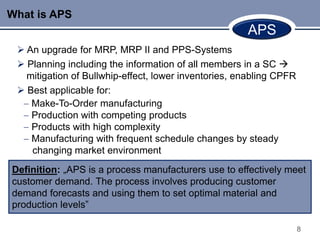
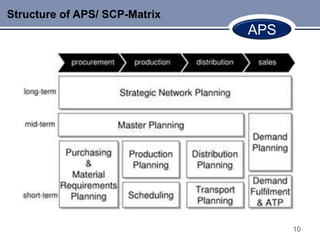
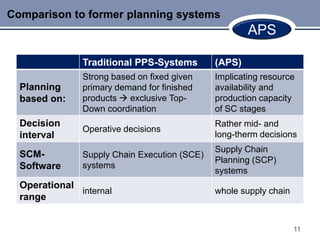
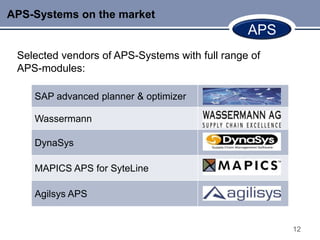
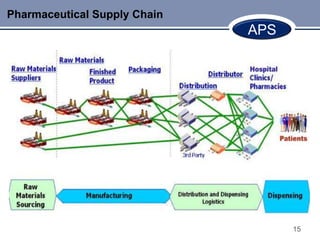
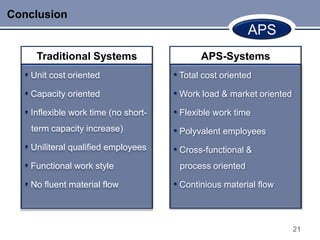
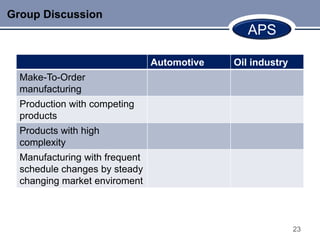
This document discusses Advanced Planning & Scheduling (APS) systems. It begins with an introduction to supply chain planning and the problems traditional systems encounter with demand fluctuations and inventory management. It then outlines the development of earlier SCM IT systems like MRP, MRPII, and ERP. APS systems aim to resolve issues with these prior systems by improving integration across the entire supply chain and enabling optimization of production planning. The document provides examples of APS vendors and modules. It also focuses on how APS benefits the pharmaceutical industry through collaborative planning, improved capacity utilization, and data consolidation across manufacturing sites. Overall, APS allows for more flexible and responsive planning in complex supply chain environments.