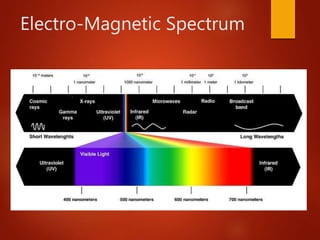
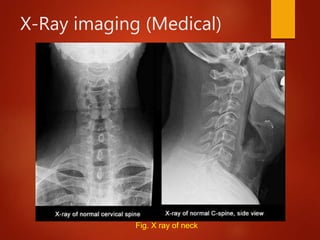
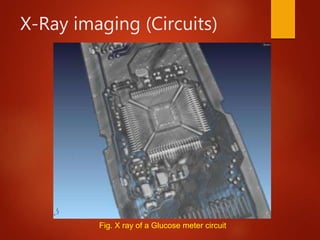
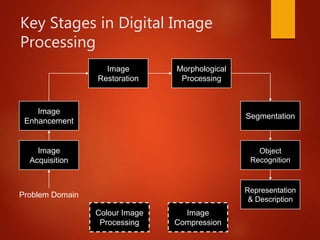
The document provides an overview of digital image processing, defining a digital image and its components such as pixels. It outlines the essential applications of image processing including enhancement, noise removal, and object recognition across various fields like medicine and law enforcement. Key stages in digital image processing such as image acquisition, segmentation, and representation are also highlighted.