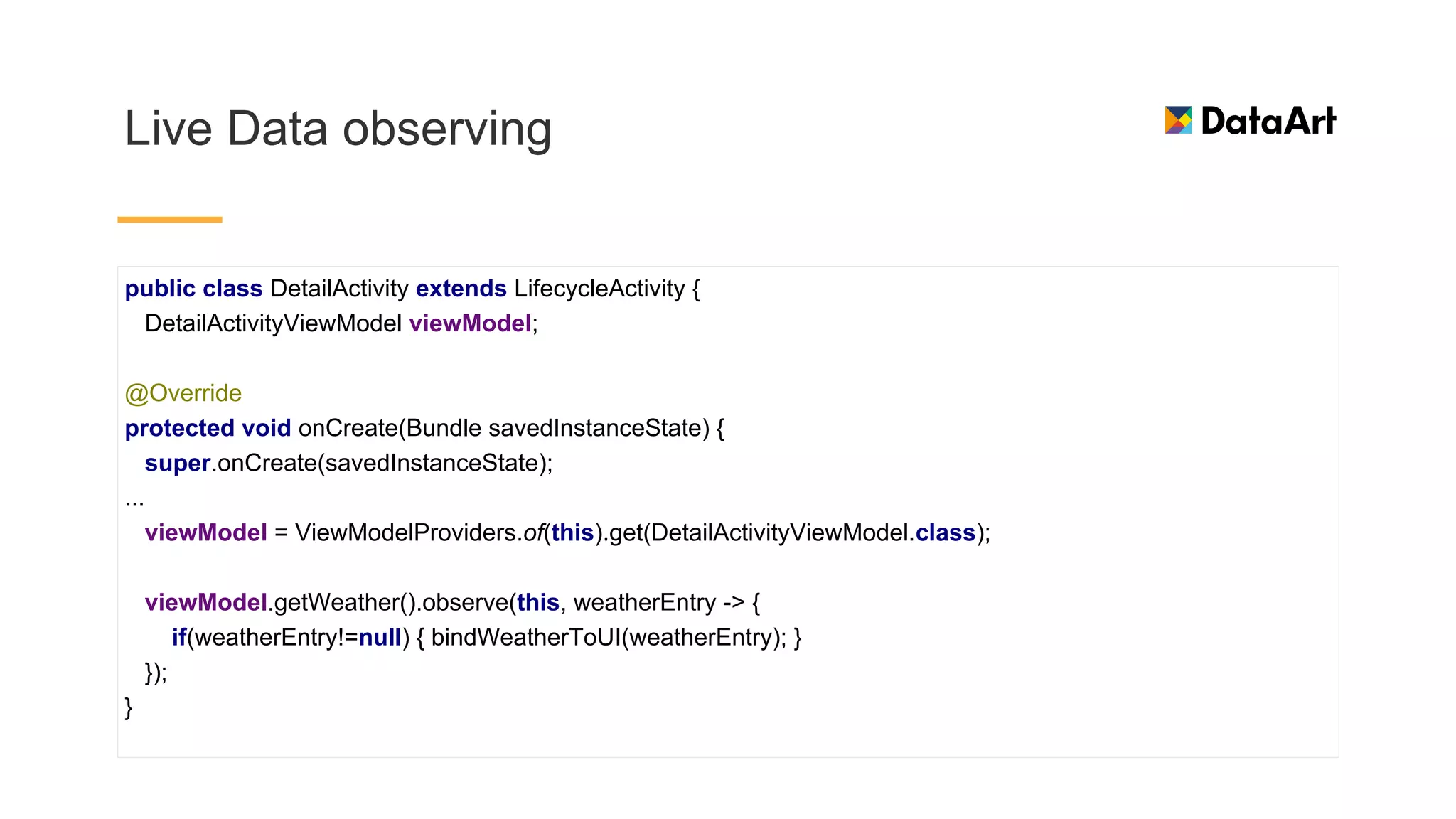
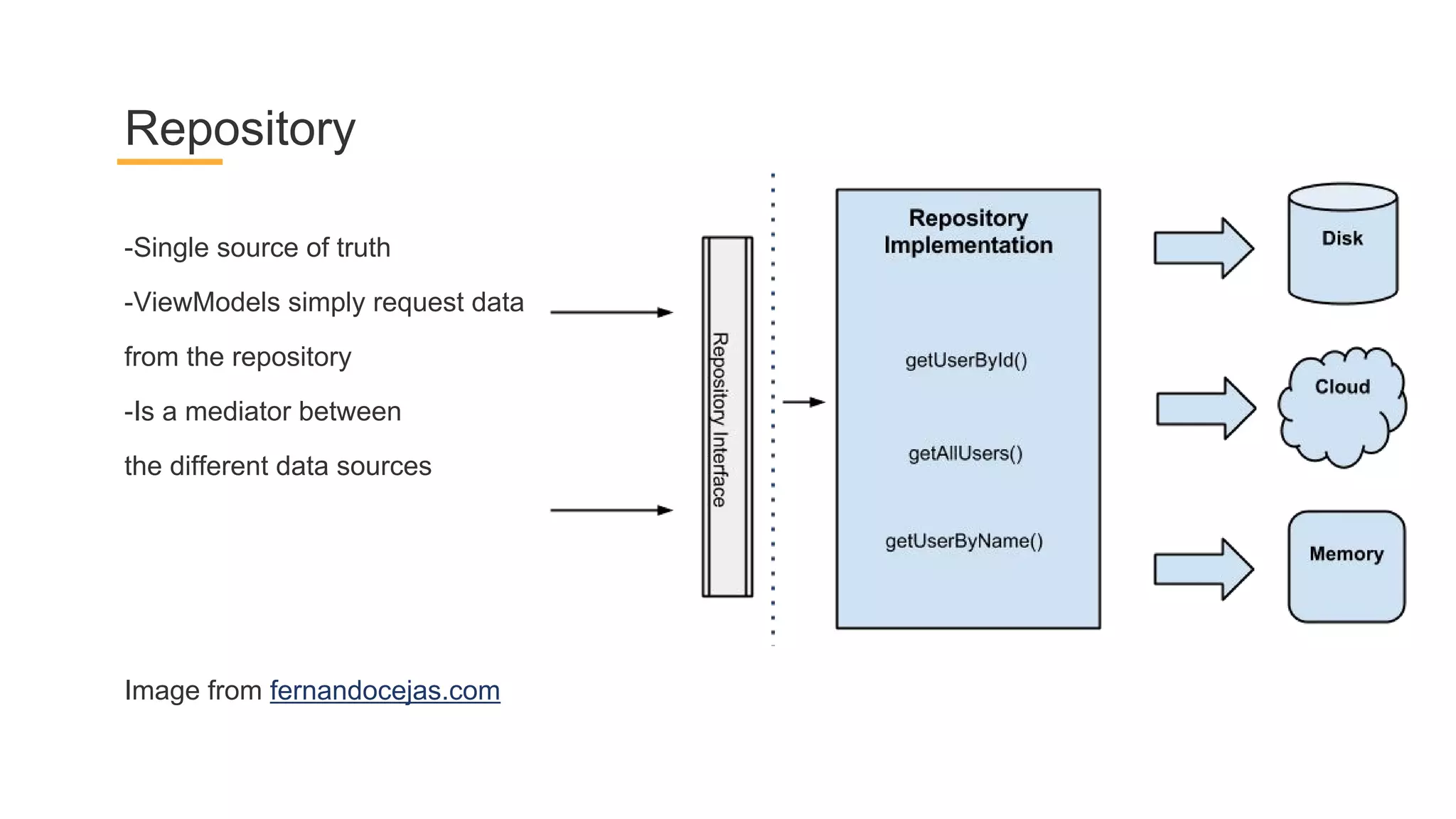
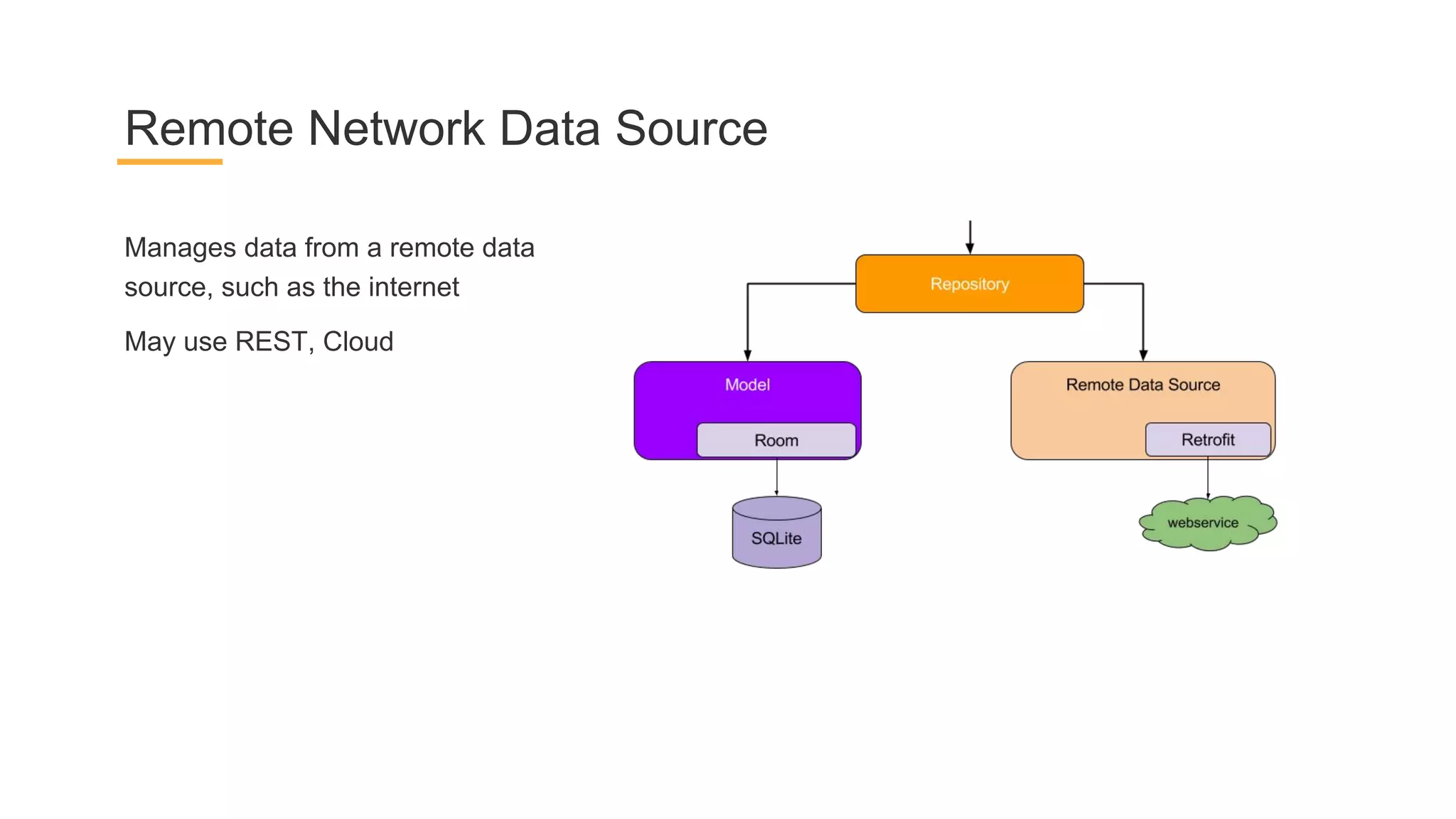
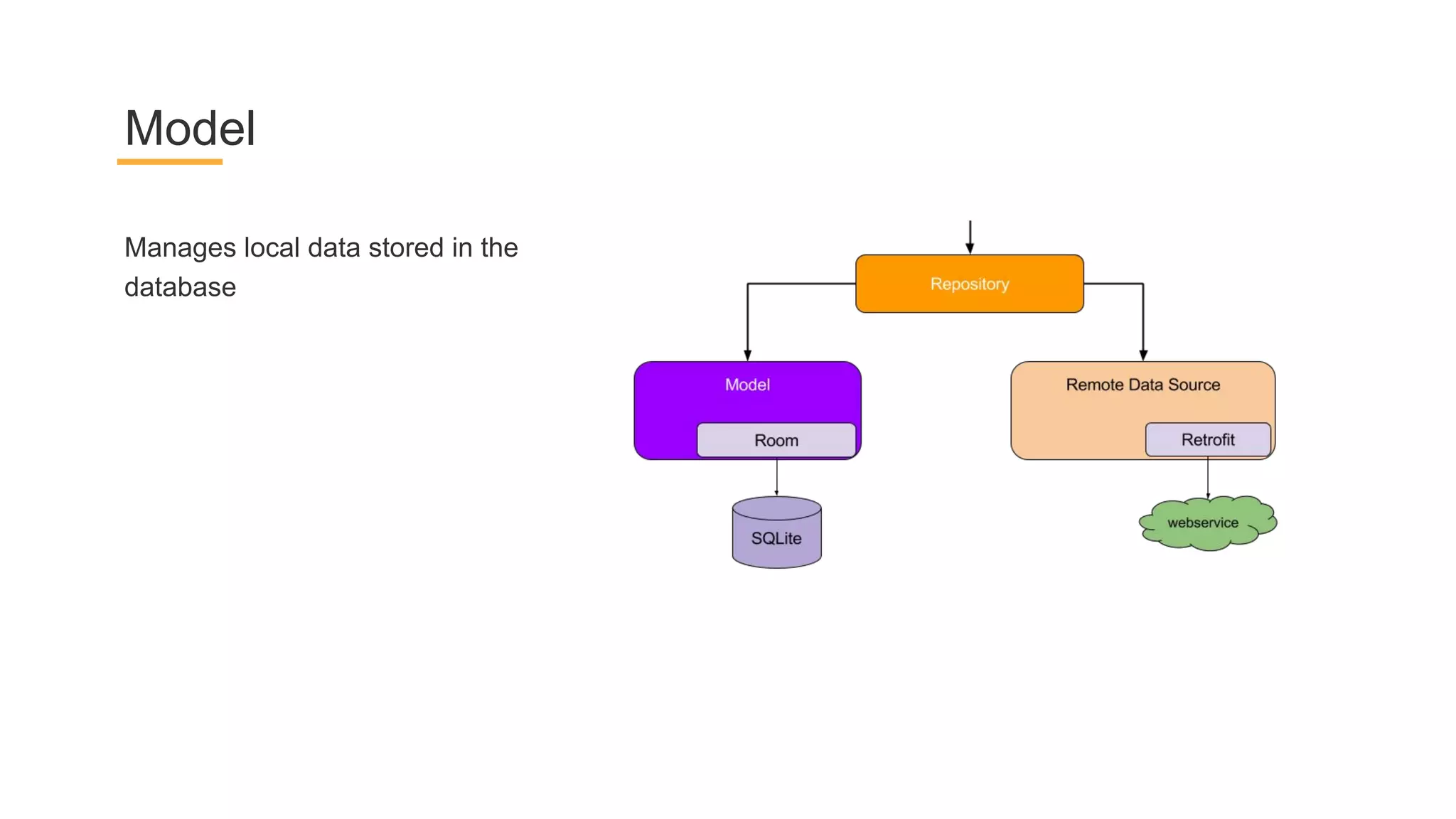
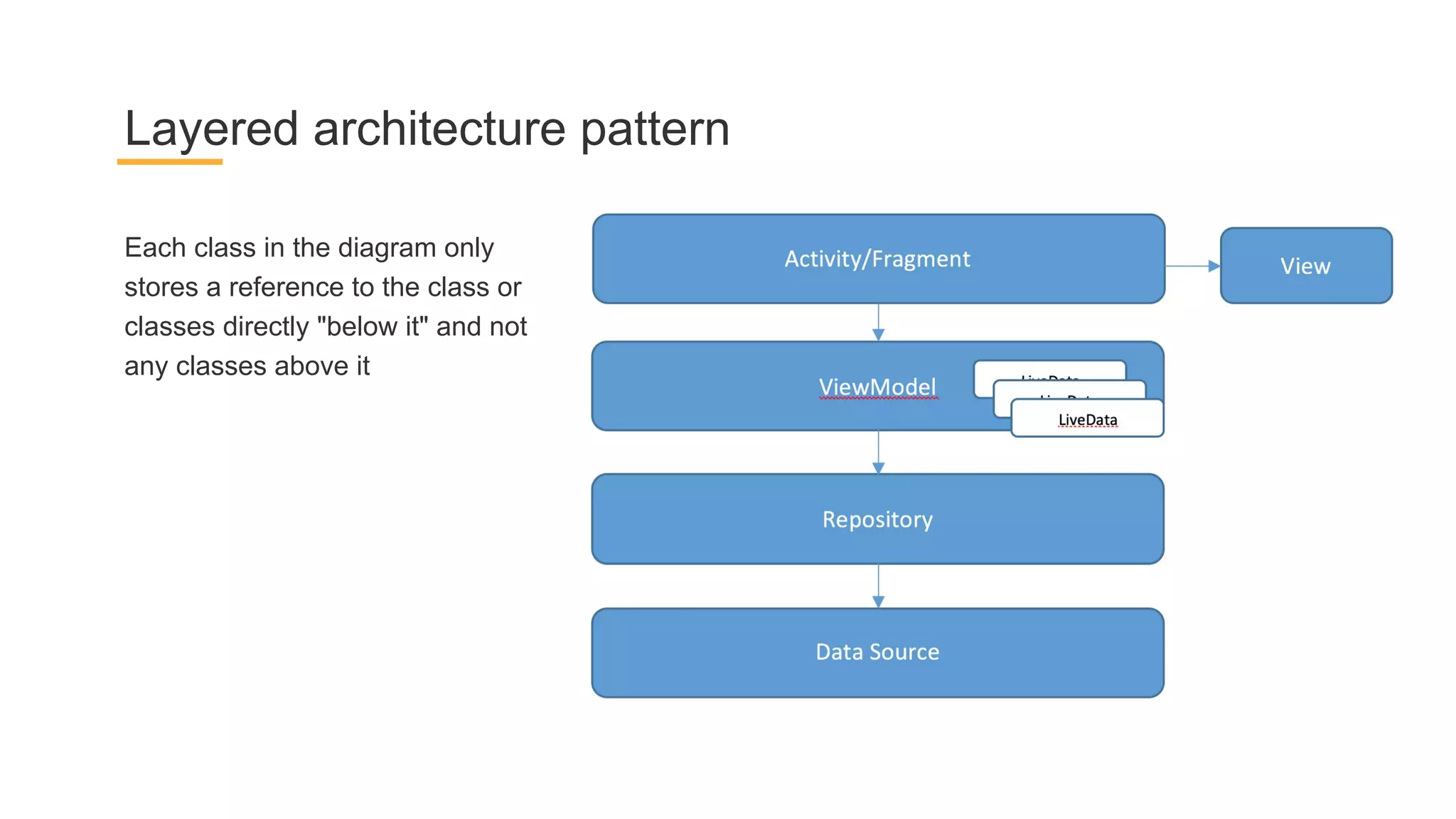
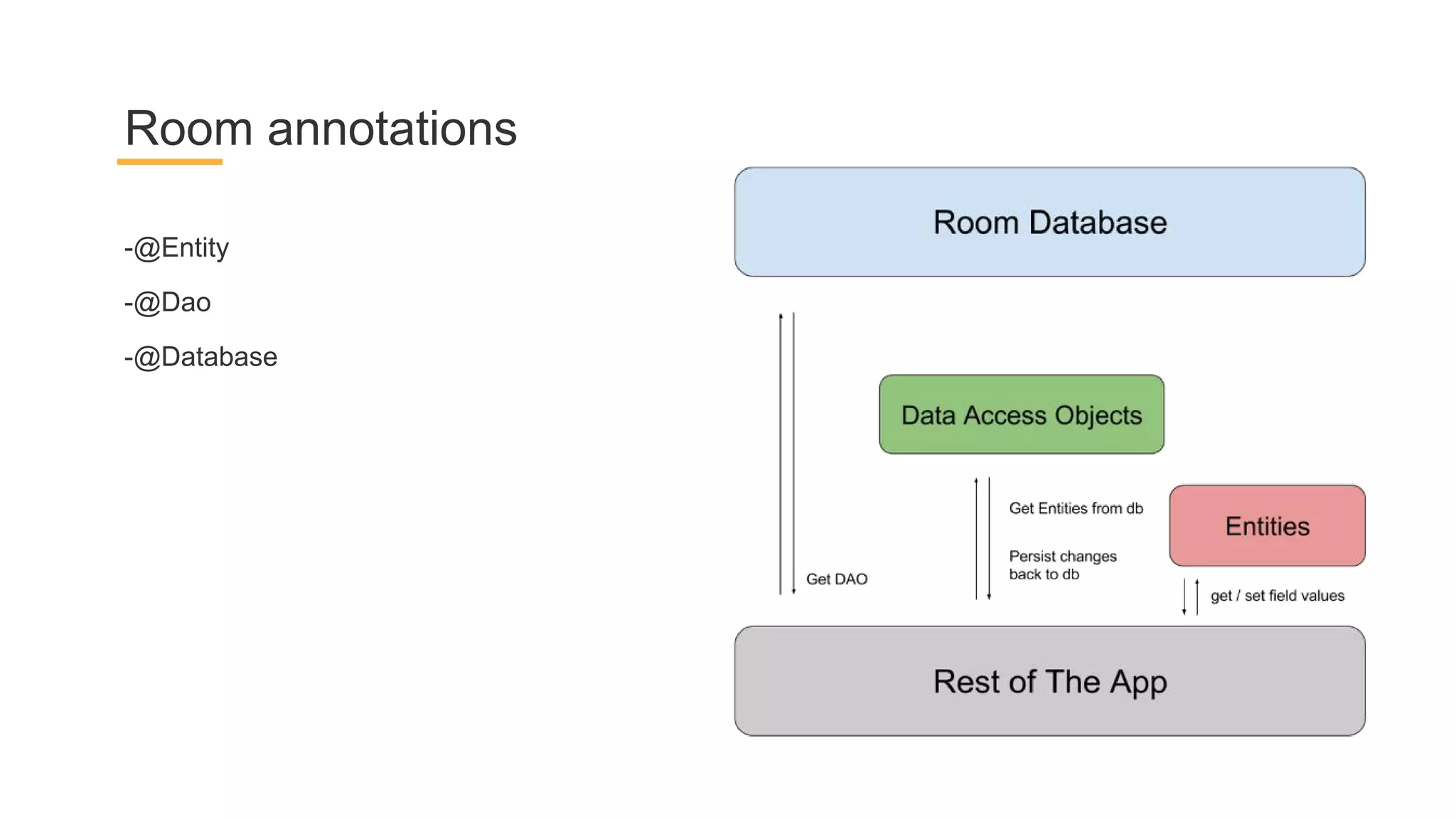
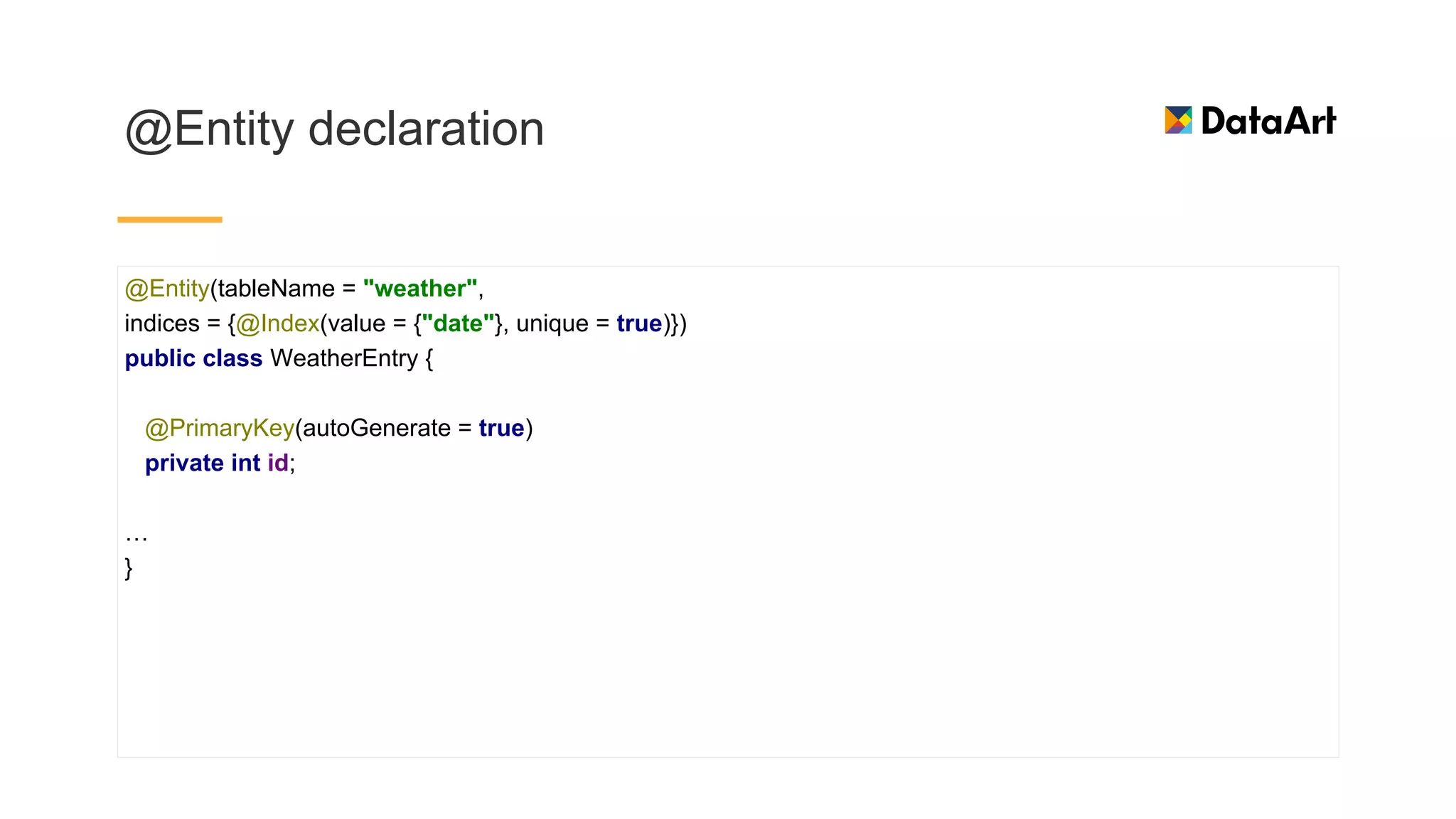
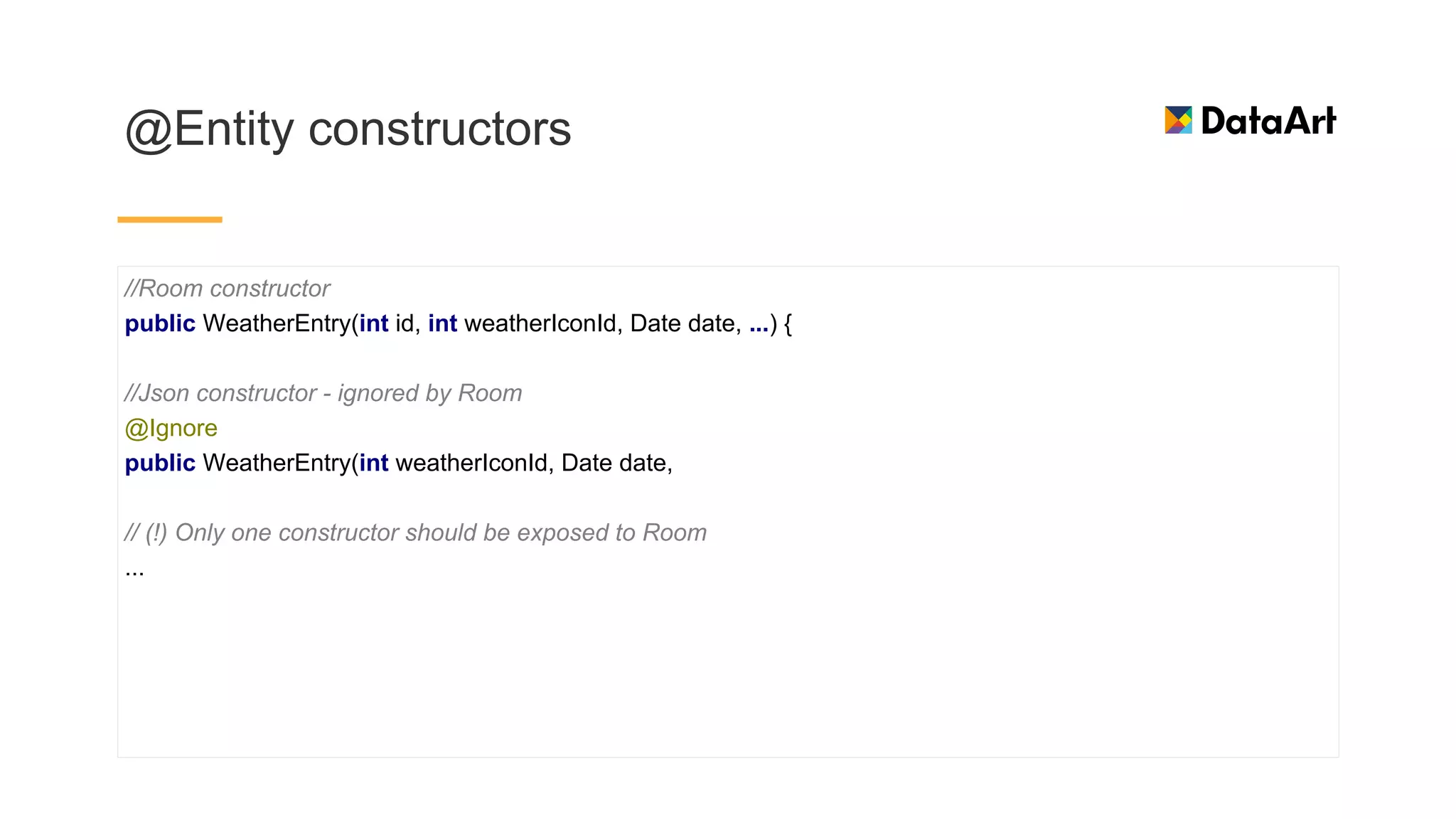
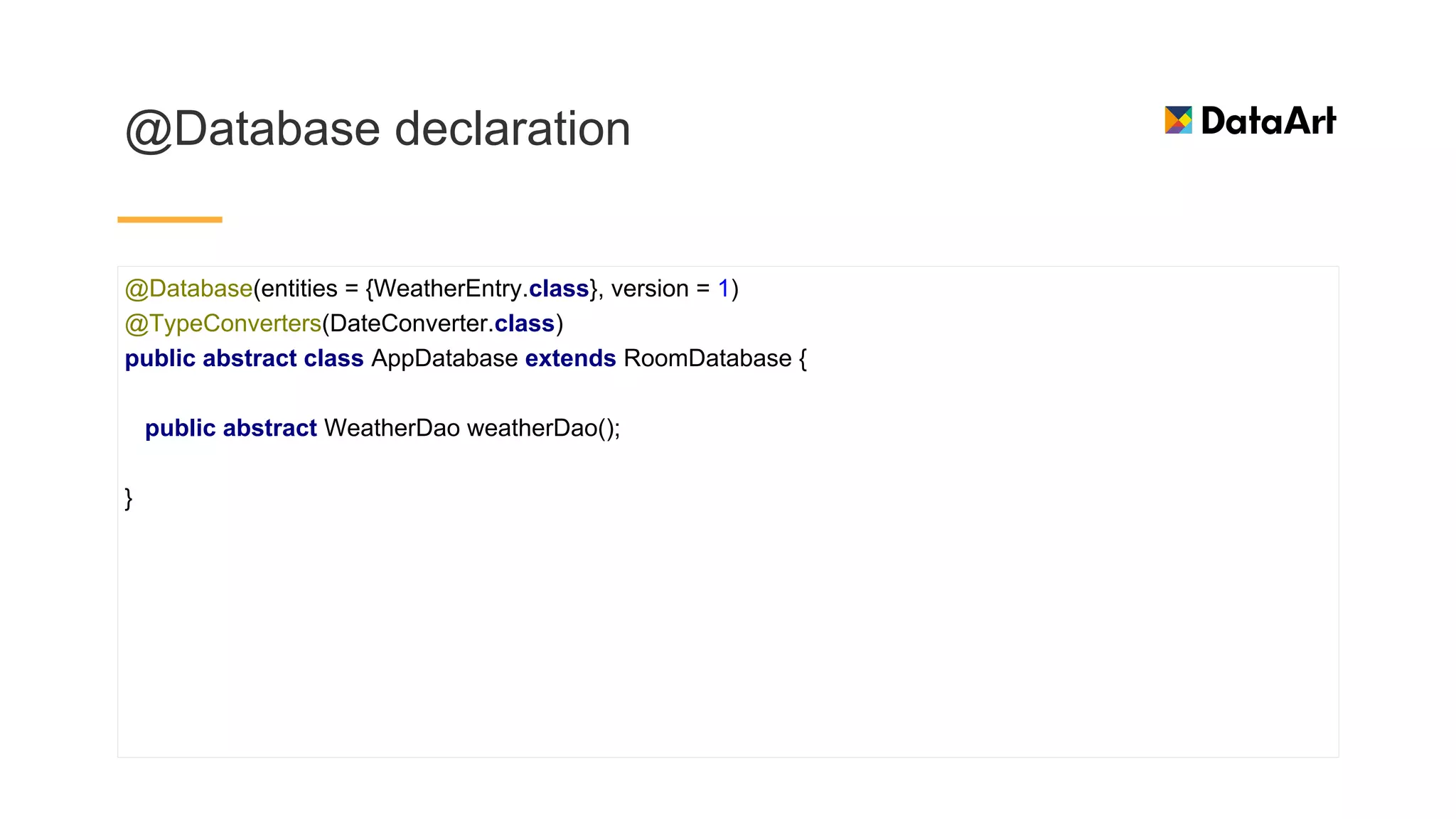
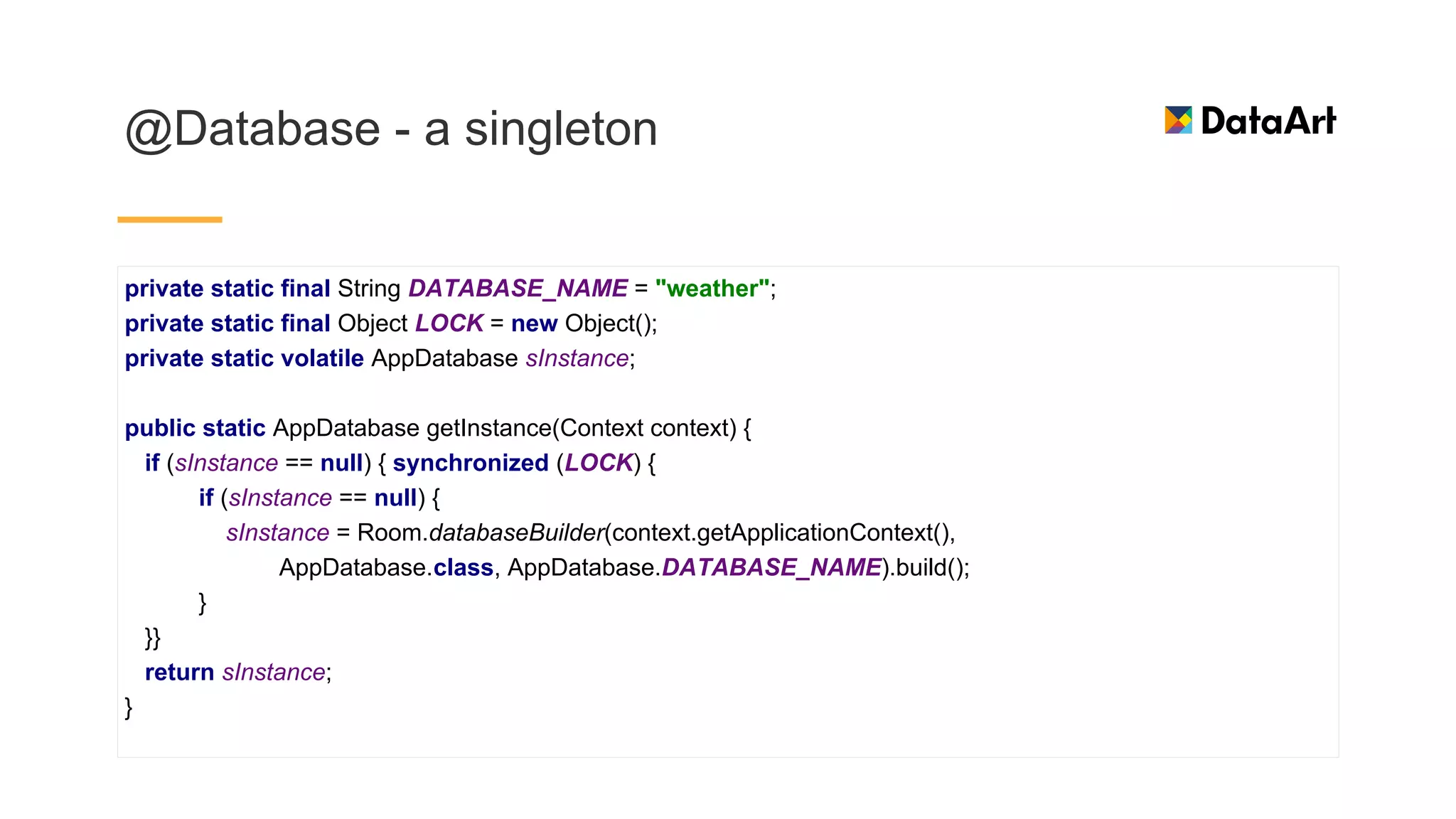
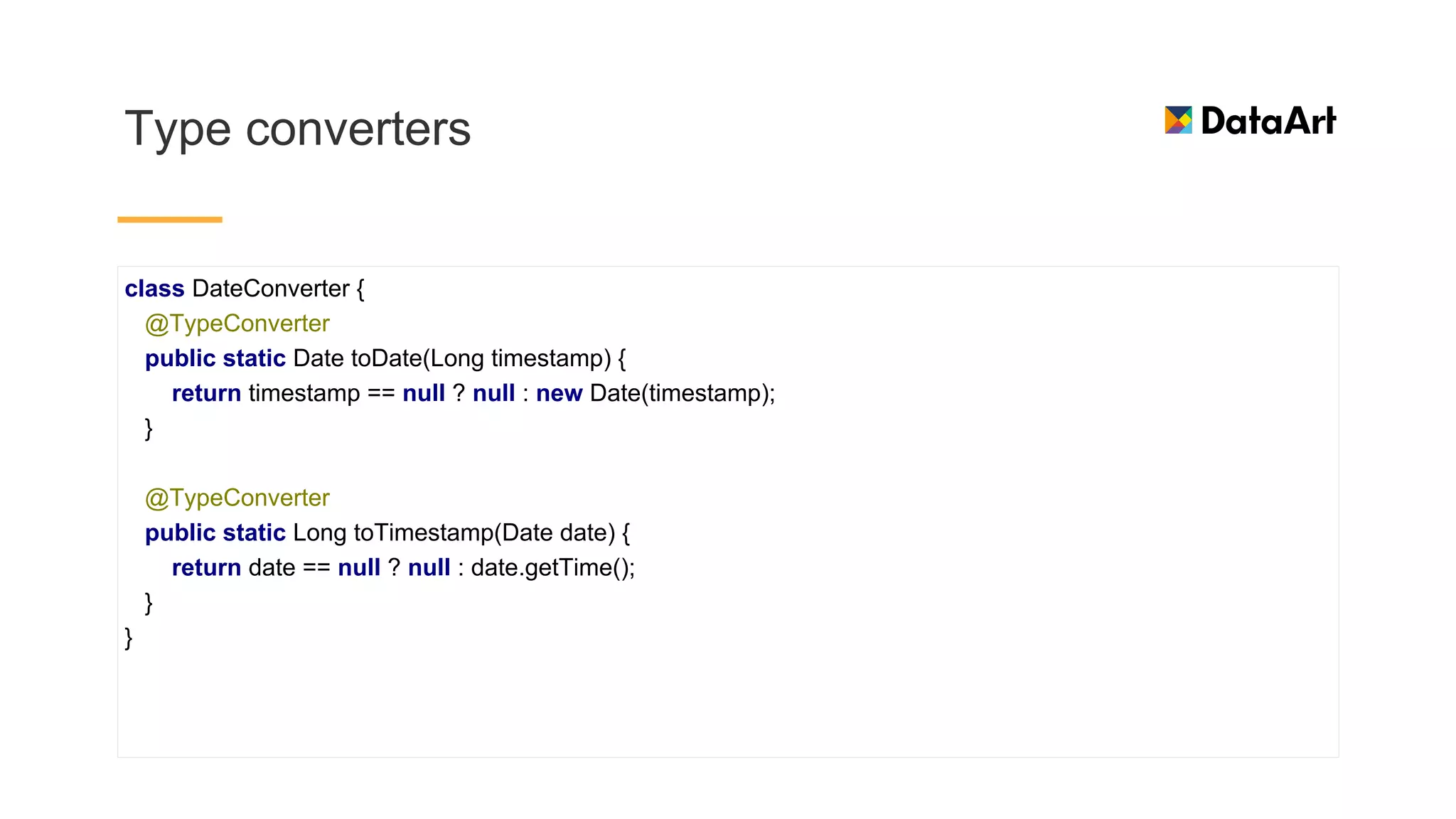
This document discusses architecture components for building modern Android applications. It covers common app architecture problems and principles like separation of concerns. It introduces key Architecture Components like Activities, Fragments, Services, ContentProviders, ViewModels and LiveData. It also discusses architectural patterns like MVC, MVP, MVVM and recommendations like clean architecture. The document emphasizes principles like modularity, separation of concerns, and testability. It provides an overview of alternatives like Room, Paging Library, and recommendations for legacy apps.
















![Repository - fetch data from network
mWeatherNetworkDataSource = weatherNetworkDataSource;
LiveData<WeatherEntry[]> networkData = mWeatherNetworkDataSource.getCurrentWeatherForecasts();
networkData.observeForever(newForecastsFromNetwork -> {
mExecutors.diskIO().execute(() -> {
mWeatherDao.bulkInsert(newForecastsFromNetwork);
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "New values inserted");
});
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/architecturecomponents-ittalk-171107110449/75/Architecture-Components-46-2048.jpg)
![Repository - use LiveData
private WeatherNetworkDataSource(Context context, AppExecutors executors) {
mContext = context;
mExecutors = executors;
mDownloadedWeatherForecasts = new MutableLiveData<WeatherEntry[]>();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/architecturecomponents-ittalk-171107110449/75/Architecture-Components-47-2048.jpg)