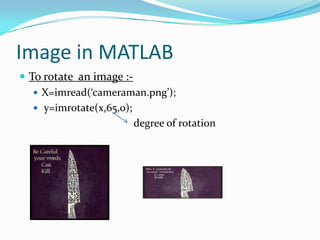
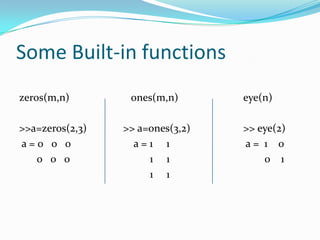
The document outlines MATLAB, describing it as a high-level programming language where everything is represented as an array. It discusses MATLAB's interface and use as a programming language, along with key features like arrays, basic operations, built-in functions, loops and conditions, graphics, images, and how to access MATLAB help. The overall focus is on introducing the basic concepts and capabilities of the MATLAB programming environment and language.


![What is MATLAB
High –level, data structured, technical computing
programming language.
Stands for Matrix Laboratory.
The basic data type is the Array (every thing is a matrix)
Scale n=1 is 1 x 1 array.
Vector a = [1 2 3] is 1 x 3 array (1-Dim).
Matrix A = [1 2 3 ; 4 5 6] is 2 x 3 array (2-Dim).
Used in linear algebra, graphic, image, simulation,.. Etc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtomatlab-121206101348-phpapp02/85/Intro-to-matlab-3-320.jpg)


![Arrays in MATLAB
>> A = [1 2 3]
output is A = 1 2 3
>> A = [1 2 3];
output is null
( ; ) means execute without displaying output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtomatlab-121206101348-phpapp02/85/Intro-to-matlab-7-320.jpg)
![Arrays in MATLAB
Matrix is 2-D array.
Vector is special case of matrix
-Vertical vector is m x 1 matrix - Horizontal vector is 1 x n matrix
>> A = [1; 2; 3] A= 1 >> A = [1 2 3] A = 1 2 3
2
3
Scale number is special case of vector
-scale is 1 x 1 vector
>>B = 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtomatlab-121206101348-phpapp02/85/Intro-to-matlab-8-320.jpg)


![Graphics in MATLAB
As soon as graphs can represented by vectors, can be
manipulated by MATLAB like a normal vectors
>> x = [1 2 3 4];
>> y = [2 4 6 8];
>>title('Figure 1');
>>plot(x,y);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtomatlab-121206101348-phpapp02/85/Intro-to-matlab-15-320.jpg)
![Image in MATLAB
As soon as images can represented by matrices, can be
manipulated by MATLAB like any other matrix.
>> x = imreade(' kids.tif ');
>>[x map] = imreade(' kids.tif ');
>>imshow(x);
>>imshow(x , map);
>>imwrite(x , ' c:img.png ' , 'png');](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtomatlab-121206101348-phpapp02/85/Intro-to-matlab-16-320.jpg)