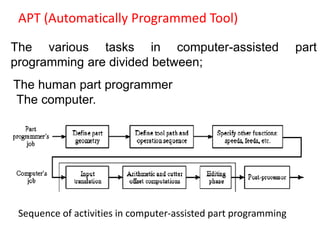
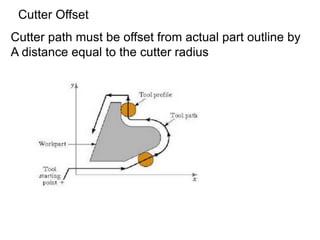
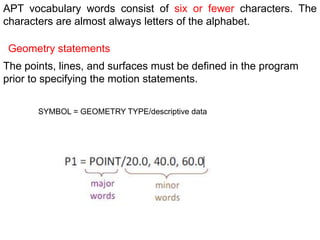
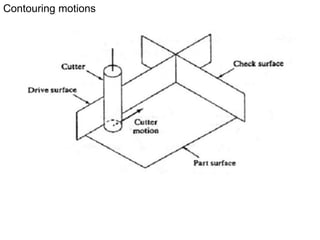
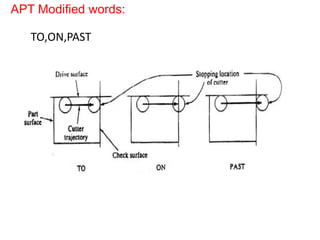
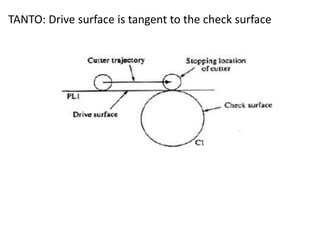
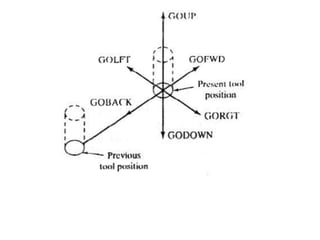
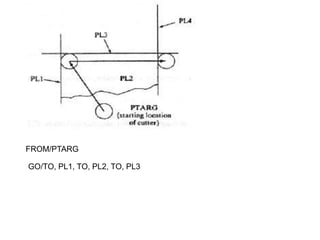
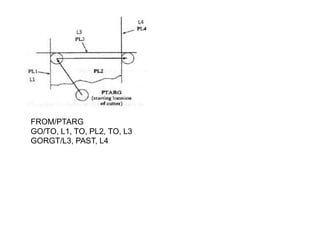
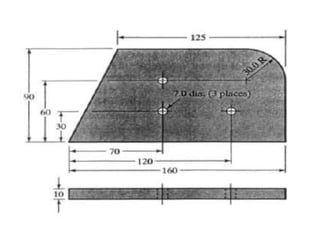
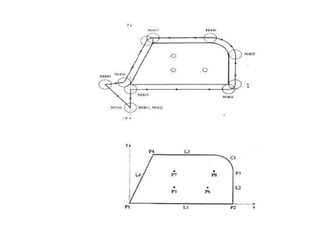
This document contains information about computer-assisted part programming using APT (Automatically Programmed Tool) language. It discusses the tasks divided between the human programmer and computer, including input translation, arithmetic computations, editing, and post processing. It also describes defining part geometry, specifying tool paths and operations, and includes examples of part programs for drilling and milling operations.