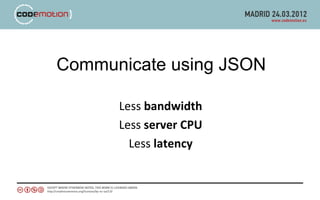
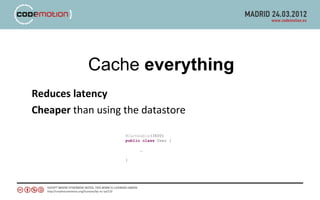
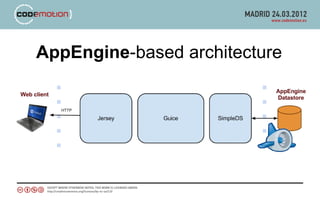
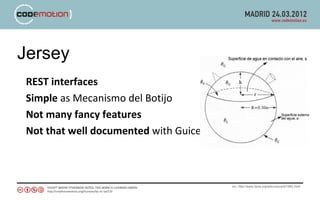
The document discusses developing applications using Google App Engine with Guice and Jersey, highlighting key components such as the App Engine SDK and various services for data management and caching. It covers the implementation of RESTful APIs, dependency injection, and best practices for optimizing performance. The author shares insights on technical choices and compares App Engine with AWS, emphasizing strengths, limitations, and design considerations for successful application development.






















![Web module
public class MyWebModule extends com.google.inject.servlet.ServletModule {
@Override
protected void configureServlets() {
// bind resources
for (Class resourceClass : getResources()) {
bind(resourceClass);
}
// jersey customization
serve("/*").with(GuiceContainer.class, ImmutableMap.of(
"com.sun.jersey.config.property.JSPTemplatesBasePath", "/WEB-INF/jsp",
JSONConfiguration.FEATURE_POJO_MAPPING, "true" // use Jackson to serialize
));
}
private Class[] getResources(boolean development) {
return new Class[] {
Users.class,
Shows.class,
Help.class
};
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codemotionappengine-120327043603-phpapp01/85/Codemotion-appengine-28-320.jpg)



![Introducing Base58
Take Base62 [a-zA-Z0-9]
Remove 0, O, caps 'i' and lowercase 'L'
Makes shorter URLs:
9223372036854775807 = CFq8pKn6mQN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codemotionappengine-120327043603-phpapp01/85/Codemotion-appengine-32-320.jpg)

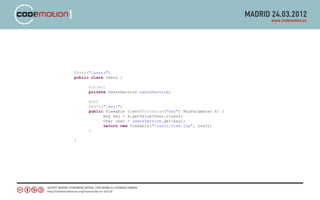
![Persistence module
public class MyPersistenceModule extends org.simpleds.guice.SimpledsModule {
@Override
protected void configure() {
this.withPersistentClasses(getPersistentClasses());
super.configure();
}
private Class[] getPersistentClasses() {
return new Class[] { User.class, Vote.class };
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codemotionappengine-120327043603-phpapp01/85/Codemotion-appengine-35-320.jpg)