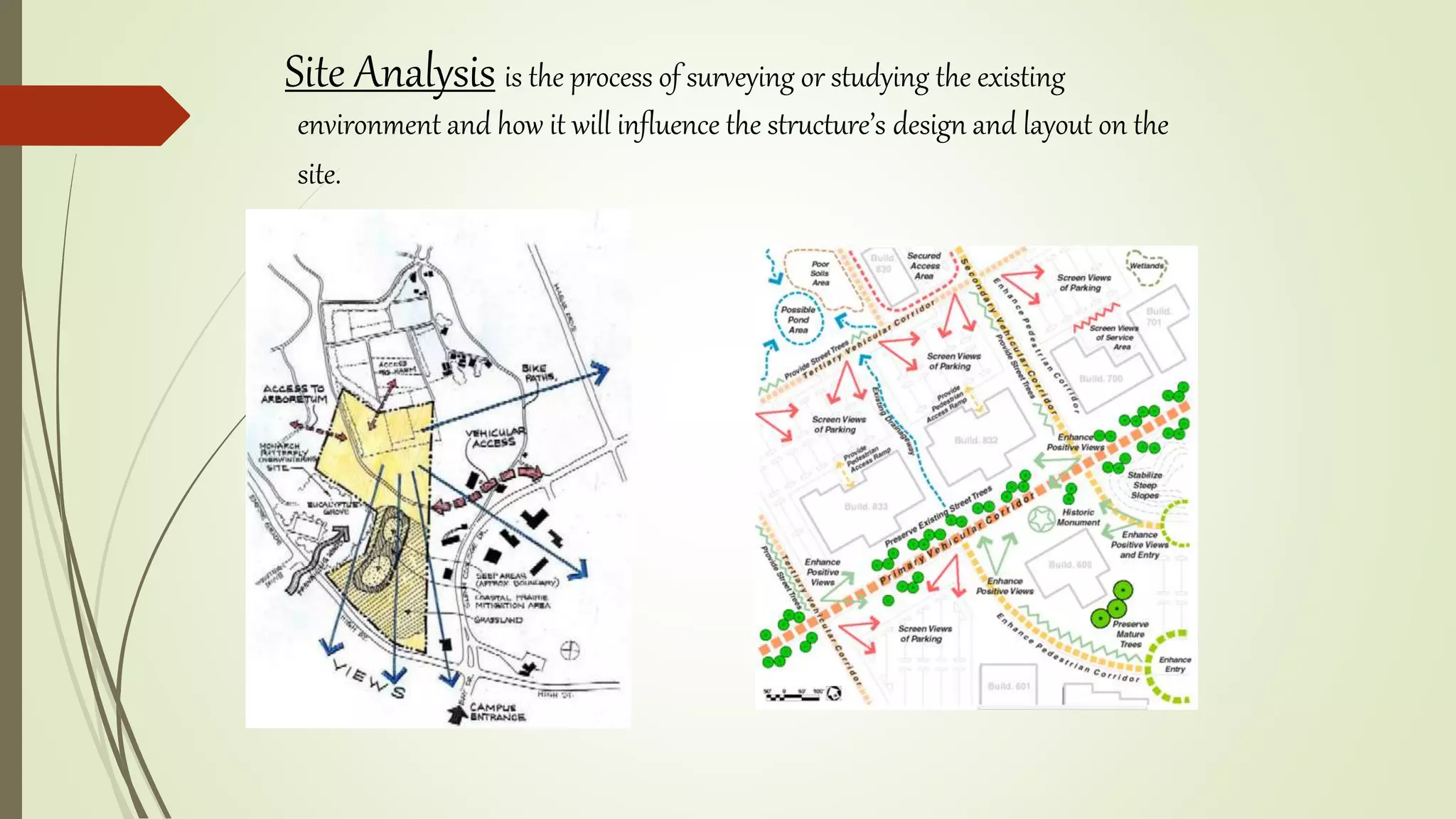
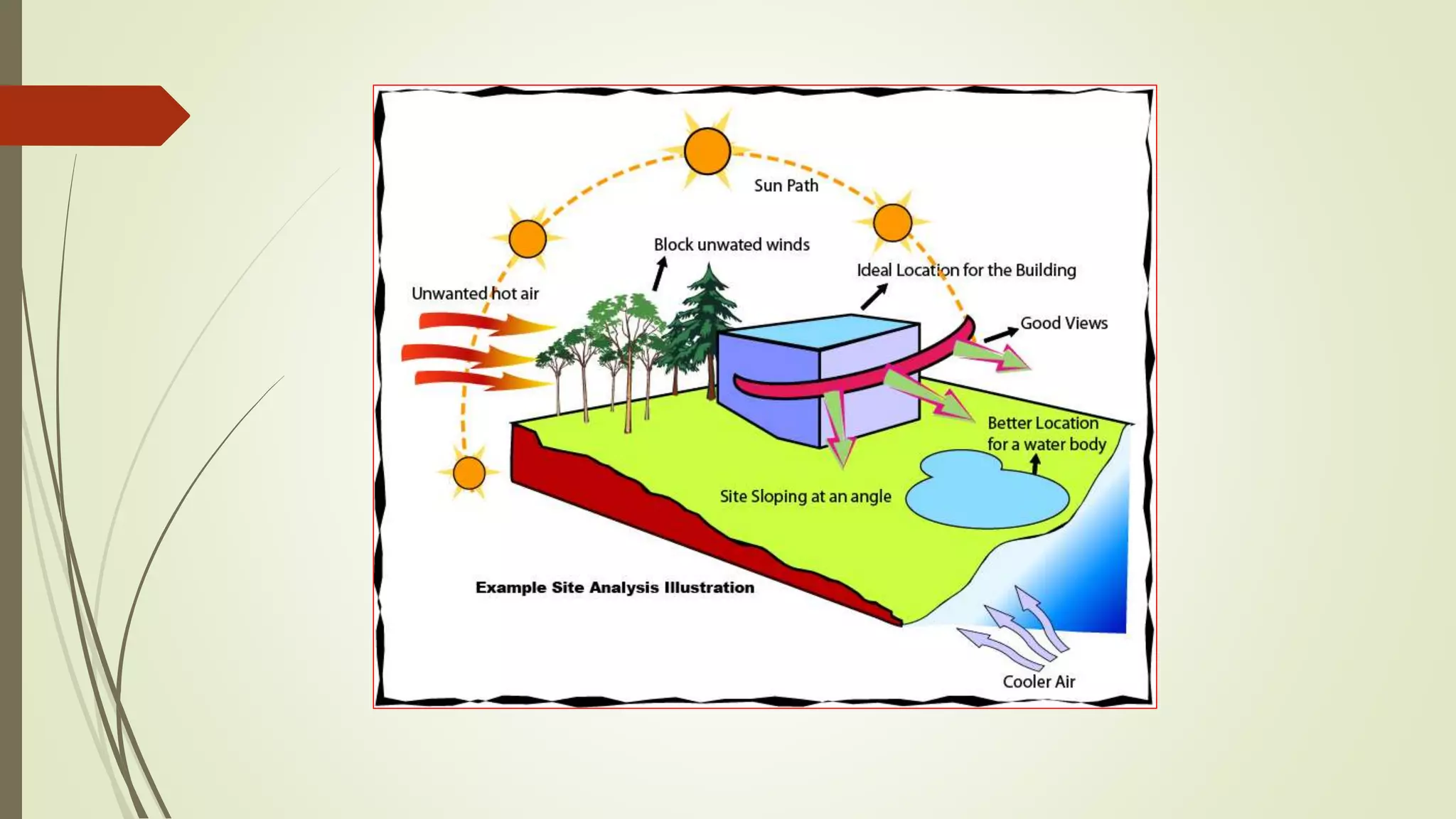
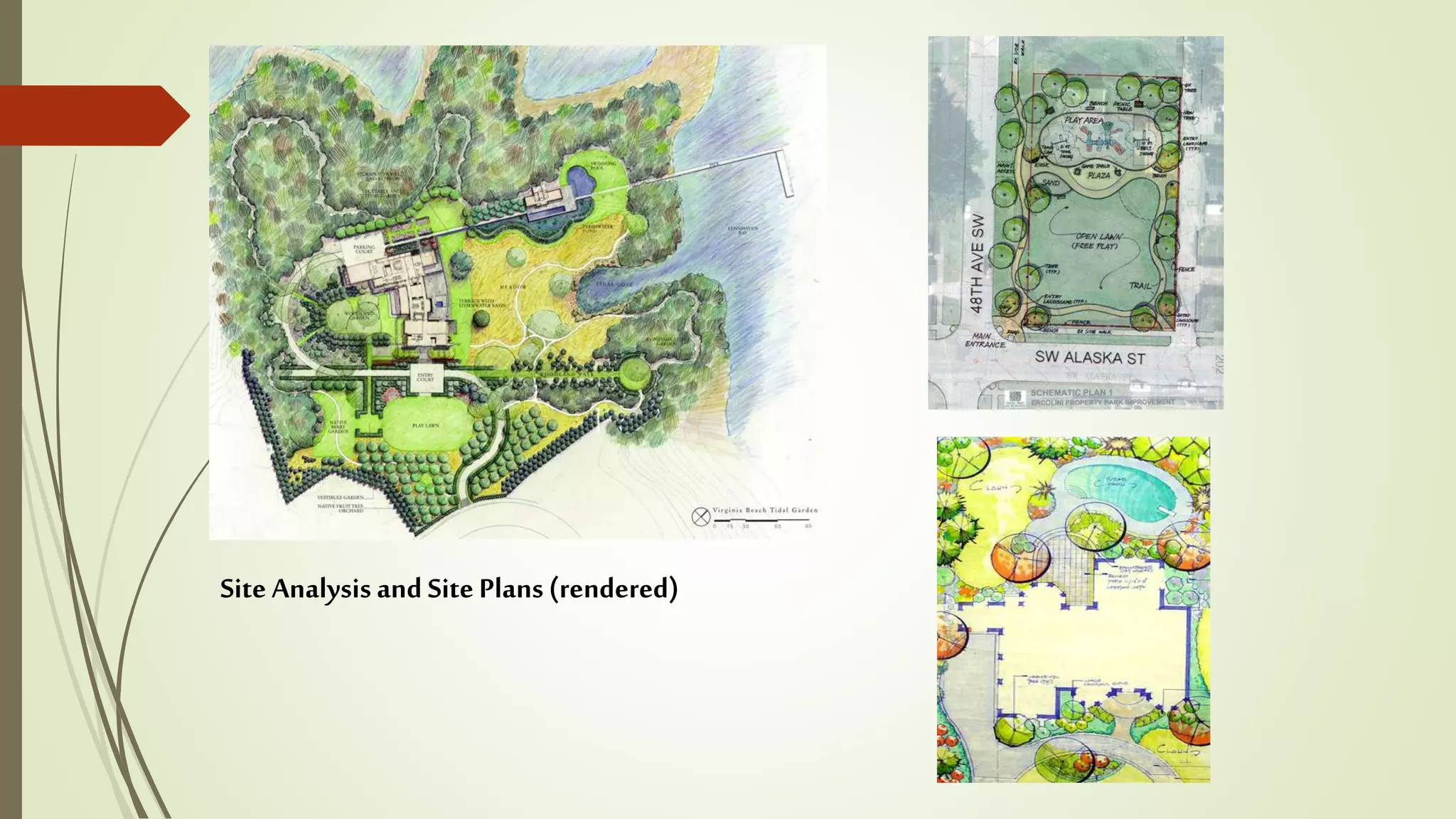
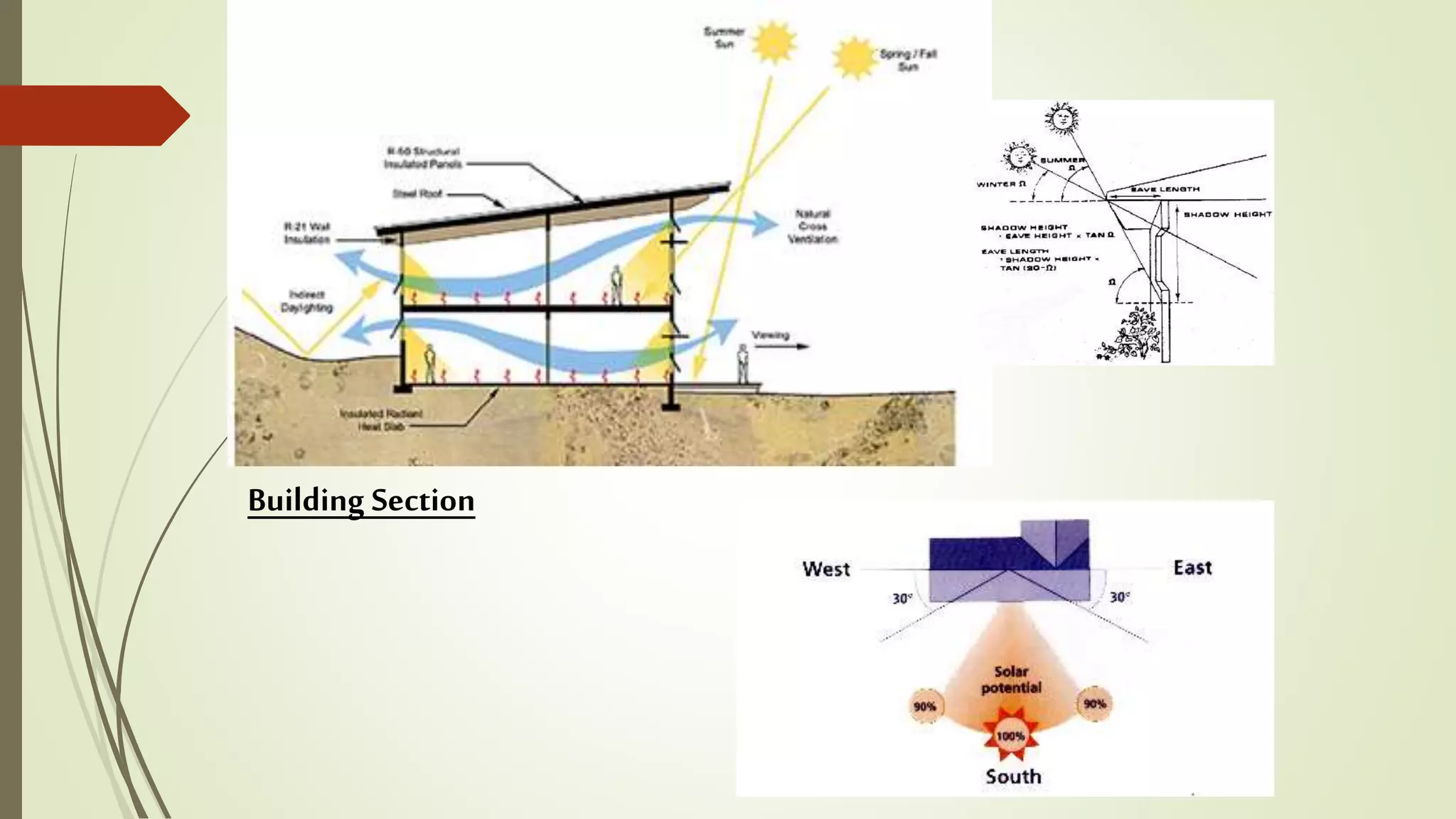
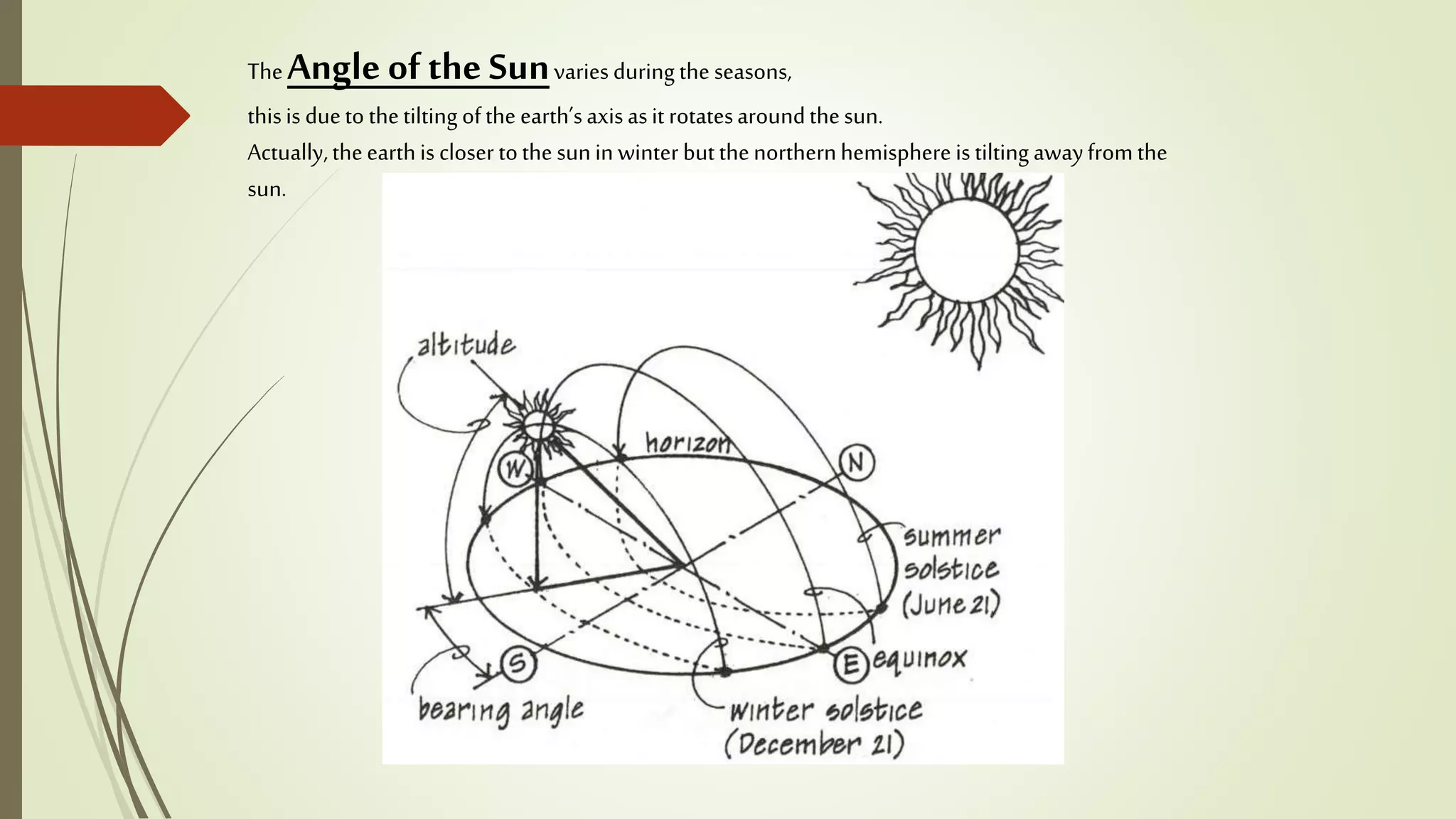
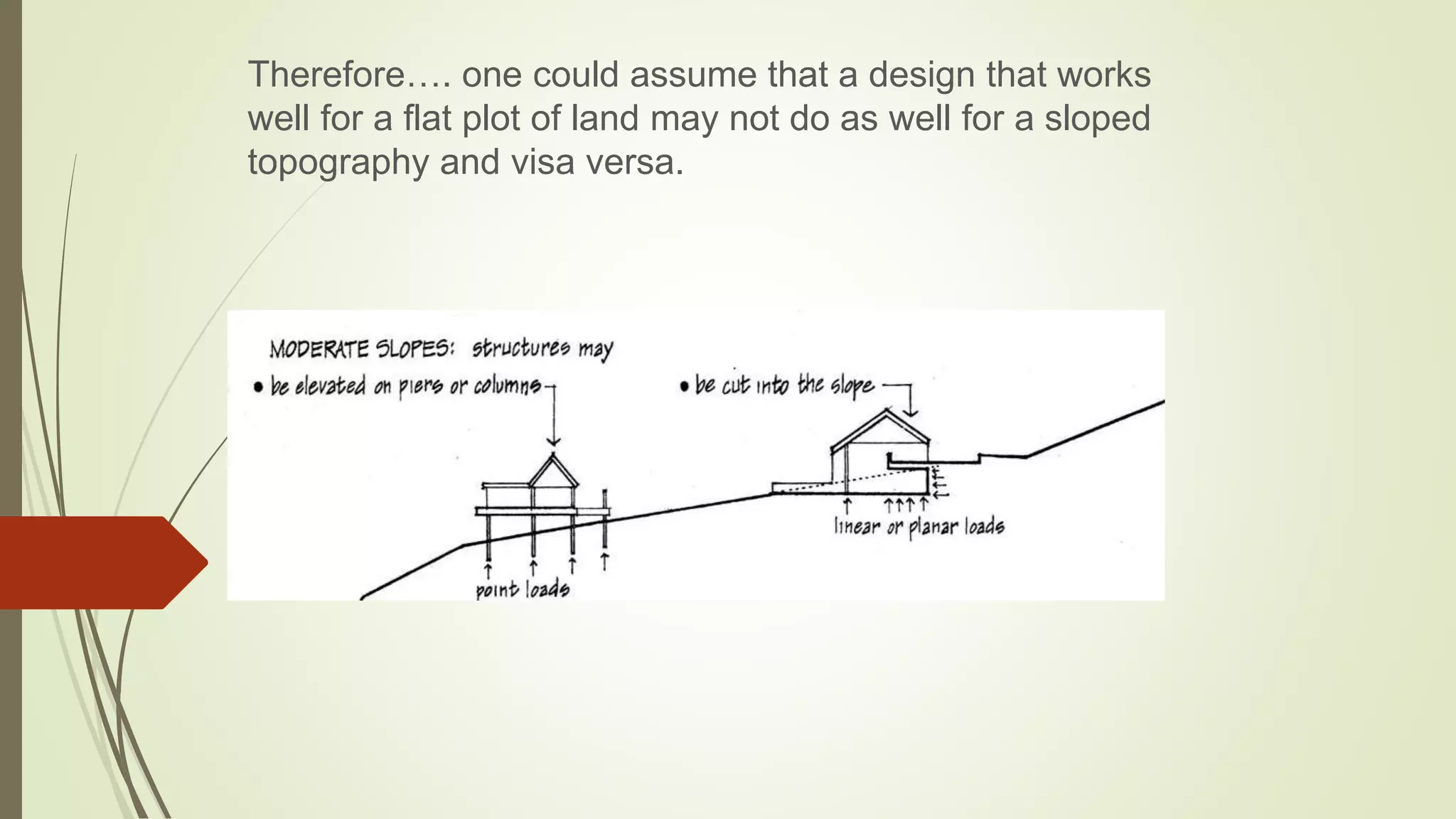
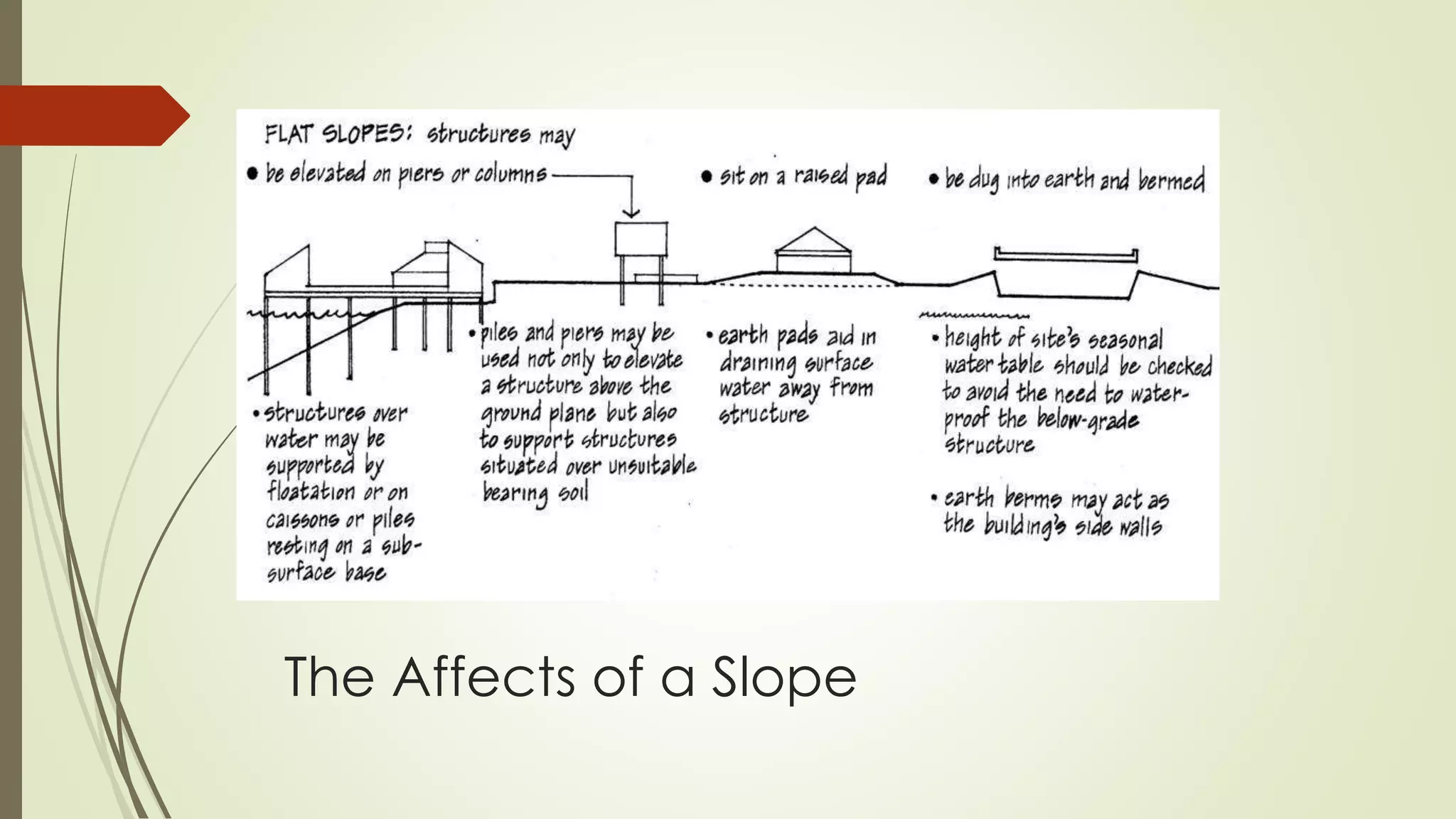
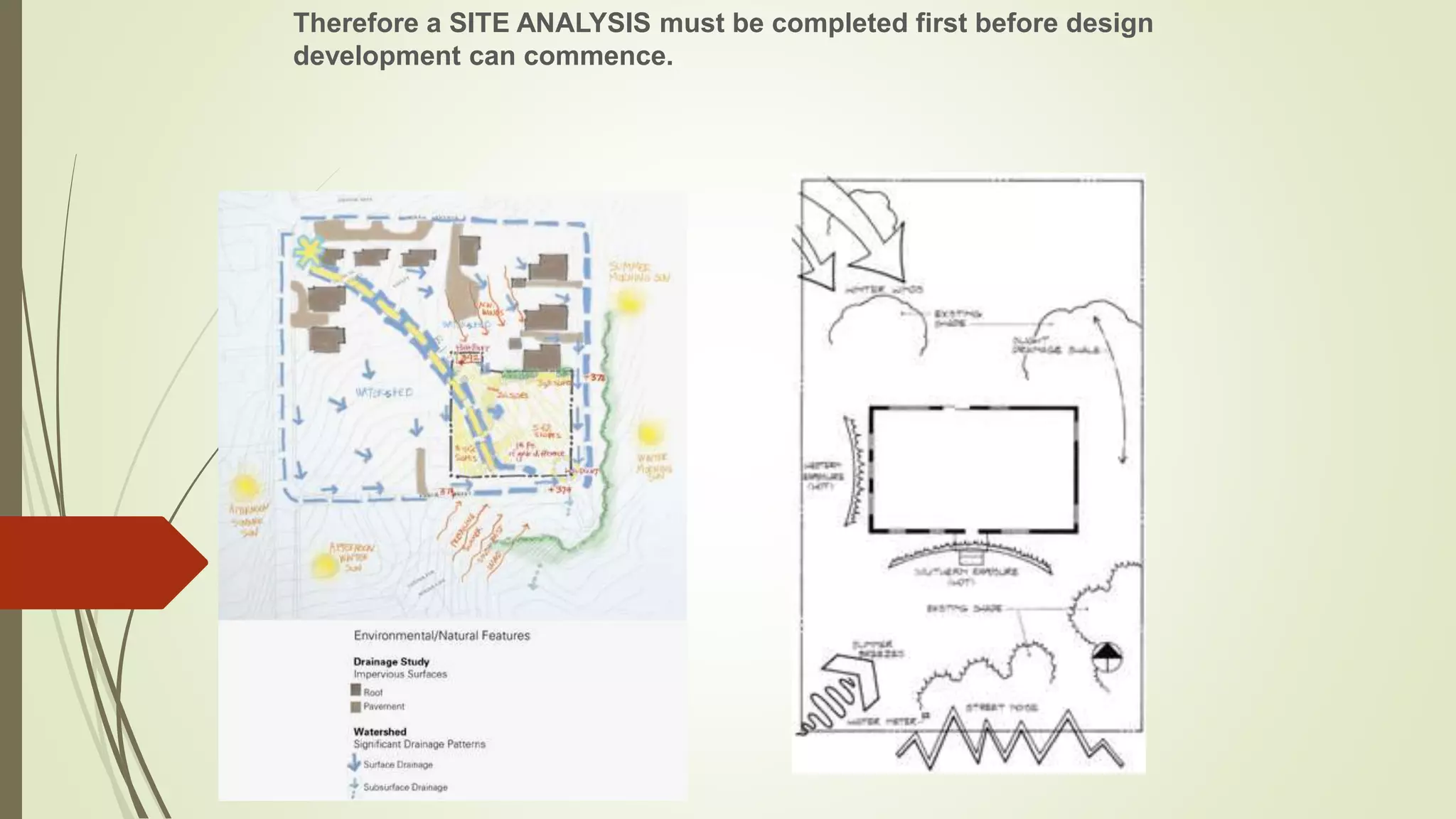
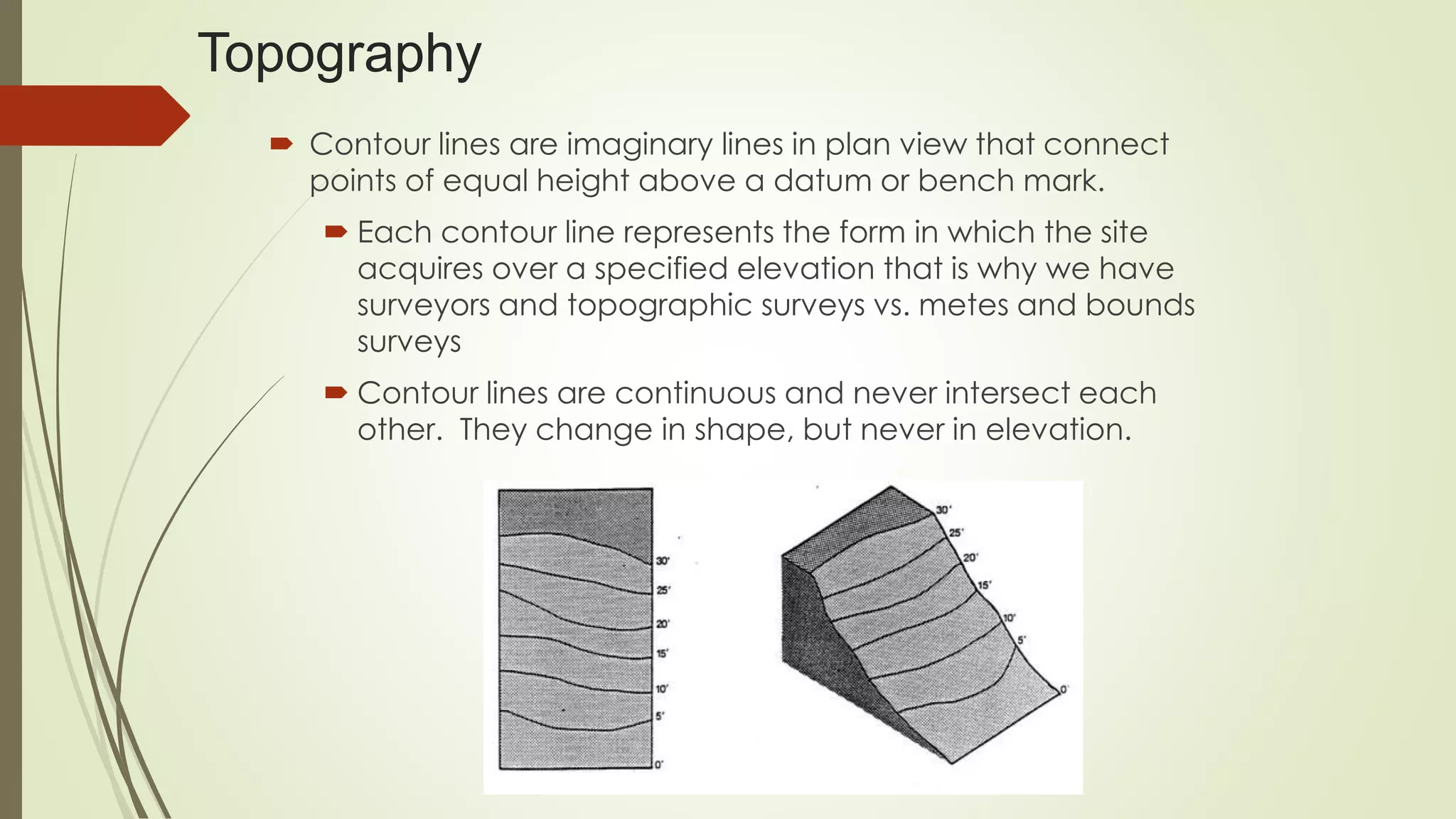
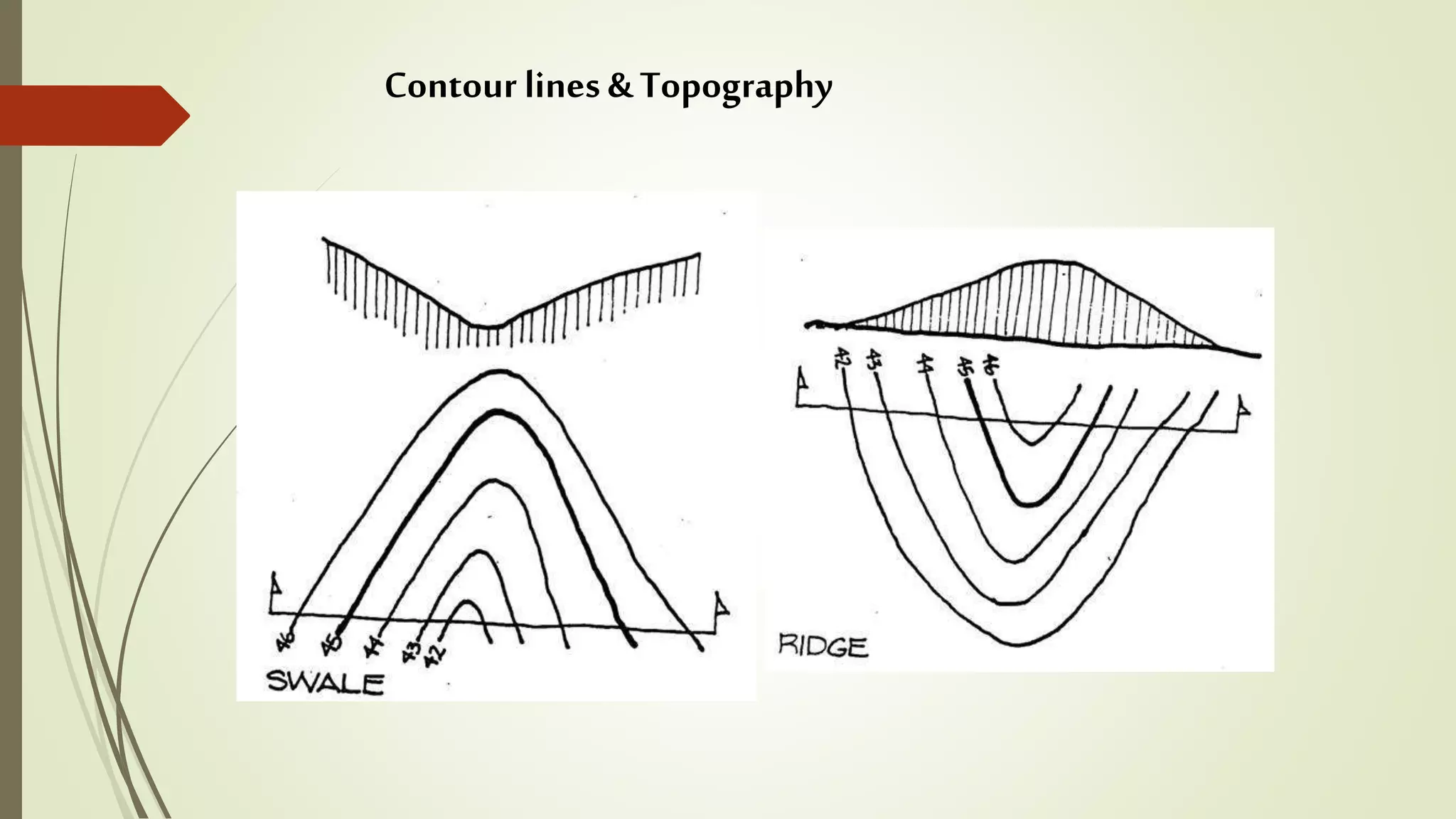
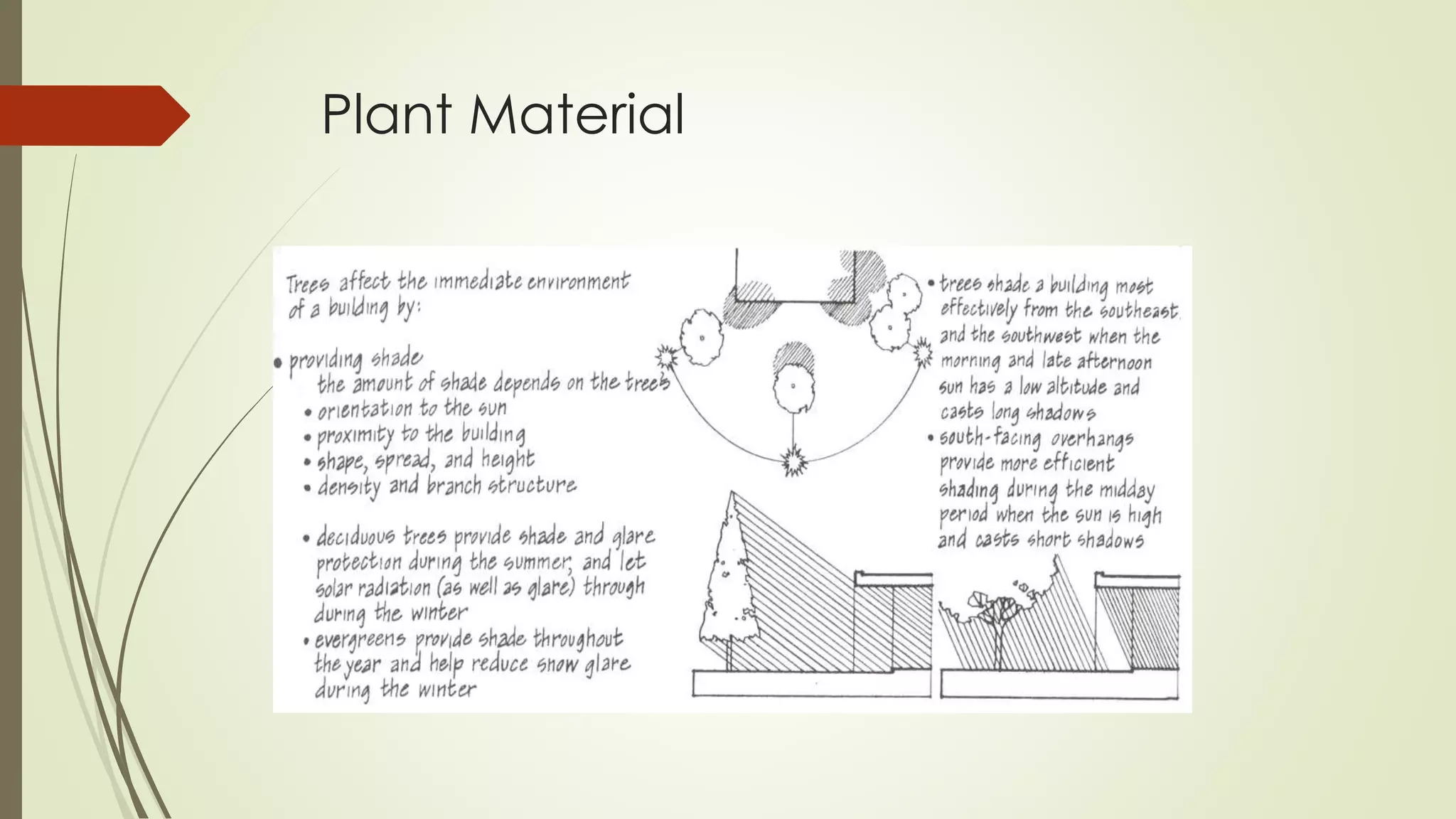
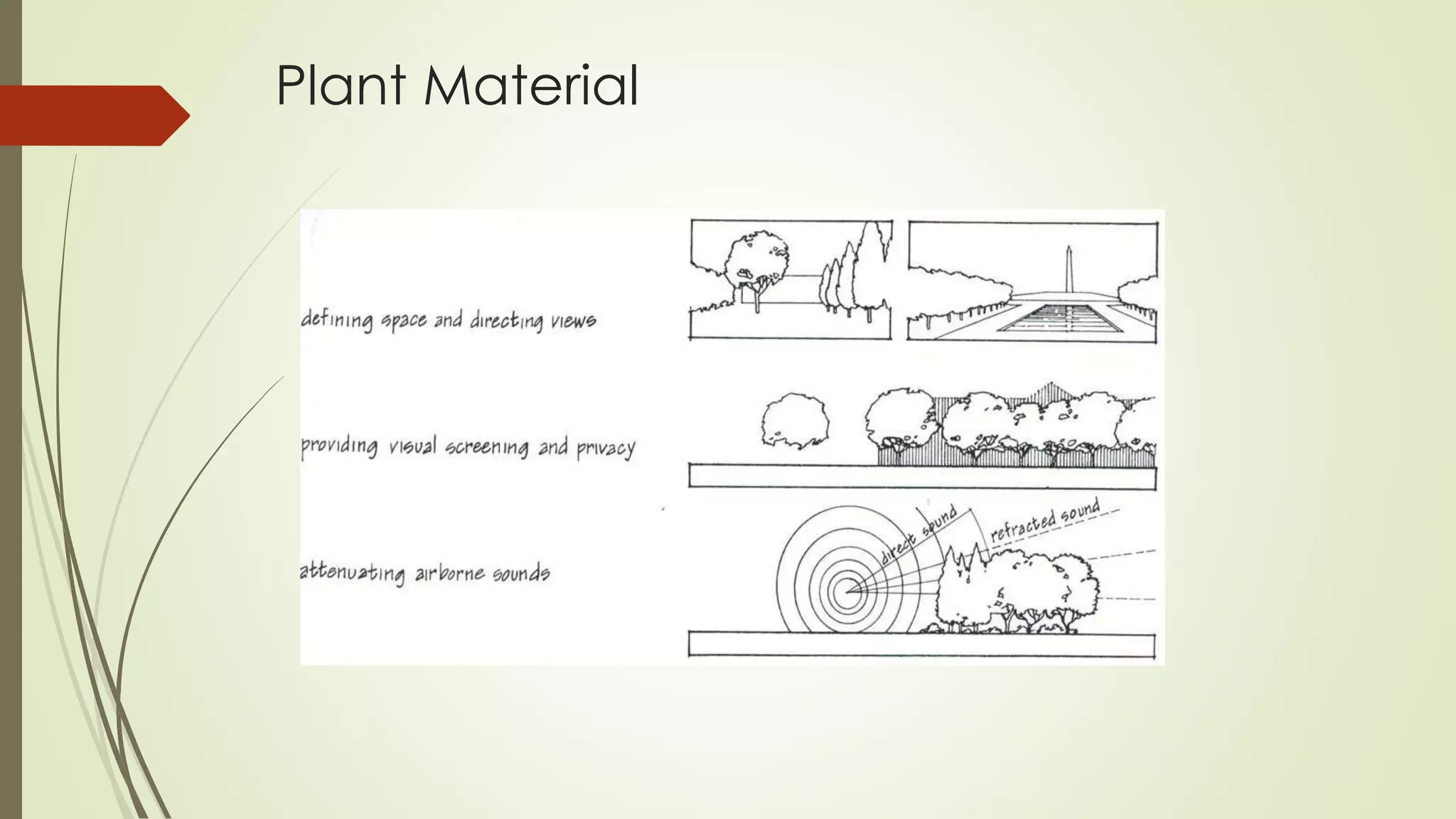
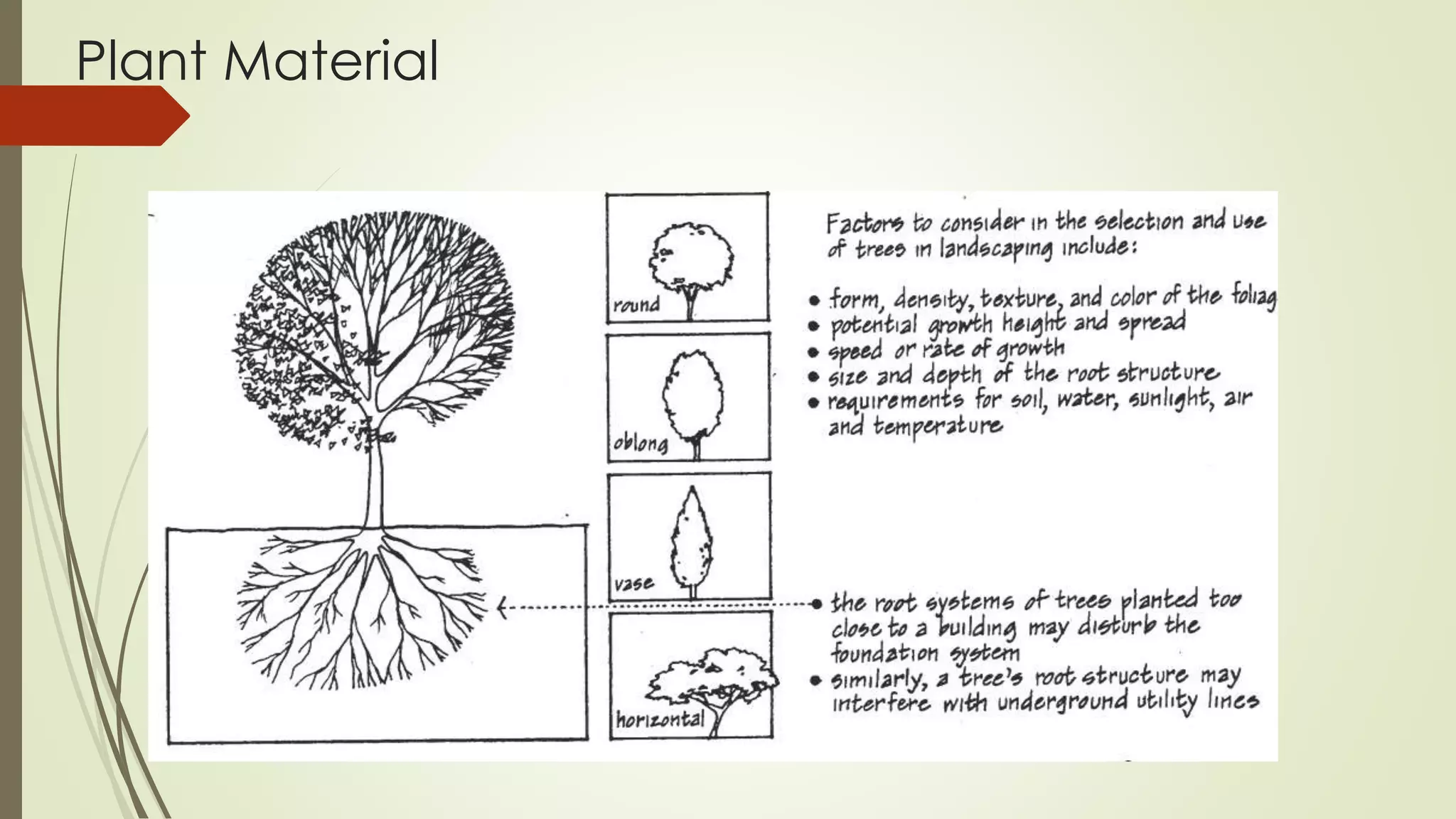
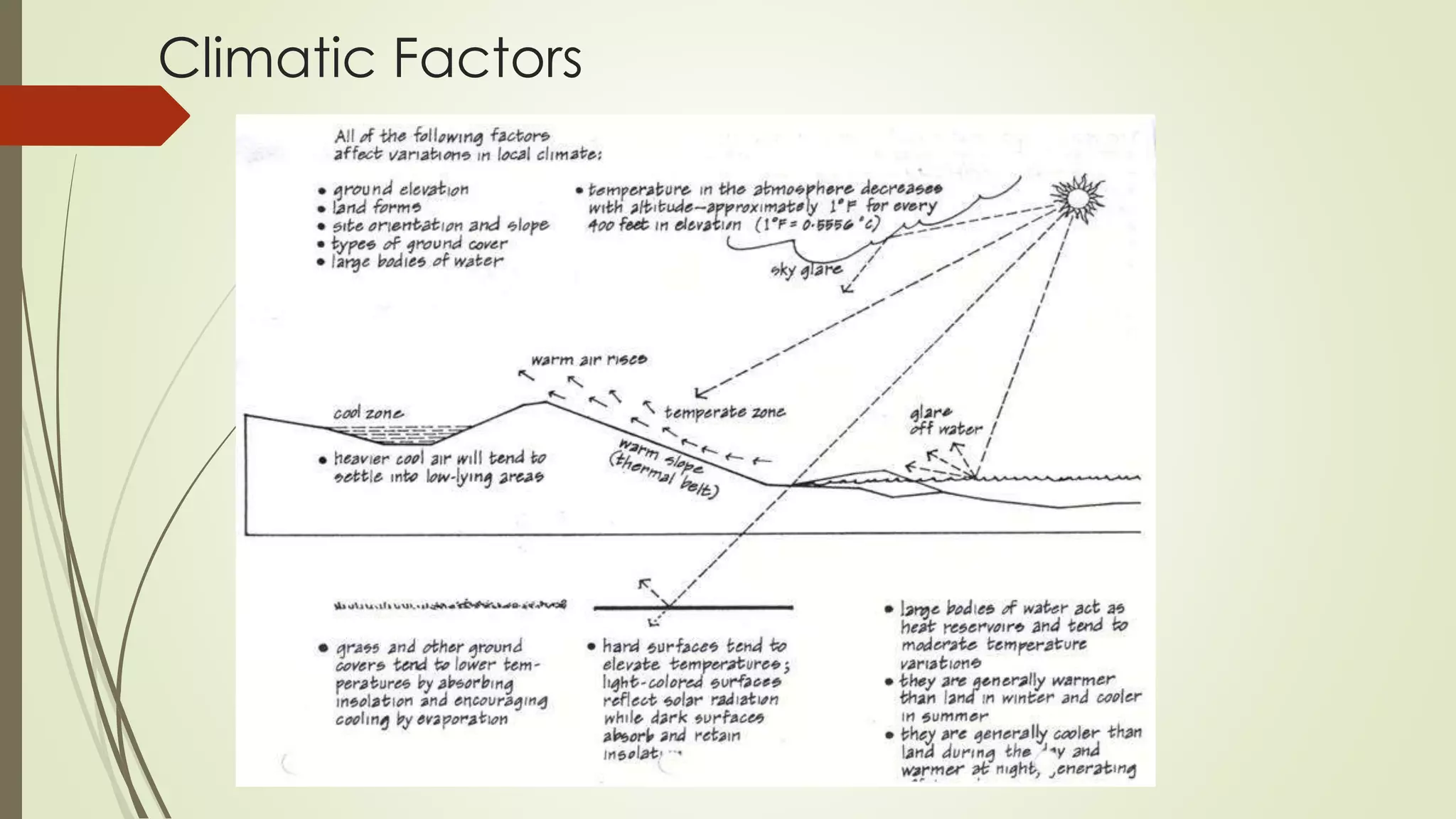
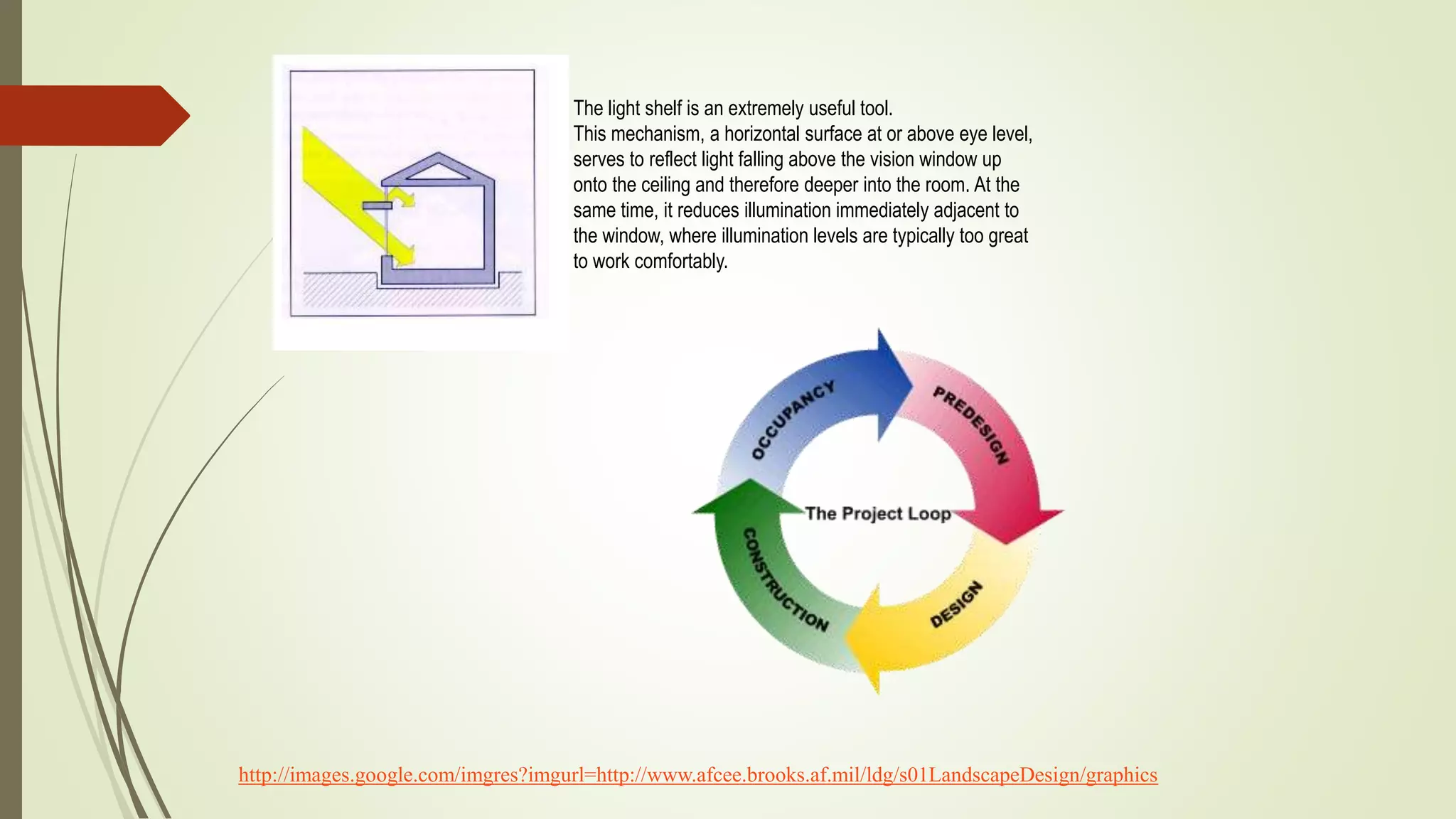
This document summarizes the key factors of a site analysis, which is the process of surveying an environment to understand how it will impact a structure's design. It lists the main considerations as topography, location, plant material, water, climate, solar orientation, winds, soil, and regulatory factors. It provides examples of how each factor like the slope of the land, soil type, and vegetation can influence foundation design, drainage, suitable plants, and microclimate. The document stresses the importance of completing a thorough site analysis before beginning design development to account for the existing site conditions.