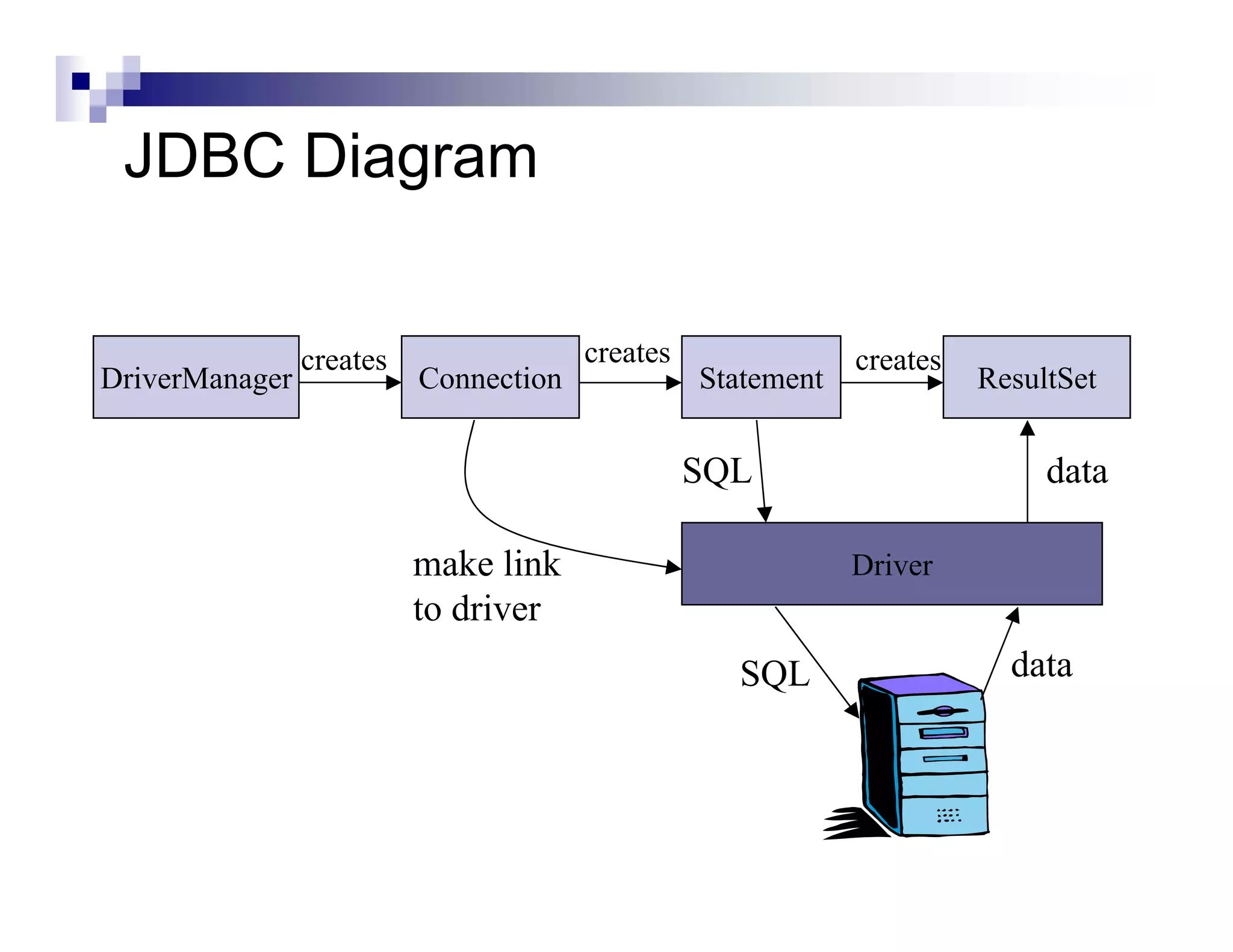
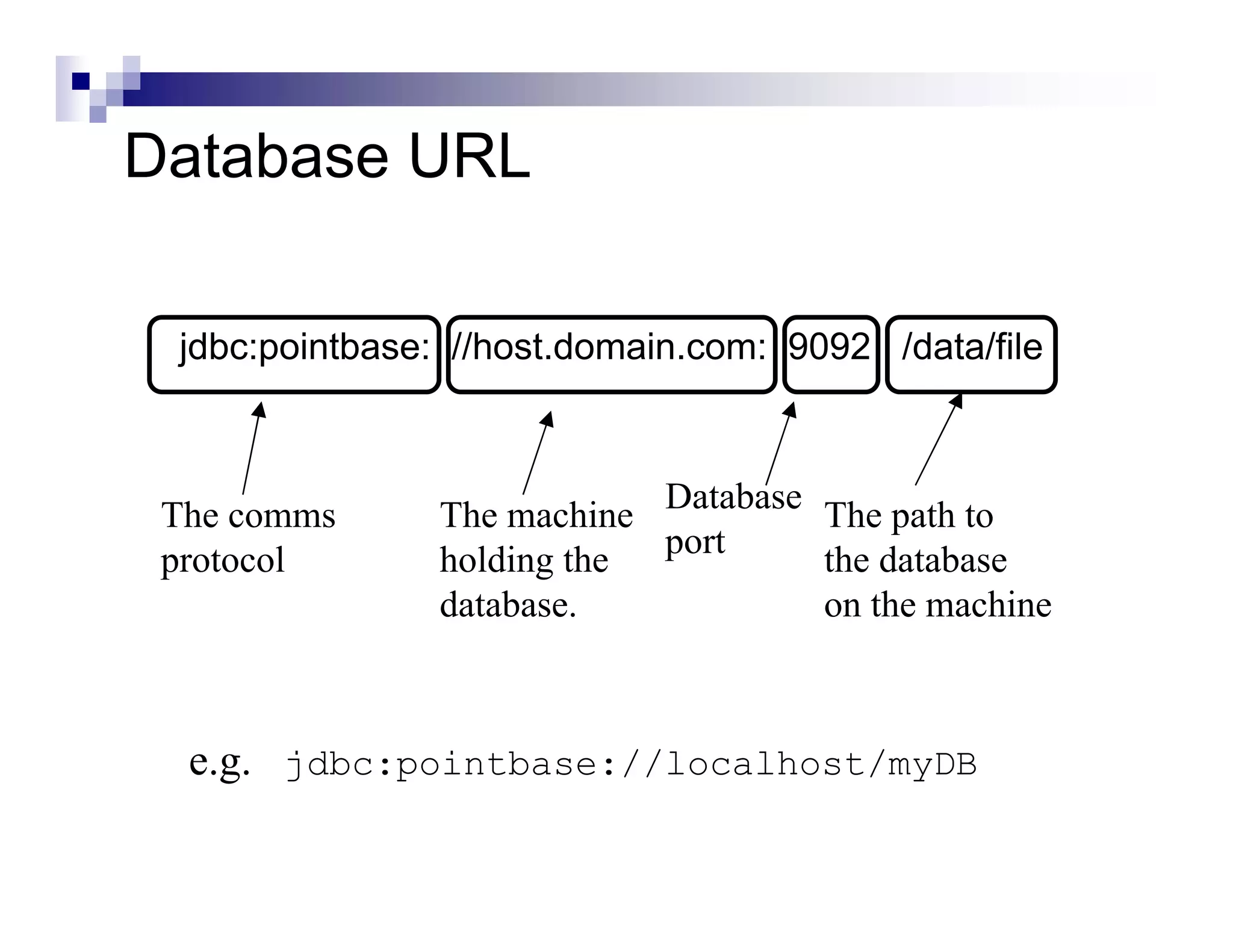
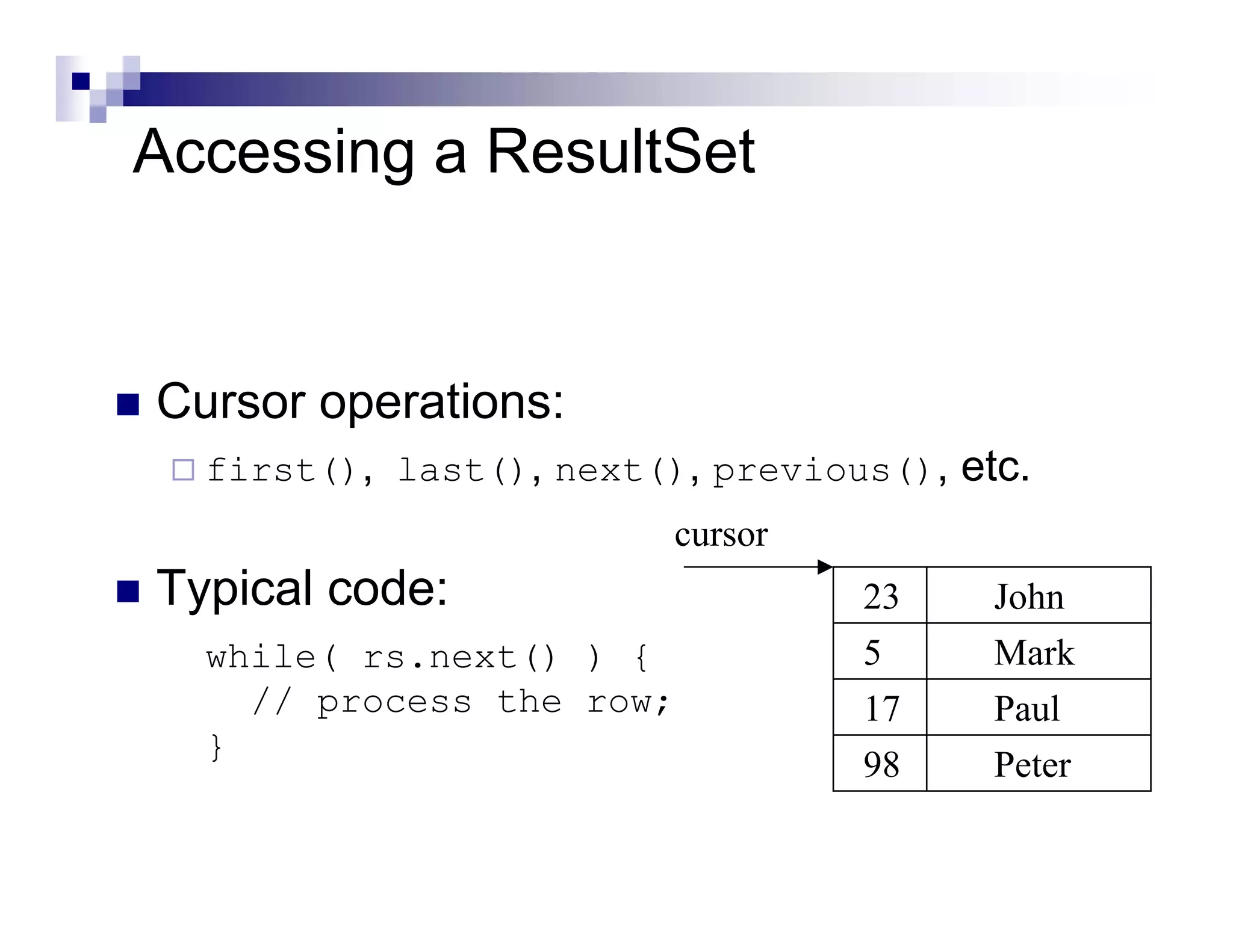
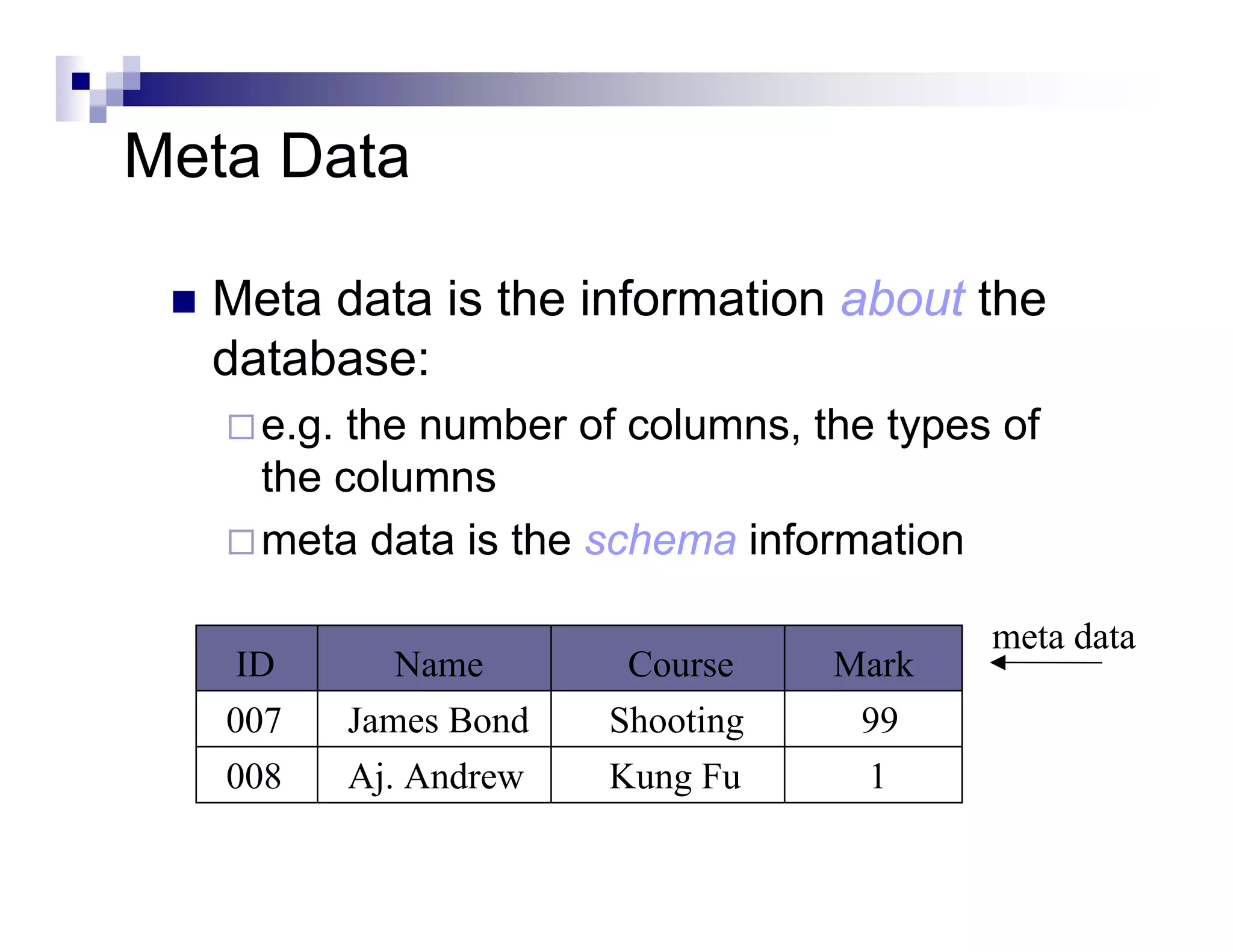
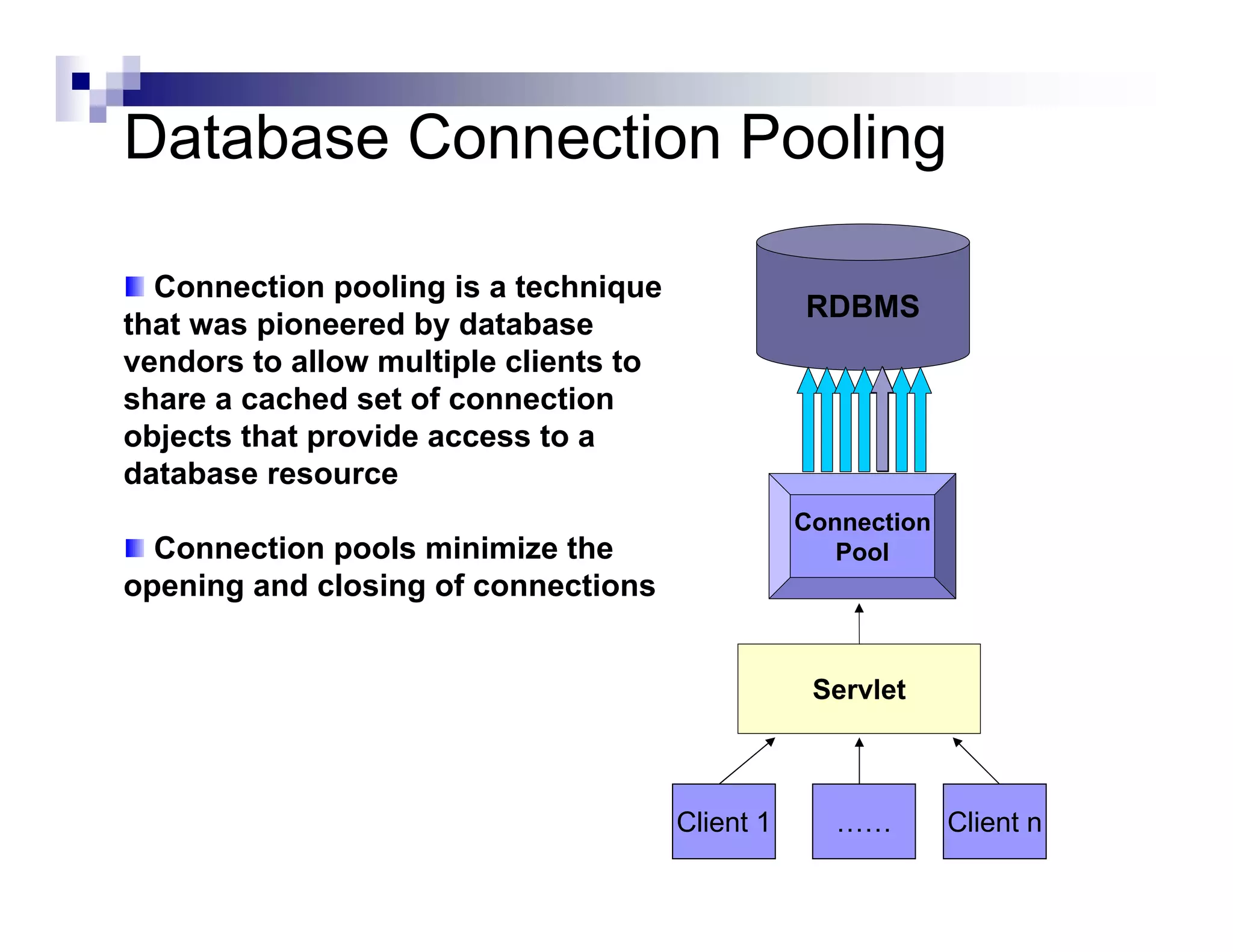
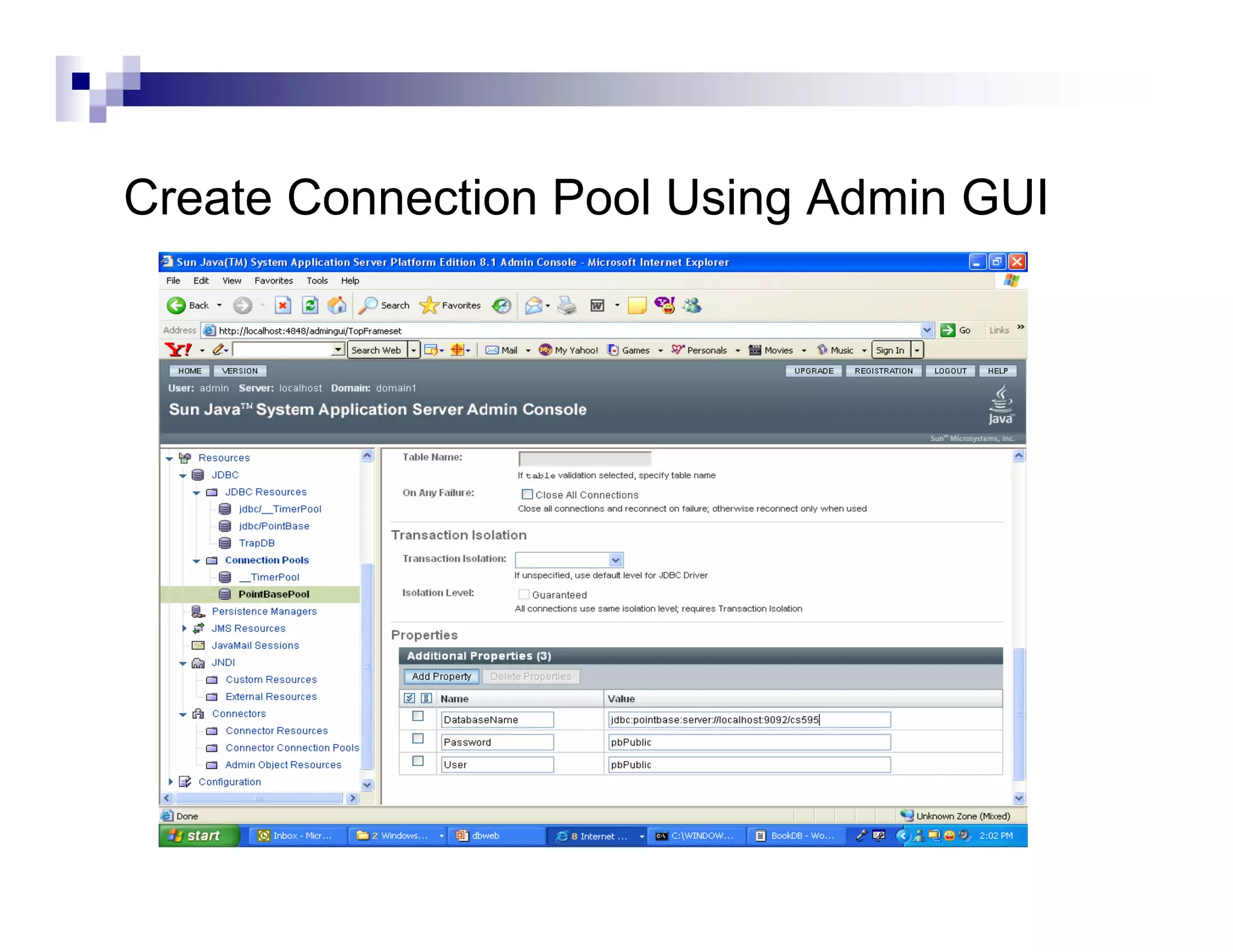
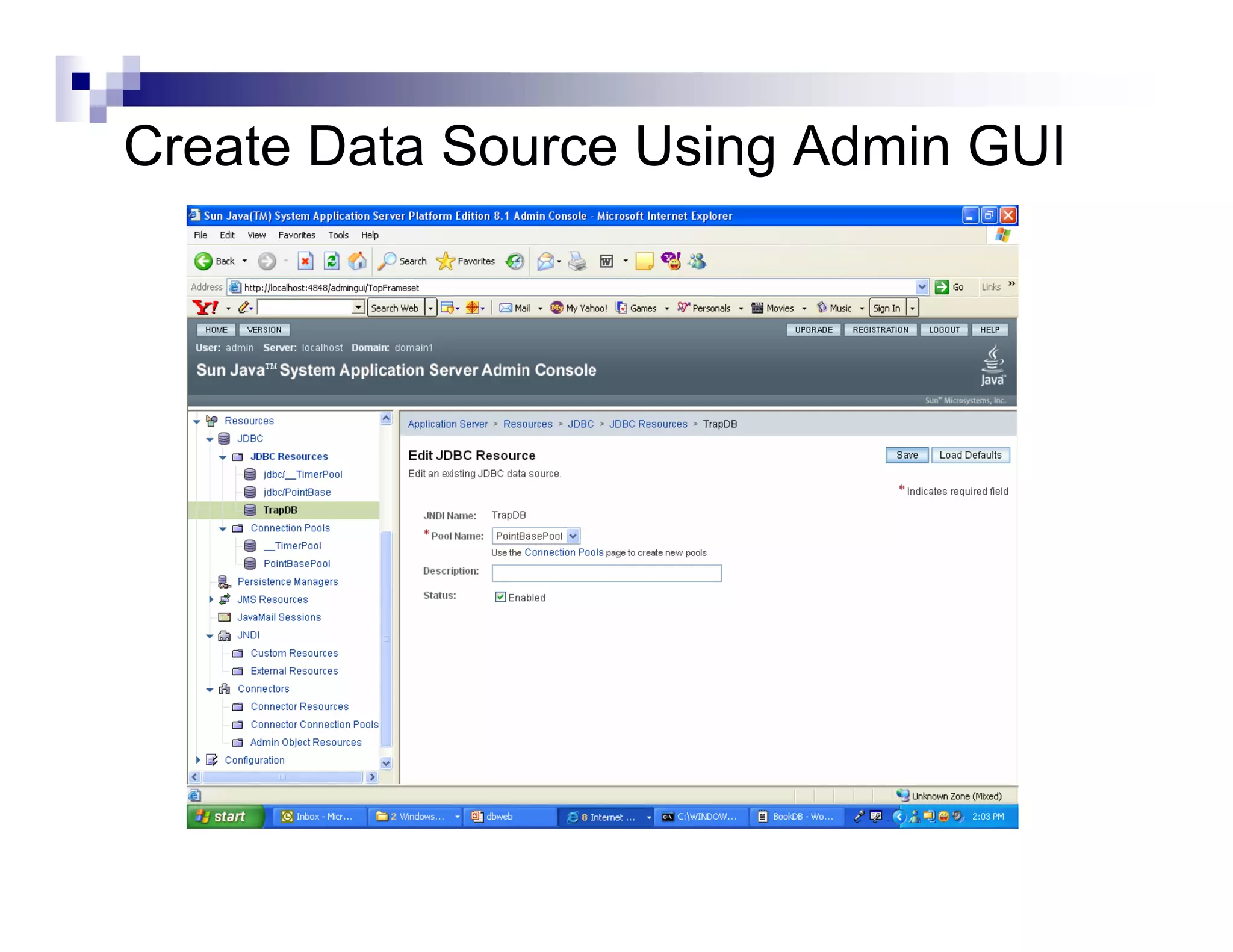
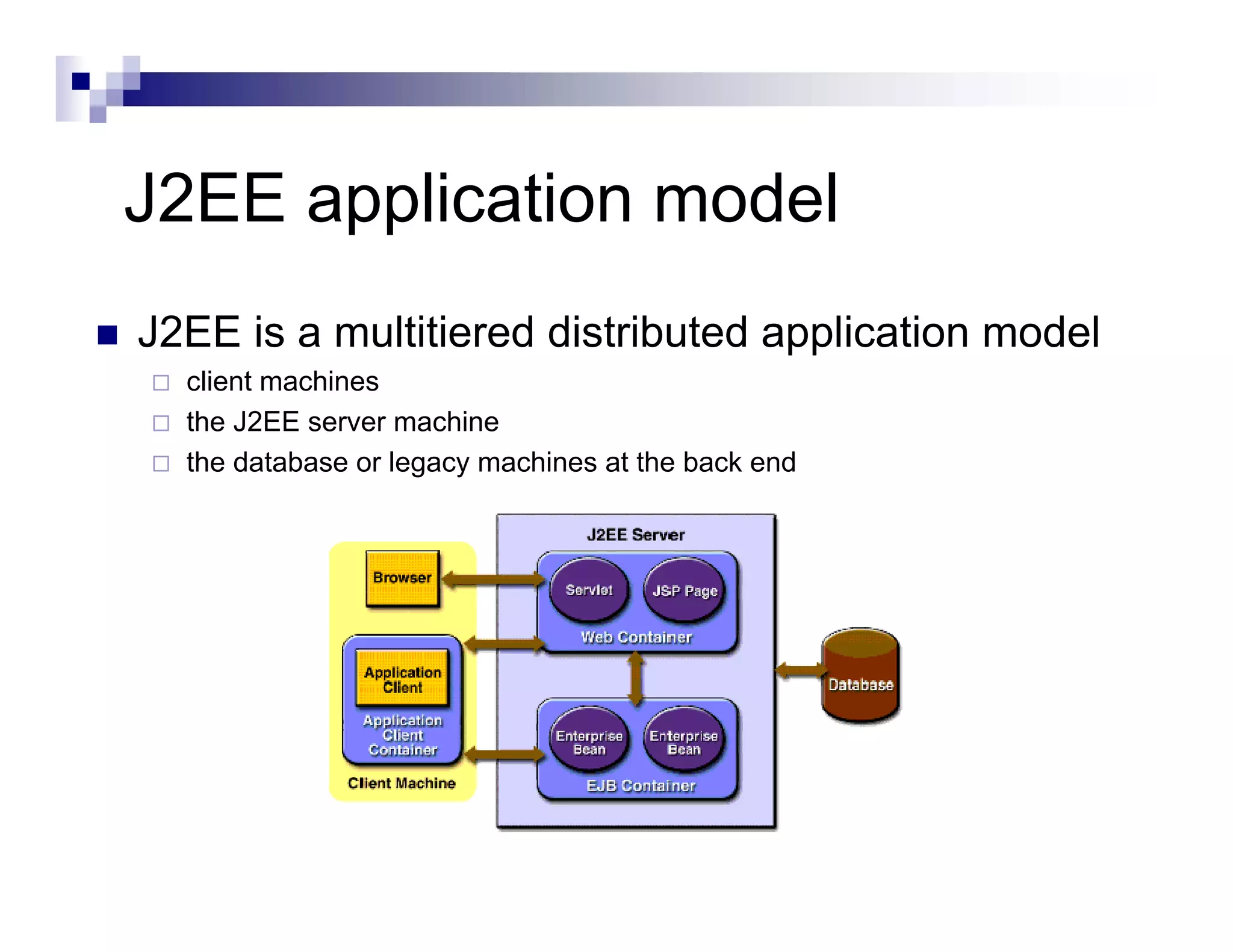
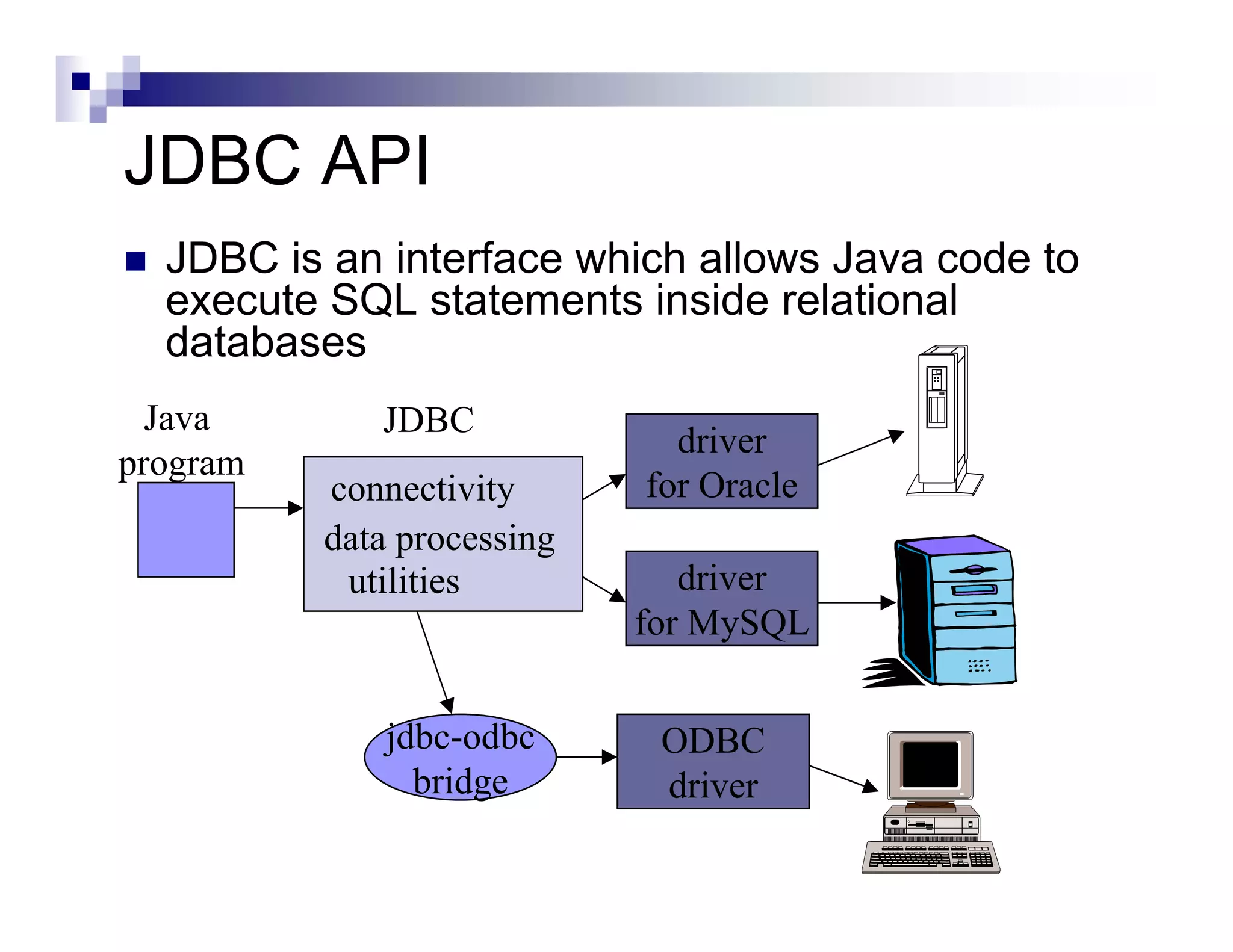
The document discusses Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) and how it allows Java code to execute SQL statements inside relational databases. It covers the JDBC API and how it provides a standard interface to different databases. It also discusses the JDBC-ODBC bridge which allows Java code to access databases via ODBC. The document provides an example of JDBC code to connect to a database, execute a query, and access the result set. It discusses using connection pooling and JNDI lookups in J2EE applications to connect to databases.




![JDBC Example
import java.sql.*;
public class SqlTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
// Step 1: Make a connection
// Load the driver
Class.forName("com.pointbase.jdbc.jdbcUniversalDriver");
// Get a connection using this driver
String url = "jdbc:pointbase://localhost/cs595";
String dbUser = "PBPUBLIC";
String dbPassword = "PBPUBLIC";
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, dbUser, dbPassword);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture17-121001005244-phpapp01/75/Lecture17-9-2048.jpg)