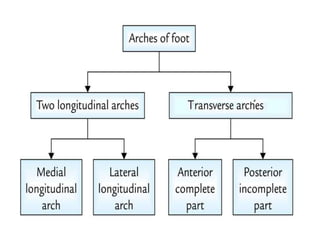
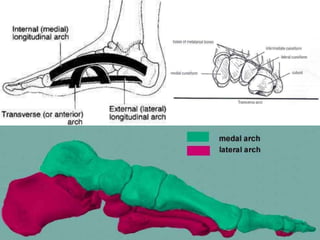
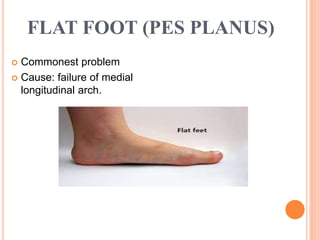
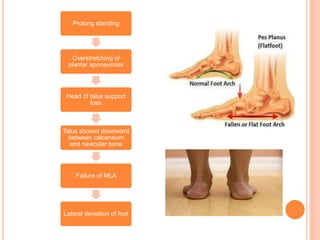
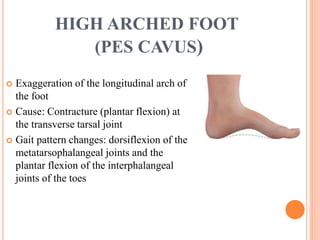
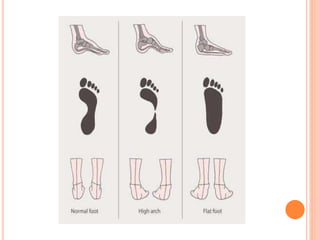
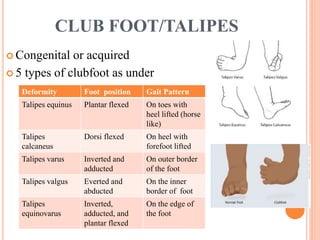
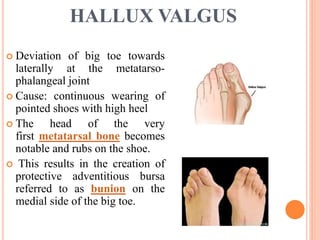
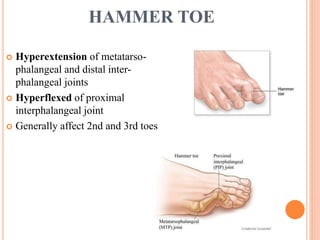
This document summarizes common foot abnormalities: flat foot, high arched foot, club foot, hallux valgus, and hammer toe. Flat foot is the most common and results from failure of the medial longitudinal arch. High arched foot is an exaggeration of the longitudinal arch. Club foot can be congenital or acquired and presents in various deformities that impact gait. Hallux valgus causes the big toe to deviate laterally at the metatarsophalangeal joint. Hammer toe involves hyperextension at some joints and hyperflexion at others, generally affecting the 2nd and 3rd toes.